- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
RFK Jr.'s Autism Controversial Comments Face Backlash From Parents And Medical Experts

Robert F. Kennedy Jr., the U.S. Secretary of Health and Human Services, is facing strong backlash after making sweeping comments during a recent press conference regarding autism and its supposed causes. As the CDC released a report revealing a rise in autism diagnoses among U.S. children now affecting 1 in 31 8-year-olds Kennedy doubled down on discredited theories linking autism to environmental exposures and vaccines, while portraying the disorder in stark, stigmatizing terms.
His remarks including claims that children with autism “will never hold a job,” “never pay taxes,” or “never use a toilet unassisted”, were swiftly condemned by parents, medical experts, and advocacy groups alike for reinforcing outdated stereotypes and misrepresenting the broad and diverse autism spectrum.
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is not a single condition with uniform symptoms or outcomes. Rather, it is a neurological and developmental condition characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. The key word is "spectrum" and it exists for a reason.
Some individuals with autism may be nonverbal and need lifelong support, while others live independently, excel in careers, write books, or even hold public office. “Autism is not a disease,” said actress and autism advocate Holly Robinson Peete in a video statement, responding to Kennedy. “It is a developmental difference and it is important to get that right.”
Her son, RJ, diagnosed 25 years ago, has “shattered a lot of 'never' off that list,” she said, referring to Kennedy’s grim portrayal. Countless parents echoed this sentiment on social media, stating that Kennedy’s generalizations erase the lived realities, milestones, and accomplishments of their children.
CDC Data Shows a Rise in Diagnoses
The CDC’s Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network reported that 1 in 31 8-year-olds in the U.S. were diagnosed with autism in 2022, compared to 1 in 54 in 2016. But experts stress that this increase is not necessarily cause for alarm. It is, in fact, a sign of progress.
The rise in autism rates is driven largely by improved awareness, broader diagnostic criteria, and increased access to evaluations and services. We are identifying children earlier and more accurately that’s a good thing.
Kennedy, however, rejected this explanation as “indefensible” and announced plans for a directive to the National Institutes of Health to investigate “environmental exposures” as the root cause — reigniting long-debunked concerns about vaccines and toxins.
Despite overwhelming scientific consensus debunking any link between vaccines and autism, Kennedy has long been associated with promoting vaccine hesitancy. His latest comments, veiled in language about “environmental exposures,” once again hint at this discredited narrative.
Leading medical organizations, including the American Academy of Pediatrics and the World Health Organization, have repeatedly emphasized that vaccines are safe, effective, and have no causal relationship with autism. Resurrecting these claims only spreads fear and confusion. It undermines public health and harms autistic people by framing their existence as a preventable tragedy.
Parents Demand a Shift in the Narrative
Perhaps the strongest rebuke came from parents of autistic children themselves. Samantha Taylor, whose 20-year-old son is on the spectrum, told Good Morning America, “Autism doesn’t destroy families misinformation does.” In a viral Facebook post, she added, “What truly causes damage is the relentless portrayal of autism as something catastrophic, rather than a different way of experiencing the world.”
Kennedy’s comments, they say, not only ignore the complexity of the condition but strip children of their dignity and potential.
“Statements like ‘they’ll never write a poem’ deny the creative genius that so many autistic individuals demonstrate,” said Peete. “It’s dangerous, it’s harmful, and it’s simply false.”
Experts Call for More Informed Leadership
While Kennedy has promised answers by September through federally backed studies, medical experts warn that his rhetoric may set back years of advocacy and research by framing autism as an “epidemic” akin to an infectious disease.
Autism is not something to be eradicated, it’s something to be understood, supported, and embraced. Families deserve resources, not fearmongering.
In the last two decades, the medical community has shifted toward neurodiversity — a perspective that recognizes neurological differences like autism as natural variations of the human genome. This philosophy emphasizes inclusivity, respect, and strength-based approaches rather than medicalizing difference.
At a time when public trust in institutions is fragile, the words of public officials matter deeply. Kennedy’s comments have triggered a reckoning not only about how autism is portrayed in the media and politics but also about how society chooses to value — or devalue — people who are different.
Advocates stress the need for policies rooted in science, not stigma, and for leadership that uplifts rather than marginalizes.
As the national conversation around autism continues, one thing is clear: the autism community — parents, children, adults on the spectrum, clinicians, and allies — is not going to stay silent in the face of outdated narratives.
Texas Sues Tylenol Makers After Trump Links Painkiller To Autism — All You Need to Know

Credits: Canva
Texas sues tylenol: Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton announced on October 28 that he has filed a lawsuit against the makers of Tylenol, accusing them of failing to warn consumers about possible risks of using the drug during pregnancy. According to USA Today, the lawsuit targets Johnson & Johnson and its spin-off company Kenvue, alleging they concealed information about Tylenol’s potential links to autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), violating state consumer protection laws.
