- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Men Have Bigger Kidneys But Does That Mean Women Pee More?
Credit: Canva
We’ve all heard the joke at some point — women take longer in the bathroom because they “pee more.” But is there any truth behind this bathroom stereotype? As it turns out, science is more complex than that, and the answer lies deep within the structure of our kidneys.
Biologically speaking, men generally have larger kidneys than women. But does that mean they produce more urine? Not necessarily.
A recent review of autopsy data has revealed some interesting findings. While men do tend to have physically larger kidneys, researchers aren’t entirely sure if this difference holds up once body size — such as height, weight, or body surface area (BSA) — is taken into account. In other words, just because a man has a bigger kidney doesn’t automatically mean it's more efficient or produces more urine.
Size Doesn’t Always Equal Output
Kidneys are vital organs responsible for filtering waste from the blood and maintaining fluid balance. Each kidney contains roughly a million nephrons — tiny filtering units that help produce urine. The number of nephrons is believed to be associated with kidney size. So, in theory, larger kidneys might have more nephrons and a higher filtering capacity.However, here's where it gets interesting: When kidney size is adjusted relative to body size, men may not actually have significantly larger kidneys than women. And in clinical settings, women often show better kidney health outcomes over time. Studies suggest that women are less likely to develop or progress to chronic kidney disease (CKD), even though they may report more frequent urination.
So Why Do Women Feel the Urge More Often?
The frequency of urination is influenced by several factors beyond kidney size — including bladder size, hormone levels, fluid intake, and even societal behavior. On average, women have slightly smaller bladders than men, which means they may feel the need to urinate more often, especially when consuming the same amount of fluids.Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause also play a significant role in urinary patterns. Estrogen, for instance, affects the urinary tract and can make women more sensitive to the urge to go.
What It All Means
So, do women pee more than men? It depends. While they may urinate more frequently due to bladder size and hormonal factors, this doesn’t necessarily mean they produce more urine overall. The larger kidneys in men may be more efficient, but that doesn’t equate to more trips to the restroom.Ultimately, urination is a deeply personal — and variable — experience. If you find yourself making more frequent bathroom visits than usual, regardless of gender, it might be worth discussing with a healthcare provider.
Because when it comes to your health, every drop matters.
Fact Check: Common Myths Around HPV Vaccine And How It Will Prevent Cervical Cancer
Credit: Canva
In a major push towards eliminating cervical cancer from India, Prime Minister Narendra Modi today launched the nationwide Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination program for girls aged 14 years.
The new vaccination drive comes as cervical cancer remains the second most common cancer among women in India, with nearly 80,000 new cases and over 42,000 deaths reported annually. As per data from the ICMR-National Cancer Registry Program (NCRP), an estimated 78,499 new cases and 42,392 deaths were reported in 2024.
Calling it a "decisive step”, the government noted that it is aimed at “strengthening the vision of ‘swasth nari’ (healthy women) while being rooted in scientific evidence, strict regulatory oversight and global best practices”.
“India's vaccination drive reflects safety, responsibility, and long-term commitment to women’s health,” it added.
The national program will use Gardasil, a quadrivalent HPV vaccine that protects against HPV types 16 and 18, which cause cervical cancer, as well as types 6 and 11.
However, social media has been rife with concerns around the safety of the vaccine, its impact on women’s reproductive health, among others.
HPV Vaccine: The Myths And Facts
Myth: HPV vaccines can cause severe side effects and even death.
Fact: The HPV vaccines come with a “confirmed strong safety record”.
“Extensive global monitoring shows a strong safety profile supported by scientific reviews. Independent evaluations have found no causal link between vaccination and chronic harm, strengthening confidence in its continued use worldwide,” the government said.
The vaccine has been licensed in India since 2008, and the new rollout follows recommendations by the World Health Organization (WHO) and approvals from the National Technical Advisory Group on Immunization (NTAGI).
“HPV vaccines have been given to hundreds of millions globally. Extensive post-marketing surveillance shows an excellent safety profile, with no causal link to serious adverse outcomes. The evidence is robust, transparent, and reassuring,” Dr. CS Pramesh, Director of the Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai, shared in a post on the social media platform X.
Myth: The HPV vaccine has never been used in India
Fact: The vaccine has been in use in India. It has been administered for years since 2008 with successful implementation in states like Punjab, Sikkim, and Tamil Nadu.
Myth: HPV vaccination does not prevent cervical cancer
Fact: The HPV vaccine has been proven to prevent cervical cancer
Studies show a 65 percent drop in cervical cancer cases among US women between 2012 and 2019 and an 88-89 percent reduction in precancerous lesions among Scottish women over a decade.
