- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
What Is Double Pneumonia? The Condition Behind Pope Francis' Hospitalization And Death
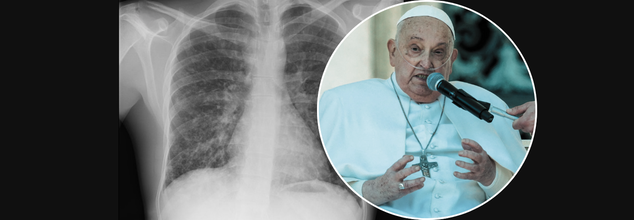
On Easter Monday, April 21, 2025, the Vatican announced the death of Pope Francis, the 266th pope of the Roman Catholic Church, at age 88. His death came just weeks after he was released from a long hospitalization for a severe respiratory condition—double pneumonia. His hospitalization had started on February 14 at Rome's Agostino Gemelli Polyclinic Hospital for bronchitis, which later developed into a more serious and complicated condition: bilateral pneumonia.
The pope’s deteriorating health underscored the seriousness of the infection. Though he was discharged on March 23 following 38 days of treatment, his condition remained fragile. Vatican officials revealed he had required noninvasive mechanical ventilation and would need extensive rehabilitation therapy, including help to regain his speech. His diagnosis also included a polymicrobial respiratory tract infection, meaning it was caused by more than one type of pathogen, complicating treatment and recovery.
What Is Double Pneumonia?
Double pneumonia, or bilateral pneumonia, is when pneumonia infects both lungs at the same time. Pneumonia itself is an infection that inflames the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs, typically filling them with fluid or pus, and compromising breathing. When this infection develops in both lungs, it is a more serious medical condition.
Although not a formal medical term, "double pneumonia" can be used to describe two general aspects of the illness:
Bilateral Infection – in which both lungs are infected, weakening total lung capacity and decreasing the body's efficiency at oxygenating blood.
Polymicrobial Infection – in which more than one pathogen (bacteria, virus, or fungus) is causing the disease, and treatment becomes more complicated and typically requires wider drug regimens.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Double pneumonia presents similar symptoms to regular pneumonia but is more serious because both lungs are affected. Symptoms include:
- Fever and chills
- Pain in both sides of the chest on breathing or coughing
- Protracted cough with mucus or phlegm
- Trouble breathing
- Low oxygen levels in the blood
- Fatigue, weakness, and muscle ache
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Confusion, particularly in elderly people
- Rapid heartbeat and breathing
- Loss of appetite
These symptoms frequently require hospitalization, particularly in elderly or those with chronic diseases like diabetes or heart disease.
What Causes Double Pneumonia?
Similar to normal pneumonia, double pneumonia can be caused by a variety of infectious causes and conditions as is regular pneumonia. Typical viral perpetrators include the influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and even the common cold. Bacterial infections such as those from Streptococcus pneumoniae or Group A streptococcus are also common offenders. In immunocompromised hosts, fungal pneumonias have the potential to progress to a more serious case of pneumonia.
The other probable etiology is aspiration, when foreign material such as food, saliva, or vomitus finds its way accidentally into the lung, causing infection and inflammation. Double pneumonia can also be classified by where one caught the infection—in the community, in hospital settings, or ventilator-associated settings. In Pope Francis' case, the polymicrobial causation of the infection suggests that it is a healthcare-acquired variant, and these are typically more resistant to standard antibiotic treatments and harder to treat, particularly in older or compromised patients.
Why Double Pneumonia Can Be Fatal?
Double pneumonia may become life-threatening based on the extent of the lung involvement and the presence of other risk factors. In the case of Pope Francis, both his advanced age and underlying health issues probably increased his susceptibility.
Severe double pneumonia complications are:
Sepsis – the infection spreads to the bloodstream and causes organ failure.
Pleural Effusions – fluid accumulation around the lungs, which impairs breathing.
Lung Abscesses – pouches of pus within or surrounding the lungs.
Pleurisy – inflammation of the membrane separating lungs and chest wall, which is very painful.
Respiratory Failure – necessitating mechanical ventilation in the most severe situations.
Multi-organ failure and death – especially in older individuals or those immunocompromised.
This compounded by the existence of a polymicrobial infection. Bacterial pneumonia can be highly responsive to antibiotic treatment, yet if a coexistent virus has infected the subject, then ensuing symptoms might resume or aggravate. Such double infection scenario promotes a deceptive phenomenon of apparent convalescence but rapid exacerbation.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Double pneumonia
Diagnosis usually includes a chest X-ray or CT scan, and sputum tests or throat swabs to determine the pathogens present. Blood oxygen saturation is also measured to gauge respiratory function. Treatment can be:
- Specific or broad-spectrum antibiotics for bacterial infection
- Antiviral medications (although less so)
- Oxygen supplementation or mechanical ventilation
- Hospitalization, particularly if both lungs are badly affected
Recovery may be slow, and in older patients, it typically requires intense rehabilitation therapy to restore strength, mobility, and speech, such as in Pope Francis's last weeks.