“These corporations lied for decades, knowingly endangering millions to fill their own pockets,” Paxton said in a statement. “When they saw accountability coming, Johnson & Johnson tried to dodge responsibility by offloading their liability to another company. By holding Big Pharma accountable for poisoning our people, we will help Make America Healthy Again.”
This marks the first lawsuit by a state government since President Donald Trump recently claimed that using Tylenol during pregnancy may raise the risk of autism — a claim that has limited scientific support.
Tylenol: Why Is Texas Suing Tylenol Makers?
Texas’s lawsuit, the first of its kind from any state, follows remarks made last month by President Trump and Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr., who jointly issued new guidance discouraging pregnant women from using acetaminophen, the active ingredient in Tylenol. They cited it as a possible factor behind autism, sparking widespread concern and confusion among expecting mothers and healthcare experts alike.
The research surrounding Tylenol’s use in pregnancy remains unsettled. While a few studies have suggested a possible link between prenatal exposure and autism, many others have found no such connection. Major medical organizations have since pushed back against Trump and Kennedy’s statements, warning that the claims could spread unnecessary fear and misinformation.
This lawsuit is the first to formally adopt Trump’s theory that acetaminophen use in pregnancy might cause developmental disorders in children. The issue has long circulated among Kennedy’s followers, but Trump’s public comments brought it into mainstream discussion.
Texas Sues Tylenol: Tylenol Maker Fights Autism Warning Label
Kenvue has strongly defended Tylenol’s safety and dismissed Trump’s allegations, calling them misleading. Johnson & Johnson has also maintained that it has always acted responsibly in its product labeling, warning users only about the proven risk of liver damage from overuse.
In an official response, Kenvue stated that it was “deeply concerned by the spread of misinformation about the safety of acetaminophen and how it may affect women and children.” The company emphasized that acetaminophen remains “the safest pain relief option for pregnant women when needed throughout pregnancy.” Without it, they argued, women could face dangerous choices, either enduring untreated pain and fever, which may harm both mother and baby, or turning to more hazardous alternatives.
Over the past few years, hundreds of lawsuits have been filed nationwide by parents who believe their children developed autism or ADHD after prenatal Tylenol exposure. The largest group of such cases, consolidated in federal court in New York, was dismissed earlier this year due to insufficient scientific evidence. Plaintiffs have appealed the ruling, with an appellate hearing scheduled for November 17.
Texas Sues Tylenol: Is Acetaminophen Linked to Neurodevelopmental Disorders?
According to The New York Times, scientists have explored possible links between acetaminophen use during pregnancy and developmental disorders for years, but the research remains inconclusive.
Medical associations have rejected the Trump administration’s recent warning, reiterating that Tylenol is still considered the safest pain reliever for pregnant women. They warn that avoiding it altogether could be dangerous, as untreated high fevers and severe pain can pose serious health risks to both the mother and the unborn child.
Is The White House Hiding Truth About President Donald Trump’s Health After His Recent MRI Scan?

Credits: Canva
President Donald Trump confirmed on Monday that he recently underwent an MRI at the Walter Reed National Military Medical Center but chose not to explain the reason behind it. The statement marks the first time Trump, 79, has spoken about his second medical visit this year.
The October 10 appointment, described by the White House as a standard yearly exam, has stirred speculation since it came just six months after his last comprehensive physical. “I did. I got an MRI. It was perfect,” Trump told reporters on his flight to Tokyo. When asked for more information, he declined to say more, saying journalists should “ask the doctors.” This has left many wondering if there is more to the story behind his current health condition.
Is The White House Hiding The Truth About Donald Trump’s Health?
The White House has declined to clarify when Trump last took a cognitive test, as his most recent medical summary does not mention one. Officials have also refused to provide any additional information about the MRI that Trump said he underwent earlier this month. His admission has renewed speculation about the 79-year-old president’s health.
While Trump maintains that he is in “excellent shape,” the timing and secrecy surrounding the MRI have raised eyebrows. MRI scans are often used to detect issues such as strokes, brain abnormalities, or tumors. “I got an MRI. It was perfect,” Trump told reporters aboard Air Force One, but no further explanation has been provided.
White House Report Did Not Mention Trump’s MRI
Despite Trump’s assurance that his doctors had released a “very conclusive” report, the official White House summary did not specify why he made a second visit to Walter Reed within the same year. Traditionally, presidents undergo one full medical examination annually.
According to CNN, White House physician Dr. Sean Barbabella’s report only noted that Trump had “advanced imaging,” a term that could refer to CT scans or other procedures. There was no mention of an MRI or any details about its purpose or findings.
Another missing detail was any reference to a cognitive assessment, which had been included in Trump’s first examination earlier this year. Following his April check-up, Dr. Barbabella’s report had spanned three pages, covering Trump’s lab work, prescribed medication, vital signs, and overall physical condition.
Donald Trump’s Medical Tests
During the April examination, Trump’s doctor confirmed that the president had taken the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), a 30-point test that screens for memory and attention issues. The report at the time noted, “A comprehensive neurological exam revealed no abnormalities in mental status, cranial nerves, motor and sensory function, reflexes, gait, or balance.” It added that Trump scored a perfect 30 out of 30 on the MoCA, showing no signs of cognitive decline.
