- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
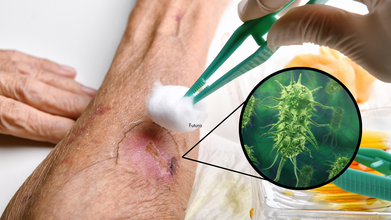
Flesh Eating Bacteria Death Toll At 4 People, 22 Hospitalized, Does It Actually Eat Your Flesh?
(Credit-Canva)
Louisiana health officials have confirmed that two more people have died and at least 22 have been hospitalized from a flesh-eating bacteria called Vibrio vulnificus. This brings the total number of deaths in the state to four so far this year.
The bacteria is found naturally in warm saltwater and brackish water, as well as in raw or undercooked seafood. Two of the most recent deaths were from people who got sick after eating raw oysters.
What Is Flesh-Eating Bacteria/Vibrio vulnificus?
Vibrio are bacteria that live in coastal waters. While most types are harmless, some can cause severe, life-threatening infections, though this is rare. The Vibrio vulnificus strain is particularly dangerous and is responsible for more than 95% of all deaths from seafood-related illness in the United States.
Each year, nearly 80,000 people in the U.S. get sick from a Vibrio infection, mostly from eating contaminated food. Of those, about 500 are hospitalized, and around 100 die.
How Do People Get Infected With Flesh Eating Bacteria?
In Louisiana, officials have recorded 22 total cases this year, and all of those people had to be hospitalized. More than 80% of these cases happened when people were exposed to the bacteria through a wound on their skin while in saltwater. The remaining cases were from people who got sick after eating seafood, such as raw oysters. The bacteria are most common in warm coastal waters, usually between May and October. Because of this, state health officials have issued a warning for residents to take precautions to prevent infections.
Does Flesh Eating Bacteria Actually Eat Your Flesh?
According to the American Society For Microbiology, the term "flesh-eating" can be a bit misleading. From the bacteria's point of view, its goal is simply to survive. Humans are not its normal home—it's built to live in the ocean. When it gets into a human wound, it uses the tools it already has to stay alive in this new environment. Damaged tissue becomes a food source for the bacteria. By destroying cells, it can also protect itself from the body's immune system. Moving deeper into the body helps it find more food and avoid other germs.
Vibrio vulnificus has a set of tools, like special toxins and proteins, that break down body tissue and fight against the body's defenses. For example, one strong toxin called RtxA1 kills human cells and attacks the body's immune cells, allowing the bacteria to spread quickly.
The bacteria also really need iron to grow. This is why people with health issues that increase iron in their blood, such as liver disease, are at a higher risk of getting a deadly, full-body infection.
Interestingly, the damage isn't just caused by the bacteria. Sometimes, the body's own immune system can make things worse by releasing chemicals that increase swelling and destroy even more tissue.
How Can You Protect Yourself From Flesh Eating Bacteria?
The best way to stay safe is to avoid these infections in the first place. The CDC advises that if you have an open wound, like a cut or a new tattoo, you should stay out of salty or brackish water, including at the beach. If you do come into contact with water or raw seafood, immediately wash the wound with soap and water.
It's also very important to be aware of the risks, especially if you have other health issues. If you get a cut in saltwater and it starts to look infected—with swelling or pain—see a doctor right away. Tell them you were in seawater. The good news is that this bacteria is very sensitive to antibiotics, so catching the infection early is the key to getting better.
Do You Have Persistent Nasal Congestion? It Could Be A Sign of Long Covid

Credits: Canva
A symptom that most people associate with a common cold could actually indicate long Covid. Typically, individuals recover from a coronavirus infection within a few weeks after symptoms begin. However, NHS guidance points out that some people can develop a more persistent illness, with symptoms lasting far longer.
Long Covid, also called post-COVID syndrome, is usually diagnosed when COVID-19 symptoms persist for more than 12 weeks. Keep reading to learn which common symptom might actually be a sign of long Covid.
One Nose Symptom That Can Also Be Long Covid
Long Covid symptoms can vary widely, and many may be mistaken for a regular cold or flu. For instance, a sore throat or a runny nose could suggest either a common cold or long Covid, depending on how long the symptom has been present.