Can Double Pneumonia Be Prevented?
Although preventing pneumonia is not always possible, there are various measures that decrease the risk:
1. Vaccination
The influenza vaccine given once a year prevents pneumonia caused by the flu. Pneumococcal vaccines protect against the most common bacterial causes of pneumonia and are recommended for children under 6, adults over 65, and immunocompromised individuals.
2. Good Hygiene Practices
Regular handwashing with soap for at least 20 seconds remains one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of infections. In addition, disinfecting high-touch surfaces such as doorknobs, light switches, and mobile devices helps reduce the risk of germ transmission. Wearing masks in healthcare settings adds a vital layer of protection, especially for vulnerable individuals and healthcare workers. It’s also important to avoid close contact with individuals who are visibly ill, as this can significantly lower the chances of catching or spreading respiratory infections.
3. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
To protect and enhance lung health, it's essential to adopt a few key lifestyle habits. Start by quitting smoking, as it's one of the leading causes of lung damage and respiratory illnesses. Limiting alcohol consumption is equally important, as excessive drinking can suppress the immune system and increase the risk of lung infections. Eating a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals supports overall immune function and lung repair. Lastly, maintaining a regular exercise routine helps strengthen lung capacity, improve breathing efficiency, and boost endurance, making your lungs more resilient to illness and age-related decline.
These preventive measures are particularly important for those who are at increased risk, such as the elderly, those with chronic diseases, and those whose immune systems are compromised.
Gamer’s Neck Develops 'Dropped Head Syndrome' After Years Of Looking At His Phone, Doctors Warn Of Debilitating Condition
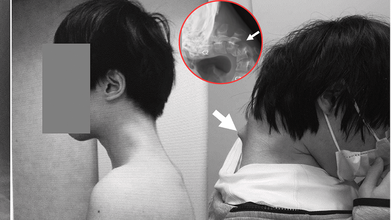
Credits: JOS Case Reports
When was the last time you caught yourself hunched over your phone, neck bent at an unnatural angle? A few minutes scrolling might feel harmless, but for one 25-year-old gamer in Japan, years of that posture ended with a shocking diagnosis, “dropped head syndrome.” His story has left doctors urging young people worldwide to rethink how long they spend staring down at their screens.
In a striking case that has unsettled health experts, Japanese doctors documented how a 25-year-old man grew a serious case of "dropped head syndrome" after years of crouching over his smartphone playing video games. The debilitating but unusual condition left him unable to lift his head, properly swallow food, or sustain a healthy weight.
In the case report released in JOS Case Reports in 2023, the patient's battle started following years of isolation from society in his teenage years. Having endured constant bullying at school, he isolated himself in his bedroom and spent many hours glued to his phone playing games, with his head leaning forward at steep angles for hours on end.
How Smartphone Overuse Weakened His Neck?
The injury was chronic. For six months, the man suffered from excruciating neck pain before he lost all ability to lift his head. His vertebrae deformed and dislocated over time, scar tissue in his spine formed, and he had trouble swallowing, leading to spectacular weight loss.
Scans established that his cervical spine had been subjected to extreme stress through unnatural posture over many years. The muscles and ligaments that were meant to keep the head upright no longer worked, and his chin would sag onto his chest.
The doctors first tried to treat it conservatively using neck collars, but the patient complained of numbness and pain, compelling the team to embark on surgery.
How Did The Doctors Treat 'Dropped Head Syndrome'?
Surgeons carried out an intricate procedure that entailed removing bruised bits of vertebrae and scar tissue, followed by the implantation of metal rods and screws to stabilize and realign the spinal posture. Six months passed before the patient regained the ability to keep his head level.
At one-year follow-up, swallowing problems had cleared up, posture was stable, and quality of life had dramatically improved.
The group concluded that the condition was caused by an "underlying developmental disorder" but that the long-term consequences of prolonged smartphone use with this posture were the biggest contributor to his illness.
What Is Dropped Head Syndrome?
Dropped head syndrome (DHS), also referred to as "floppy head syndrome," is an uncommon disorder that involves, at times severe, weakness of the neck muscles, resulting in a "chin-on-chest" posture.
It is most commonly linked to neuromuscular disorders like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson's disease, or specific muscular dystrophies. The patients tend to use their hands to support their heads and can have difficulties with eating, talking, and walking.
In ALS, DHS happens in approximately 1–3% of the patients and is typically progressive with a grim prognosis. But as this Japanese case suggests, DHS may also arise due to non-neurological etiologies such as trauma, drug abuse, or—as in this instance—chronic mechanical stress of posture.