By contrast, Trump’s latest medical update, released after his October visit, was a brief five-paragraph note with no mention of any cognitive evaluation. When reporters asked if the president had taken one, the White House did not respond.
Trump did, however, bring up cognitive tests during a speech on Monday, mocking Democratic congresswomen Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez and Jasmine Crockett as “low IQ” individuals who “wouldn’t do well” on such exams. Yet he stopped short of revealing when he last took the test or what his latest score might have been.
So, Is the White House Really Hiding the Truth About President Donald Trump’s Health?
Trump’s second visit to Walter Reed in six months, along with visible bruising on his hands and swelling in his ankles, has added to speculation about his condition. His acknowledgment of an MRI, which is absent from the official White House report has only intensified public curiosity. The lack of transparency surrounding the test and not mentioning details in the official statement have led many to question whether the White House is concealing information about the president’s health.
As U.S. Measles Cases Surge, Could The Country Lose Its Elimination Status?
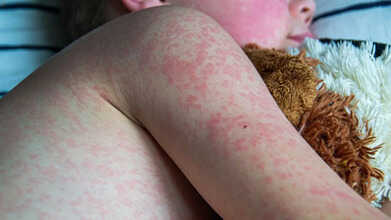
Credits: Canva
Measles has held “eliminated” status in the United States since 2000, a designation that means there had been no year-long, uncontrolled spread of the virus within the country for decades. But that milestone is now in jeopardy.
The infection is spreading again, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has reported 1,596 confirmed cases this year, the highest annual total in over thirty years. The actual number could be higher, says Dr. Paul Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Measles Case Surge In The US
Since August 2025, more than 100 people have been infected in the Utah–Arizona border region, forming the second-largest measles cluster in the U.S. this year. Most patients were unvaccinated, and the virus has now moved beyond small religious circles into the general population. This outbreak followed the earlier “Southwest wave,” which infected over 880 people in Texas, New Mexico, and Oklahoma, sending national measles numbers to a 34-year record high.
Experts warn that the current pattern resembles the major outbreaks seen in the early 1990s, before widespread vaccination programs curbed transmission. The largest outbreak occurred in West Texas, where 99 people were hospitalized and two unvaccinated school-age children died — the first measles deaths in the country since 2015. The Texas Department of State Health Services declared that outbreak over in mid-August. New Mexico has also reported a measles-related death, according to CNN. In response, the CDC has sent emergency teams to Utah, Arizona, Minnesota, and South Carolina to help limit the spread.
What Is Causing Measles to Increase in the U.S.?
In Mohave County, Arizona, vaccination coverage among kindergartners dropped from 91% in 2019–20 to 78% in 2024–25, with a similar decline noted in southwest Utah.
Public health experts stress that at least 95% vaccination coverage is necessary to prevent the virus from spreading. Both Utah and Arizona allow parents to exempt children from school vaccine mandates on personal or religious grounds, leaving pockets of unprotected populations.
According to The Times of India, vaccine hesitancy has deepened since the Covid-19 pandemic, fueled by political polarization and a decline in public trust toward health authorities. Notably, most of the affected towns voted heavily for Donald Trump in the 2024 election, underscoring how politics and misinformation continue to shape vaccination decisions.
Will the U.S. Lose Its Measles Elimination Status?
In November, the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), the regional arm of the World Health Organization (WHO) will hold its annual Measles and Rubella Elimination Regional Monitoring and Re-Verification Commission meeting to review each country’s elimination status.
The WHO defines a loss of elimination status as continuous transmission lasting longer than 12 months. While there are no direct penalties, re-establishing measles as an endemic disease would mark a major public health setback, leading to avoidable deaths and straining local healthcare systems.
Countries that lose their elimination status are required to submit a corrective action plan, typically involving intensive vaccination efforts, stronger surveillance, and faster outbreak responses.
Although President Donald Trump signed an executive order in January to withdraw the U.S. from the WHO, PAHO officials said they still expect representatives from the CDC and the National Sustainability Commission to attend next month’s meeting.
In August, local health authorities declared the end of the West Texas outbreak, which had caused 762 infections over seven months, according to state data. Neighboring New Mexico also reported 100 linked cases and one adult death, bringing the total fatalities from the outbreak to three which were two children in Texas and one adult in New Mexico, all unvaccinated.
Despite these containment efforts, new clusters continue to appear in Utah, Arizona, and South Carolina, and investigators are examining whether these are connected to the Texas outbreak. If transmission persists into January, the United States could officially lose the measles elimination status it earned in 2000.
The CDC calls the elimination of measles one of the country’s most significant public health achievements, made possible through a highly effective vaccination program and improved control efforts across the Americas. However, MMR vaccine coverage in both the U.S. and Canada has been steadily falling, with sharper declines noted after the Covid-19 pandemic.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