What Are Common Symptoms Of Long Covid
Other symptoms may include:
- Memory or concentration difficulties, often referred to as brain fog
- Shortness of breath
- Joint aches and muscle pain
- Extreme fatigue
- Hair loss or skin rashes such as hives
- Nasal congestion or a runny nose
- Headaches, dizziness, or vertigo
- Pins and needles or widespread body aches
- Persistent cough
- Abdominal pain or diarrhoea
- Nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and reduced appetite
- Trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- Elevated temperature
- Changes in senses, including vision issues, earaches, tinnitus, or altered taste and smell
- Anxiety and depression
- Sore throat
- Sudden confusion (delirium), especially in older adults
- Chest pain or tightness, and noticeable heart palpitations
How To Know If You Have Long Covid Or Common Cold?
Telling the difference between a common cold and COVID-19 can be tricky, as many symptoms overlap. You can look for clues such as when the symptoms started, the intensity of fatigue, and whether you have experienced loss of taste or smell, a hallmark of earlier COVID variants. The only way to be sure is to take a COVID-19 test.
Long Covid stands apart from both a cold and acute COVID-19 because its symptoms, like fatigue, shortness of breath, and cognitive difficulties, persist for weeks or months after the initial infection.
Long Covid Complications
Some people, particularly those who had severe COVID-19, may experience effects on multiple organs or develop autoimmune conditions lasting weeks, months, or even years. These multi-organ effects can involve the heart, lungs, kidneys, skin, and brain. Many of these complications share symptoms with commonly reported long Covid issues. Consequently, people who have had COVID-19 may be at higher risk of developing or worsening conditions such as:
- Diabetes
- Heart problems
- Blood clots
- Neurological disorders
If you suspect you have long Covid, your GP may run several tests to rule out other causes of your symptoms, including blood tests. They might also monitor your heart rate and oxygen levels.
In some cases, further investigations such as an ECG or X-ray may be required. Some patients may be referred to a team of specialists at a post-COVID syndrome clinic for comprehensive evaluation.
Thinking Of Getting Your Flu Shot? NHS Says ‘Wait’ If You Have This One Symptom
Credits: Canva
As the crisp autumn air settles in, flu season returns, bringing the familiar symptoms of fever, and cough. Each year, influenza , commonly known as the flu, impacts millions of people. For most, it causes a mild to moderate illness, but for some, it can be serious, potentially leading to hospitalization or even death.
Even though the onset of flu season may feel routine, it is crucial to remember that the virus evolves annually, making yearly vaccination an essential measure for staying healthy. That said, the NHS has advised delaying your autumn vaccination if you experience one specific symptom. The health service advises that you should “wait until you’re feeling better” before getting the flu jab.
NHS Flu Vaccination
The flu shot is offered on the NHS every year during autumn or early winter for individuals at higher risk of severe flu complications. Those eligible include people aged 65 and over, as well as those with certain long-term medical conditions. According to the NHS website, the vaccine protects against the “most common types” of flu strains each year. While it’s still possible to catch the flu after vaccination, symptoms are generally milder and shorter in duration.
One Symptom That Means You Should Postpone Your Flu Jab
This year’s autumn and winter vaccination program is underway, with appointments available through GP practices, the NHS app, and select pharmacies. However, there are circumstances in which vaccination should be delayed. The NHS recommends: “If you have a high temperature, wait until you’re feeling better before having your flu vaccine.”
Some individuals may also be at risk of allergic reactions to the injection. “Most people eligible for the flu vaccine can receive it,” the NHS confirmed, adding: “You should not get the vaccine only if you’ve had a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to a previous dose or to an ingredient in the vaccine.” Some flu vaccines in the UK contain egg protein, so anyone with an egg allergy should inform the healthcare professional administering the shot.
Side Effects Of The Flu Vaccine
The NHS notes that side effects are typically mild and usually resolve within one to two days. These can include:
- Pain or soreness at the injection site
- A slightly raised temperature
- Aching muscles or body
The NHS clarifies: “The injected flu vaccines used in the UK do not contain live viruses. They cannot give you flu.”