Can Screen Time Be Associated With Dangerous Conditions?
Although this instance is unusual, physicians caution it shows an expanding medical danger associated with mobile phone addiction. Over 6.8 billion individuals across the globe currently have access to smartphones, with four to seven hours of average screen time per day. Among game players and youth, use can be much higher.
Protracted downward neck posture—a sometimes termed "tech neck"—is already associated with headache, eye strain, and degeneration of the cervical spine. This is the extreme example of DHS and serves to illustrate how serious the effects can be when posture is neglected.
How Does Dropped Head Syndrome Affect Everyday Life?
DHS is more than just an inconvenient posture. The deformity affects simple functions such as swallowing, speaking, and breathing. It inhibits mobility, renders everyday activities challenging, and results in social withdrawal and isolation. In younger individuals, it even generates a chain of physical disability that multiplies mental health issues.
In this patient's life, bullying during childhood and later ostracism provided fertile ground for technological dependence. His case is particular about pointing to the juncture of mental well-being, online tendencies, and bodily well-being—a synergistic combination that is all the more pertinent in contemporary societies.
Organizations like the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons have already warned of increasing incidence of posture-related spinal disorders in young people. The majority will never suffer from DHS, yet milder but chronic neck and back ailments are sweeping up teenagers and young adults.
Elizabeth Jarman from Médecins Sans Frontières, citing parallel access problems with diabetes care, emphasized that the first step to prevention is awareness. In the case of digital health, professionals are calling for schools, workplaces, and families to include posture education and frequent movement as part of daily practice.
Can Dropped Head Syndrome Be Prevented?
Prevention of dropped head syndrome due to posture is easy in principle:
- Avoid repetitive forward flexion of the neck.
- Take frequent breaks from screen time.
- Do neck-strengthening and posture-improving exercises.
- Employ ergonomically arranged seating and screen configurations.
But putting these measures into practice takes awareness and discipline—two qualities usually lacking in the fast-engagement era of mobile gaming and social media.
Is Surgery the Only Option for DHS Treatment?
For cases as bad as the Japanese gamer's, surgery is still the only real option. Surgical procedures are not without hazard, though, from infection to nerve damage. Even if successful, recovery is long and needs rigorous rehabilitation.
Due to the relative infrequency of DHS, there is no gold standard for surgical treatment. Each case has to be assessed on its merits, weighing risks against benefits.
This is an extreme case, but it is one that should serve as a warning to young people everywhere. The frequency of "tech neck" complaints in clinics, alongside rising screen time, indicates there could be more cases of spinal deformities emerging if awareness is not given high priority.
As the Japanese physicians who attended to the gamer stressed, the illness might have been precipitated by the integration of physical posture and pre-existing susceptibilities, but excessive use of smartphones in uncomfortable positions may produce unimaginably tragic results.
Brain’s ‘Clean Sweep’ Could Help You Lower Your Risk Of Dementia

(Credit-Canva)
Our body is like a self-maintaining machine, it is equipped to help us heal ourselves, recharge after a long day’s work as well as having its own warning system to ensure places that need help come to notice, i.e., pain. However, did you know your brain could also actively be stopping you from developing mental health conditions? Yes, your brain and body are not as defenseless as you may think it to be, with the help of sleep, your brain is actively keeping you from developing certain issues.
The brain has a unique way of getting rid of waste, almost like a personal cleanup crew. This process, called the glymphatic system, is thought to work best while we're sleeping. But what happens if our sleep is disrupted?
Researchers believe that a lack of good sleep might stop this system from working correctly, leading to a build-up of waste or toxins in the brain. Some are suggesting this buildup could increase a person's risk of developing dementia.
How the Brain Clears Out Waste
Every cell in your body creates waste, and outside the brain, a system called the lymphatic system takes care of it. But the brain doesn't have these vessels, so how does it stay clean?
About 12 years ago, scientists discovered the glymphatic system. It uses a fluid that surrounds your brain and spinal cord, called cerebrospinal fluid, to "flush out" toxins. This fluid flows through the brain, collects waste, and then drains it away.
Waste products
According to the National Institute of Health one key waste product is a protein called amyloid beta (Aβ). When Aβ builds up, it can form plaques in the brain. These plaques, along with other protein tangles, are a clear sign of Alzheimer's disease, the most common type of dementia.
Sleep and waste
Studies in both humans and mice have shown that Aβ levels increase when you're awake and then drop quickly while you sleep, like the 2018 study published in the Annals of neurology.. This supports the idea that the brain is more actively "cleaning" during sleep.
How Is Sleep Connected To Dementia?
If sleep helps clear toxins, what does long-term disrupted sleep, like that from a sleep disorder, mean for your brain's health?
