- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
Think Mosquitoes Bite You More Than Others? 5 Weird Biological Reasons Why
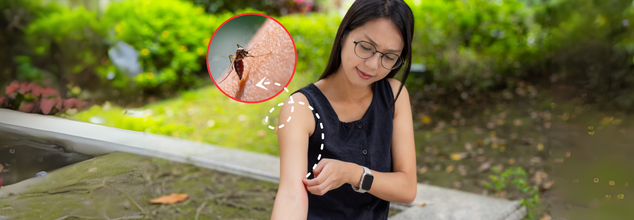
When summer arrives and the air grows thick with warmth, it brings with it an unwelcome guest—mosquitoes. That irritating buzz in your ear, the sharp sting on your skin, and the maddening itch afterward can quickly turn a pleasant evening into a nightmare. But have you ever noticed that mosquitoes seem to swarm around you more than others? If you find yourself swatting away bites while your companions remain unbothered, you're not alone—and you're not imagining it.
Turns out, mosquitoes do play favorites, and science has a few fascinating explanations for why that might be. From your blood type to your wardrobe, your scent to your sweat, here’s a deep dive into the weird and wild biological reasons why mosquitoes might just love you more—and what you can do about it.
Before we decode their behavior, it’s important to understand the threat they pose. Mosquitoes are among the deadliest creatures on earth, not because of their bite itself, but because of what they can carry. From Dengue, Malaria, and Chikungunya to Zika Virus and Japanese Encephalitis, mosquitoes are silent vectors for disease that impact millions globally. According to the World Health Organization, mosquito-borne illnesses claim over a million lives each year—making them far more than a backyard pest.
Why Do Mosquitoes Bite?
Contrary to popular belief, mosquitoes don’t bite for food. Male mosquitoes survive entirely on nectar, while females seek out blood to obtain proteins vital for egg development. That’s right—only the females bite, and they do it for reproduction.
But mosquitoes don’t choose their targets randomly. Their decision to bite you is rooted in biology and chemistry. Female mosquitoes are equipped with a suite of sensory tools that allow them to detect carbon dioxide from nearly 160 feet away, identify specific skin odors, and even spot you based on the color of your clothes. Here are five weird biological reasons mosquitoes may find you more irresistible than others.
1. Your Blood Type
There’s long been speculation that mosquitoes prefer certain blood types, and science offers some support. A 2004 study found that mosquitoes landed on people with Type O blood nearly twice as often as those with Type A. A more recent 2019 study reinforced this finding, observing mosquitoes feeding more frequently from Type O blood samples.
While the exact mechanism isn’t fully understood, researchers believe it’s related to secretions on the skin associated with specific blood types—particularly in people known as “secretors,” whose blood type antigens are found not just in their blood but in their saliva, sweat, and skin.
2. The Color of Your Clothing
Mosquitoes are highly visual and rely on sight to locate hosts, especially in the daylight. Studies show that darker colors—black, navy, and red—stand out more to mosquitoes. These colors retain more heat and contrast strongly with green, natural environments, making you an easy target.
Light-colored, loose-fitting clothing offers more than just summer comfort—it can be your first line of mosquito defense.
3. You Emit More Carbon Dioxide
Every time you exhale, you release carbon dioxide, one of the key cues mosquitoes use to track humans. Larger individuals, people who are pregnant, or anyone who’s physically active emits more CO₂ and is more likely to attract attention.
According to research published in Chemical Senses, mosquitoes detect carbon dioxide using an organ called the maxillary palp, which enables them to lock in on their target from a shocking distance of up to 164 feet.
4. Your Body Odor
Human sweat contains a mix of compounds—like lactic acid, ammonia, and uric acid—that mosquitoes find irresistible. Newer research highlights the role of carboxylic acids, which are produced when beneficial skin bacteria break down sebum (the waxy substance secreted by your skin).
Interestingly, even the most expensive perfumes or colognes may not mask these natural odors. Genetics, hygiene, and lifestyle factors like exercise can all impact how your skin smells to a mosquito.
5. Alcohol
Yes, even your choice of beverage can make a difference. A small study found that mosquitoes were more likely to land on participants after they had consumed beer. While the sample size was small and the findings modest, it raises interesting questions about metabolism, body temperature, and skin chemistry post-consumption.
Why Some People Swell More Than Others After Bites?
Mosquito bites don’t affect everyone equally. Some people develop small red dots; others end up with itchy welts. The difference lies in your immune response. When a mosquito bites, it injects saliva that contains anticoagulants and proteins. Your immune system releases histamine to combat these foreign substances, which causes inflammation and itchiness. People with stronger immune responses tend to have more visible reactions.
Remedies To Protect Yourself
Forget citronella candles and unverified home remedies. The most effective repellents contain DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus. For those preferring natural alternatives, plant-based repellents such as neem oil, lavender, and citronella can help, though they may need more frequent application.