Flu shots can generally be given alongside other vaccines, such as COVID-19 or shingles vaccines. They are not usually administered with the RSV vaccine, though simultaneous vaccination may be advised if a doctor or nurse deems it appropriate.
Eligibility For Flu Vaccine
Flu vaccines are recommended for everyone aged six months and older, with a focus on high-risk groups such as children under five, adults 65 and older, pregnant women, and those with chronic health conditions. Individuals who have previously had a severe allergic reaction to a flu vaccine should consult a healthcare provider before receiving the shot.
Recent updates to vaccine policies, particularly around COVID-19 vaccines, have caused some confusion. Many wonder if getting the flu jab has become more complicated. The good news is that flu vaccines remain widely accessible. Pharmacies, GP offices, public health clinics, and many workplaces continue to offer the seasonal injection, often at little or no cost.
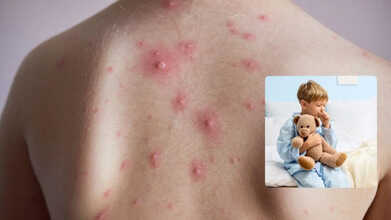
Kollam Faces Chickenpox Outbreak: How To Recognize Symptoms Early
Credits: Canva
Kerala is on high alert as chickenpox cases are rising quickly in Kollam district. Over the past week alone, health authorities have confirmed more than 100 new cases, with numbers continuing to climb. This sudden spike has prompted officials to take swift action to prevent further spread. But why is chickenpox, often considered a seasonal illness, circulating now? And what early signs should you watch for to know if you or someone around you might have it?
Chickenpox Cases Surge Rapidly In Kollam
While chickenpox usually appears more often during the summer months, health officials say unpredictable weather during the rainy season is also playing a role in this surge. Authorities warn that the disease can lead to serious complications in children, teens, older adults, pregnant women, and people with weakened immune systems. Residents are being urged to follow preventive measures and seek medical attention promptly to contain the outbreak.
What Is Chickenpox And How Does It Spread?
Chickenpox, caused by the varicella-zoster virus, is extremely contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets or direct contact with someone who is infected. In children, it often starts as a mild rash accompanied by fever, but it can spread quickly in crowded areas.
The virus can also be transmitted through coughing or sneezing, and it is most infectious a day or two before the rash appears and in the early days of the rash. In individuals with weak immunity, the dormant virus may reactivate later in life, causing shingles (herpes zoster).
Why Is Kollam Facing A Chickenpox Outbreak?
The varicella-zoster virus spreads very easily through coughs, sneezes, or close contact with an infected person. Kollam’s warm, humid post-monsoon climate creates ideal conditions for the virus to multiply. While the first wave of cases was mostly among children, doctors now warn that adults are also increasingly vulnerable, according to The New Indian Express.
How To Detect Chickenpox Symptoms Early?
Spotting chickenpox early means looking for general warning signs like fever, fatigue, headache, and loss of appetite, which usually appear one to two days before the rash. The rash itself starts as tiny red spots that later form fluid-filled blisters and eventually scab over. Paying attention to these early symptoms—especially after known exposure—can help identify the infection sooner.
How To Spot The Chickenpox Rash
The first rash usually shows up as small red bumps on the face, chest, or back. These bumps quickly turn into blisters filled with fluid, which are contagious. Over a few days, the blisters break and crust over, forming scabs. It’s common to see spots, blisters, and scabs all at the same time, according to the CDC.
Stages Of Chickenpox
The Mayo Clinic explains that chickenpox progresses in three main stages:
- Incubation Stage (10–21 days): After exposure, the virus remains inactive. Infected individuals typically show no symptoms during this period.
- Prodromal Stage (1–2 days): Early signs include fever, tiredness, headache, loss of appetite, and body aches. This is also when the virus can start spreading to others.
- Rash Stage (5–10 days): Red, itchy spots appear first on the face and chest, spreading across the body. These spots develop into fluid-filled blisters that scab over within a few days. Mild fever, itching, and discomfort are common during this stage.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, complications are uncommon but can include pneumonia, brain inflammation (encephalitis), and bacterial skin infections. Vulnerable groups, such as infants, pregnant women, older adults, and people with weakened immunity are at higher risk of severe illness.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