Countries with early HPV vaccine adoption have also shown large declines in HPV infection, high-grade cervical lesions, and cervical cancer incidence.
"Even when considering the rarest side effects, HPV vaccines are overwhelmingly safe. The protection they offer against cervical cancer far outweighs the minimal risks. Parents are encouraged to vaccinate their daughters on time," said Dr. Neena Malhotra, Professor and Head of Department, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, AIIMS New Delhi on X.
Myths: Are Multiple Doses Needed?
Fact: A single dose of the quadrivalent HPV vaccine is effective. It provides strong protection against HPV infection. It helps prevent cervical cancer.
“Strong global and Indian scientific evidence confirms that a single dose provides robust and durable protection when administered to girls in the recommended age group," the government said.
Rare Diseases Day: How AI Is Transforming Early Diagnosis
Credit: Canva
For all major diseases, early detection is key to improving treatment outcomes. However, when it comes to rare diseases, it is unpredictable, making it more challenging to diagnose. In such a scenario, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a major role -- from early diagnosis to treatment, said health experts on Rare Disease Day.
Rare Disease Day is annually observed on February 28 to raise awareness about the lesser-known conditions and the underlying challenges for people suffering from them.
While many of the rare disorders are genetic, they often also surface without any prior family history. In some cases, they are diagnosed in infancy, while in others the manifestation is years late.
The advanced AI technology is, however, now enabling clinicians to better understand the patients’ genetic profiles and patterns that were not clearer earlier. The technology is also paving the way for earlier and more accurate diagnoses, bringing hope to thousands of patients worldwide.
“AI is revolutionizing the fight against rare diseases by speeding up diagnosis, research, and development of treatments. Rare diseases often take years to diagnose because of the lack of data, overlapping symptoms, and unclear diagnosis,” Dr. Vinit Banga, Director, Neurology, Fortis Escorts Hospital, Faridabad, told HealthandMe.
“AI algorithms can process medical records, genetic information, and images to identify patterns that may escape human detection, allowing for earlier and more accurate diagnoses,” he added.
AI Simplifying Rare Disease Diagnoses, Drug development
In a February paper published in the journal Nature, researchers from the Shanghai Jiao Tong University in China presented an AI system called DeepRare -- a multi-agent system for rare disease differential diagnosis decision support, powered by large language models, integrating more than 40 specialized tools.
Using the specialized tools and knowledge sources, the agentic AI system generates ranked diagnostic hypotheses for rare diseases. Each of the tools was also accompanied by reasoning that links the conclusions to verifiable medical evidence.
Similarly, Harvard University-based researchers in a paper also published in the Nature journal in 2025 described an AI tool called PopEVE, which can identify genetic variants most likely to cause severe disease or death.
The model was able to identify more than 100 novel alterations responsible for undiagnosed, rare genetic diseases.
"AI is cutting short the diagnostic odyssey from years to weeks. Large-scale genomic projects help create a vital reference architecture for India and the global community,” Dr. Sudheendra Rao N R, MBBS, PhD, Scientific Advisor, Organization for Rare Diseases India, told HealthandMe.
By integrating deep phenotyping with AI, clinicians can decipher unknown genetic variants and accelerate the development of both repurposed and next-generation precision-therapies, the expert added.
AI can also help researchers identify new drug targets for the treatment of rare conditions.
Dr. Banga said that AI is also instrumental in accelerating drug development by processing enormous amounts of biomedical data to discover new targets for drugs and repurpose existing ones. Importantly, AI is cutting down on time and expenses.
“Machine learning algorithms enable the prediction of patient responses to particular treatments, making it possible to develop personalized treatment strategies,” the expert said.
Further, AI-enabled infrastructure is helping to achieve geographic neutrality, delivering the same caliber of healthcare screening to rural villages and Tier-3 cities as to Tier-1 hubs, ensuring a high-quality healthcare gateway that is no longer defined by where the patient lives.
Moreover, AI-based platforms bring together researchers from across the globe, making it easier to share data.
What Is A Rare Disease
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines a rare disease as an often debilitating, chronic, or degenerative condition affecting 1 or fewer per 1,000 population.
Rare diseases do not have epidemiological data, are at high risk of misdiagnosis, and often also lack effective treatments.
According to the WHO ICD-11 (International Classification of Diseases), there are over 5,500 rare diseases. It also assigns unique identifiers (URIs) to them for better tracking.
There are estimated to be over 7,000 distinct rare diseases affecting more than 300 million people globally.
