Melasma Explained: Why It Occurs and How To Treat Skin Discoloration
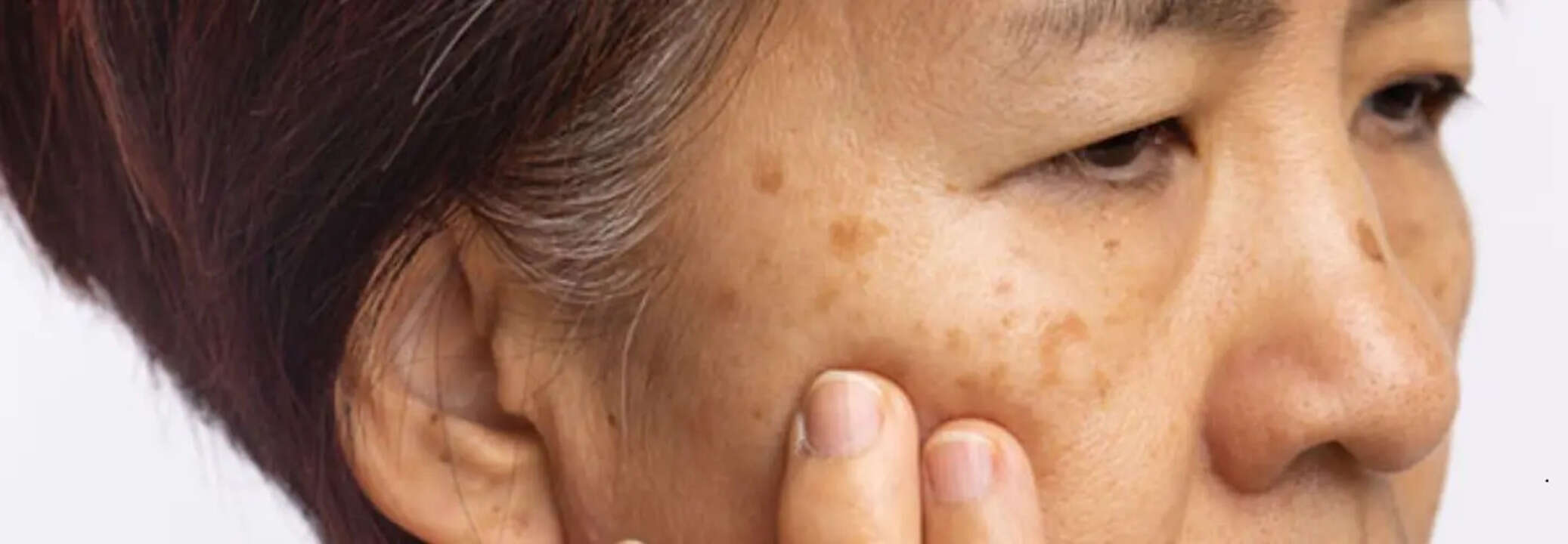
Melasma (Credit: Canva)
SummaryMelasma is a common skin condition that majorly affects women. This article details its symptoms, causes and how to get it treated.
End of Article

Melasma (Credit: Canva)