Sleep Apnea
This common condition causes a person's breathing to stop and start repeatedly during the night. This can lead to a long-term lack of sleep and reduced oxygen, both of which may cause toxins to build up in the brain. Studies have linked sleep apnea to a higher risk of dementia, and some research shows that treating sleep apnea helps clear more Aβ from the brain.
Insomnia
Having trouble falling or staying asleep over a long period has also been linked to an increased risk of dementia. While these links are promising, scientists are not yet sure if treating these sleep problems directly lowers the risk of dementia by removing toxins from the brain.
Does Sleep Aid Brain Health?
Another study, published in the Nature publication 2024, showed that neurons act like miniature pumps. During sleep, these neurons produce rhythmic bursts of electrical energy that create waves. These waves are not just a sign of a sleeping brain; they actually push fluid through brain tissue, effectively washing away waste.
This discovery helps explain why a good night's sleep is so important for brain health. As Dr. Jonathan Kipnis, the senior author, said, "We knew that sleep is a time when the brain initiates a cleaning process to flush out waste and toxins it accumulates during wakefulness. But we didn’t know how that happens."
The researchers believe the brain might adjust its cleaning method based on the type and amount of waste, similar to how we adjust our hand motions when washing dishes—using big, slow movements for large messes and faster, smaller ones for sticky spots.
Propranolol For Anxiety: Why Are Women Taking Popular Heart Medicine For Panic Attacks

(Credit-Canva)
Panic attacks, anxiety, tremors are common for people to experience, and until recently there was not a sustainable solution for it. However, some women revealed how they use this popular heart medicine, propranolol, to not only reduce these symptoms, but to also ensure that they perform better in different situations like dates and presentations.
Described by many influencers to be a ‘magic pill’ that helps us calm down their jitters, new data shows a rise in the number of prescriptions for propranolol. However, is it safe? And what are the health implications of using the same?
How Beta-Blockers Like Propranolol Work
According to Cedar Sinai experts, when you face a stressful situation, your body goes into "fight-or-flight" mode. This response is triggered by stress hormones like adrenaline and noradrenaline, which make your heart beat faster and your blood pressure rise. Doctors explain that beta-blockers interrupt this process. They prevent those stress hormones from causing those physical reactions.
- Selective beta-blockers mainly affect your heart.
- Nonselective beta-blockers, on the other hand, have a broader effect, including on the brain.
Experts note that for anxiety-related issues like panic attacks or performance anxiety, nonselective beta-blockers can "turn down the volume" on your body's stress response. This allows you to think more clearly and cope better.
Propranolol For Anxiety: Does It Help?
Doctors often prescribe a nonselective beta-blocker called propranolol to help with anxiety, panic attacks, and PTSD. It's usually taken as needed for specific stressful situations, not for daily use.
One of its benefits is that it works quickly—in about 20 to 30 minutes—without causing sleepiness or brain fog, which is a common side effect of other fast-acting anxiety medications.
Doctors explained that many patients are more open to trying propranolol because it's typically known as a heart medication, which helps remove the stigma some people feel about taking "psych meds."
Propranolol for Migraines: Does It Help?
According to the National Library of Medicine, Beta-blockers are a common and effective type of medicine used to prevent migraines. The most frequently used one is propranolol.
Treatment with propranolol typically starts at a low dose of 40 mg per day. This can be gradually increased up to 320 mg daily, if needed. It's important to be patient, as it can take up to 12 weeks at the right dose before you notice the full benefits of the medication.
Is Propranolol Safe for Pregnant Women?
The role of propranolol in pregnancy has been an important conversation. Some important notes about propranolol and pregnancy that were addressed in the MothertoBaby medical journal are
Getting Pregnant
It is not known if propranolol makes it harder to get pregnant. It can, however, cause erectile dysfunction in men, which could make conception difficult.
Miscarriage
There have been no studies to see if propranolol increases the risk of miscarriage.
Birth Defects
Every pregnancy has a 3-5% chance of birth defects. It is not known if propranolol increases this risk. However, studies on beta-blockers in general have not shown a higher chance of birth defects.
Other Pregnancy Issues
Some studies have linked propranolol to slower baby growth, but it’s not clear if this is caused by the medicine itself or the health condition being treated. The medication does not appear to increase the risk of other problems like premature birth.
Baby's Health After Birth
If you take propranolol in late pregnancy, your baby might have temporary symptoms like a slow heart rate or low blood sugar. Not all babies will have these symptoms, but it’s crucial to tell your healthcare providers so they can monitor your baby and provide the best care.
Long-Term Effects
No studies have been done to see if propranolol affects a child's learning or behavior later in life.
If you are pregnant or planning to be, it’s important to talk to your doctor before stopping or changing how you take your medication. They can help you weigh the benefits of treating your condition against any potential risks.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