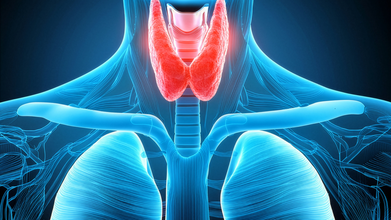
Rare Diseases Day: A Parenting Guide For Congenital Hypothyroidism
Credit: Canva
Do you know that congenital hypothyroidism, a rare disability, affects about 1 in 2,500–3,000 newborns globally, but in India, the incidence is higher -- approximately 1 in 1,000 births.
India records nearly 26 million births annually, with an estimated 10,000 babies born each year with Congenital Hypothyroidism.
This means 27 babies are born every day in India, with the condition that more than one is born every hour. Early treatment within the first 2 weeks of life can ensure normal brain development, while delayed treatment can reduce IQ by 30–50 points.
Congenital Hypothyroidism (CH) is a condition present at birth in which a baby’s thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone.
The thyroid is a small gland located in the neck. It produces a hormone called thyroxine (T4), which is essential for brain development, growth, and overall body metabolism. The thyroid hormone is especially important in the first few weeks of life.
The thyroid hormone helps in:
- Brain development
- Physical growth
- Bone development
- Muscle strength
- Energy regulation
If a baby does not receive enough thyroid hormones soon after birth, it can lead to permanent intellectual disability and growth problems.
The good news is that congenital hypothyroidism is easily detectable and completely treatable if identified early.
What Causes Congenital Hypothyroidism? What Are The Symptoms?
Congenital Hypothyroidism may occur because:
- The thyroid gland is completely absent
- The thyroid gland is underdeveloped
- The gland is present but does not function properly
- Rarely, the baby cannot produce or use the thyroid hormone correctly
One of the biggest challenges with Congenital Hypothyroidism is that most babies look completely normal at birth.
However, over time, some signs may appear:
- Excessive sleepiness
- Poor feeding
- Constipation
- Prolonged jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- Hoarse cry
- Large tongue
- Puffy face
- Cold or dry skin
- Slow growth
How Is Congenital Hypothyroidism Detected?
1. Newborn Screening Test (Heel-Prick Test)
- This is the most important test.
- A few drops of blood are taken from the baby’s heel.
- It is usually done 48–72 hours after birth, but can be done soon after birth on the cord blood, too.
- Test measures Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH).
- If TSH levels are high, it suggests that the thyroid is not functioning properly.
- This test is simple, safe, quick, and affordable
2. Confirmatory Blood Tests
If the screening test is abnormal, the doctor will order:
- Serum TSH test
- Free T4 (thyroxine) level
- High TSH and low T4 confirm the diagnosis
3. Thyroid Scan
In some cases, imaging tests are needed. The ultrasound of the neck (less accurate) and Nuclear Medicine Thyroid scan (more accurate) may be done to check whether the gland is absent, small, or misplaced. However, treatment should not be delayed while waiting for imaging.
When Should Treatment Start?
Treatment should begin as early as possible -- ideally within the first 14 days of life. Starting treatment within the first two weeks allows normal brain development.
Delaying treatment increases the risk of permanent intellectual disability.
Doctors will monitor:
- TSH levels
- T4 levels
- Baby’s growth and development
Initially, blood tests are done every 2–4 weeks, then less frequently as the child grows. Proper follow-up ensures the dose remains correct. Some babies may need treatment for life.
In certain cases, doctors may reassess thyroid function after 3 years of age to see whether the condition is temporary or permanent. Most children who receive early and proper treatment grow up with completely normal intelligence and physical development.
Can Congenital Hypothyroidism Be Prevented? Why Early Screening Is So Important
Most cases cannot be prevented. However:
- Universal newborn screening can prevent intellectual disability
- Ensuring adequate iodine intake during pregnancy helps reduce risk
- The key is early detection—not prevention
A baby with Congenital Hypothyroidism may look perfectly healthy. Without screening, diagnosis may be delayed until symptoms appear—by then, brain development may already be affected.
With early testing the diagnosis is simple; treatment is affordable; and outcome is excellent. But without testing:
- Intellectual disability can occur
- Growth may be affected
- The child may require lifelong support
Congenital Hypothyroidism is one of the most preventable causes of intellectual disability in children. A small heel-prick test in the first few days of life can protect your baby’s brain forever.
If you are expecting a baby or have a newborn, speak to your doctor about newborn thyroid screening.
Early diagnosis. Simple treatment. Normal life.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