Want an extra layer of protection? Look for sunscreens that also offer mosquito repellent features—perfect for beach days and hikes alike.
How to Make Your Home Mosquito-Free?
A few strategic changes can turn your home into a mosquito fortress:
- Eliminate stagnant water in pots, buckets, and bird baths—mosquitoes breed in still water.
- Use ceiling fans to disrupt mosquito flight patterns.
- Install window screens and keep doors shut during dawn and dusk.
- Add mosquito-repelling plants like marigold, basil, and lemongrass to your garden.
- Taking cues from global solutions like the Caribbean’s approach to community fogging and public awareness can also make a lasting impact.
Understanding why mosquitoes target you is more than a fun fact—it’s a survival skill. Armed with knowledge and the right protection, you can reclaim your summer without constantly itching or worrying about disease.
You Are Much Less Likely To Get Opioid Prescriptions For Lower Back Pain Than Before- Is Healthcare Getting Better?
(Credit-Canva)
Emergency rooms are handing out significantly fewer opioid prescriptions to people experiencing lower back pain. Researchers reported in the Annals of Emergency Medicine on July 12 that the rate of opioid prescriptions for back pain in ERs dropped by more than half between 2016 and 2022.
Dramatic Decline in Opioid Prescribing
Just a few years ago, in 2016, almost one out of every three visits to the ER for back pain ended with a prescription for opioid painkillers. But by 2022, that number had fallen dramatically to just over one in ten visits. This big drop means that doctors are learning from the available information and changing the way they practice medicine, especially as more people become aware of the widespread problems caused by opioid addiction. It's a positive sign that medical professionals are actively working to curb the opioid crisis.
Understanding the Study and Patient Experience
To figure this out, researchers looked at records from nearly 53 million ER visits for low back pain that happened between 2016 and 2022. These records were gathered by a national health statistics centre. The study found that when people went to the ER for back pain, they were usually in a lot of discomfort, rating their pain at more than 7 out of 10. On average, they had to wait about 37 minutes before a doctor saw them and spent around four hours in the emergency room getting treatment.
Why Opioid Usage Is Risky For Patients
A 2023 study even found that opioids may not be as effective for back pain. Published in the JAMA network, a 2023 study conducted a trial on those who were experiencing back pain. The trial involved 347 adults who had been experiencing pain for up to 12 weeks. Everyone in the study received standard care, which included reassurance, advice to avoid bed rest, and encouragement to stay active. Half of the participants also received a combination of oxycodone and naloxone (an opioid), while the other half received a placebo (a dummy pill).
The study also revealed that while side effects were similar for both groups, there was a significant difference in the risk of opioid misuse. One year later, 20% of the participants who took opioids were at risk of misusing them, compared to only 10% of those who received the placebo. This suggests that even for short-term pain relief, opioids carry a greater risk of future misuse.
NSAIDs Emerge as Preferred Treatment
Now, when you go to the ER with low back pain, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, often called NSAIDs (like ibuprofen), are the most common painkillers prescribed. They're given to almost 29% of patients. It's not just about prescriptions either; fewer patients are actually given opioids while they are being treated in the ER. That number went down from 35% of cases in 2016 to less than 25% by 2020, showing a clear shift away from immediate opioid use during emergency care for back pain.
Next Issues People Must Tackle
Even though there's good progress with reducing opioids, ER doctors still have some areas where they could improve how they treat back pain. For example, many patients with back pain are still getting X-rays that they don't really need. In 2022, about 37% of patients had an X-ray, which is pretty much the same as in 2015. In fact, in 2021, almost 44% of cases involved an X-ray, which was the highest rate. It's tough to get this number down because deciding whether to order an X-ray can be complicated and depends on what both the doctor and the patient think is best.
AI Can Now Help Identify Diabetic Eye Disease That Can Destroy Your Vision For Life
(Credit-Canva)
Doctors may soon have a powerful new tool to help catch a serious eye disease caused by diabetes. Researchers have created an AI-powered retina tracker that is incredibly accurate at finding diabetic retinopathy, a condition that can lead to blindness. In a news release by the Endocrine Society, researchers detail how this new AI technology revolutionizes health and eye care, bringing it to the next level.
Fast, Accurate, and Accessible Eye Screening
This new program, called the Simple Mobile AI Retina Tracker (SMART), showed over 99% accuracy in its ability to screen for diabetic retinopathy. This impressive result was announced recently at a medical conference.
SMART uses advanced AI to quickly and accurately look at images of the retina – the light-sensing part at the back of your eye. What makes it truly special is that it can work on any device with internet access, even basic smartphones.
This means eye specialists can screen patients more easily and quickly. It also allows general doctors to include eye exams during regular visits. Most importantly, it helps bring high-quality eye checks to places where there aren't many eye doctors.
Tackling Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a condition where tiny blood vessels in the eye leak and damage the retina. It's a major cause of blinedness that could be prevented, affecting over 100 million people worldwide.
To develop SMART, researchers trained the AI using thousands of retinal images from a diverse group of patients across six continents. When they tested the AI on new images, it could detect diabetic retinopathy almost every time, processing each image in less than one second. The tracker could also tell the difference between diabetic retinopathy and other eye conditions.
Symptoms And Issues Associated With Diabetic Retinopathy
According to the US National Eye Institute, Diabetic retinopathy is an eye problem that can affect anyone with diabetes. It happens when high blood sugar damages the tiny blood vessels in your retina, the light-sensing part at the back of your eye. Early detection and managing your diabetes are key to protecting your vision.
Diabetes harms blood vessels throughout your entire body. In your eyes, this damage begins when high blood sugar changes the tiny blood vessels that feed your retina. These changes make it harder for blood to flow, leading to some blood vessels getting blocked or starting to leak fluid or blood.
Warning Signs
In its early stages, you usually won't notice any problems with your vision. However, some people might notice subtle changes, like difficulty reading or seeing things far away. These changes might even come and go.
As the condition gets worse, blood vessels in your retina can start to bleed into the jelly-like fluid that fills your eye. If this happens, you might see dark, floating spots or streaks, almost like cobwebs. Sometimes these spots clear up on their own, but it's crucial to get medical help right away. If left untreated, scars can form at the back of your eye, or the bleeding might start again or get worse.
Who Will This New AI Help?
Developing this new AI has the potential to make eye care available to a vast number of people globally, simply by using mobile technology. Experts believe this innovation could screen billions worldwide, significantly cutting down vision loss from diabetic retinopathy. It could also completely change how healthcare is provided.
Anyone with diabetes can get diabetic retinopathy, whether they have type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes (diabetes that develops during pregnancy).
Your risk goes up the longer you've had diabetes. In fact, over half of people with diabetes will develop diabetic retinopathy eventually. The good news is that you can significantly lower your risk by keeping your blood sugar levels under control.
Women with diabetes who become pregnant, or those who develop gestational diabetes, are at a higher risk. If you have diabetes and are pregnant, you should get a full eye exam with dilated pupils as soon as possible.
This research highlights how AI can be a positive force, helping to bridge gaps in medical care and offering hope to millions who are at risk of losing their sight.
Most Common Cause Of High Blood Pressure May Be The Most Overlooked One - New Guidelines Reveal

(Credit-Canva)
It is not uncommon for doctors to misidentify a health condition or misdiagnose due to lack of information or conflicting symptoms. However, many times these mistakes can lead the patient to get the wrong treatment, and cause problems like prolonged treatment, more health problems as well as patients feeling unheard.
A new report suggests that doctors are often missing a common, hormone-related reason for high blood pressure. This overlooked condition, called primary aldosteronism, could be affecting a significant number of people with high blood pressure without them even knowing. According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, most doctors fail to identify this condition, even though it is the most common cause of high blood pressure.
More Common Than Thought
Research shows that as many as 30% of high blood pressure patients seen by heart specialists, and 14% of those seen by general doctors, actually have primary aldosteronism. This condition occurs when the adrenal glands (small glands located on top of your kidneys) produce too much of a hormone called aldosterone.
Despite how common it might be, many people with high blood pressure are never given a simple blood test to check for primary aldosteronism. In other cases, they might finally be tested years after their high blood pressure diagnosis. By this time, the condition can already lead to serious health problems.
Misdiagnoses in other health problems are also very common. According to a 2023 study published in the JAMA journal, every year, a staggering number of people—around 795,000—either die or are left with permanent disabilities because of mistakes in their diagnosis or related issues in healthcare. Even with a more conservative estimate, the number is still very high, at about 549,000 people harmed.
Why Is It Important to Diagnose?
People with primary aldosteronism face a higher risk of heart and blood vessel problems compared to those with regular high blood pressure.
Aldosterone helps control the balance of sodium (salt) and potassium in your blood. When aldosterone levels are too high, your body can lose too much potassium and hold onto too much sodium, which directly leads to higher blood pressure. Studies have shown that individuals with primary aldosterosteronism are:
- Nearly 2.6 times more likely to have a stroke.
- Twice as likely to experience heart failure.
- 3.5 times more likely to develop an irregular heartbeat.
- 77% more likely to end up with heart disease.
A simple and inexpensive blood test could help identify more people with primary aldosteronism, ensuring they get the right treatment.
New Guidelines and Treatment Options
The new report suggests that everyone diagnosed with high blood pressure should have their aldosterone levels checked. If primary aldosteronism is found, specific treatments for that condition should be given.
There are prescription medications available to treat primary aldosteronism. These include drugs like spironolactone and eplerenone, which help lower blood pressure and increase potassium levels in the body.
Doctors might also recommend surgery to remove one of the two adrenal glands if only one gland is making too much aldosterone. Patients are also usually advised to follow a balanced low-sodium diet and try to lose weight to help manage the condition.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

