- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Why Is Exposure To Morning Light Important For Health?

Light regulates almost all mechanisms inside the body. Therefore, sleep, mood, and even metabolic health will vary with it. For those who consider light, this is particularly crucial during mornings, when it becomes a natural synchronizer of their circadian rhythms and their health. Let's dig in as to why morning light is important for healthy life:.
Our body clock, or circadian rhythm, consists of a complex system of biological processes that function in approximate 24-hour cycles. The internal timekeeper within us is controlled by some environmental cues, but the main one is light. Our central body clock is contained in the hypothalamus section of the brain and interfaces with clocks in individual cells throughout the body. They affect different functions such as sleep-wake cycles, digestion, and hormone discharge.
This central clock is reset daily by morning light exposure. A light-sensing cell found in the retina sends signals to the brain to mark a new day. This has the effect of synchronizing bodily functions with external environmental change, optimizing health and productivity.
Benefits of Morning Light for Sleep and Mental Health
One of the very important benefits of morning light is its effect on sleep quality. When morning light resets our body clock, it enables better regulation of melatonin - a hormone that makes one sleep. Melatonin production declines due to bright light experienced during the morning hours and creates a feeling of freshness in the body. Later during the night, melatonin increases once again, preparing our body for sleep.
In addition to sleep, morning light also helps improve mental health by inducing serotonin production. Serotonin, commonly known as the "feel-good" hormone, is essential for mood regulation and emotional well-being. The lack of serotonin has been associated with depression and anxiety. Exposure to natural light daily can reduce the risk factors associated with these conditions and improve overall mental health.
Role of Morning Light in Metabolism and Physical Health
Morning light doesn't just affect sleep and mood; it also affects physical health. Research has shown that getting early sunlight exposure can lead to better metabolic function and fewer chances of obesity. In addition, morning light exposure also controls cortisol levels, the stress hormone that peaks at its highest in the early hours. Proper regulation of cortisol helps maintain energy levels, boost immune function, and help control blood sugar.
Light exposure also impacts our digestive system. The gut is a circadian-based organ, and processes like movement of waste are more effective during the day. Therefore, morning light helps us get these processes in sync to ensure proper digestion and absorption of nutrients.
Why Timing Matters
The timing of light exposure is as important as the light itself. Exposure to light in the morning adjusts our circadian rhythms with the natural day-night cycle, thus better health in general. On the other hand, exposure to artificial light at night disrupts the rhythms, causing sleep problems, metabolic disorders, and even chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
For sleep disorders victims, light therapy is among the most recommended treatment plans that should be followed. Early exposure to bright light that is achieved through sunlight exposure or daylight simulators in any light box can correct imbalances in the body clocks and reduce symptoms of insomnia among other circadian rhythm diseases.
How to Get Morning Light into Your Daily Routine
You don't have to do much to incorporate morning light into your day. Small actions can add up:
- Spend 30 to 45 minutes outside within an hour of waking.
- Take a walk or enjoy breakfast on the porch to maximize exposure.
- Let sunlight directly hit your skin and eyes (don't wear sunglasses).
- The light coming through windows or umbrellas isn't as effective.
Consistency is key. Try to wake up at the same time every day and add light exposure to your morning routine. Even on overcast days, natural light has good effects. Open windows or take a step outside to garner its benefits.
Effect of Light Misalignment
While morning light is beneficial, exposure to light at the wrong time can have serious health consequences. Light pollution, even from dim artificial sources, disrupts the natural sleep-wake cycle. This can impair heart rate, glucose metabolism, and mental health, increasing the risk of depression and anxiety.
Night owls and night shift workers are especially susceptible to these impacts, as their routines frequently conflict with the natural cycles of the body. Research indicates that such mismatched exposure to light increases risks for chronic diseases, such as cancer and cardiovascular disease.
Apart from effects on sleep and metabolism, morning light impacts attention, alertness, and productivity. Mental acuity is greater in the afternoon and evening but is heavily influenced by the amount of early light exposure. Activities requiring concentration - such as driving or working-on benefit from a well set body clock.
It regulates morning light with respect to muscle activity and blood pressure. Since the liver and kidneys break down toxins and drugs in the human body, that too speaks to the importance of maintaining one's health and fitness level.
Exposure to morning light is a simple and powerful tool for improving your health. From regulating sleep to mood, boosting metabolic, and physical functions, exposure to morning light is abundant and well-documented. Find ways to incorporate morning light into your daily routine in the form of stepping outside in the morning, having a breakfast al fresco or opening your windows.
Get your body clock aligned to natural light and pave a way for better health and improved well-being and a more productive day.
Unique Symptoms Of Sepsis: What To Know About TIME
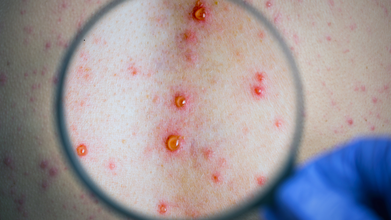
Credits: Canva
Sepsis that happened by a lick from a pet dog led to a woman losing all four of her limbs. Health and Me had previously reported that a Birmingham based woman, 56-year-old pharmacy worker Manjit Sangha caught sepsis from the lick of her pet dog. She spent her night in coma in the hospital and had to lose all her limbs. This happened because bacteria from dog's lick entered her body through a cut or a scratch. This led to sepsis, where the immune system's reaction to infection damaged the body's own tissues and organs.
This has brought a lot of attention on what sepsis is and what are the symptoms one must be aware of. As per the Sepsis Alliance, one must know about TIME to be aware of sepsis.
Unique Symptoms of Sepsis
TIME stands for temperature, infection, mental decline and extremely ill. If you notice these symptoms, rush to the hospital.
- T for Temperature: If you notice your body temperature rising or falling
- I for Infection: If you see signs or symptoms of any infection
- M for Mental Decline: If you feel confused, sleepy and difficult in rising
- E for Extremely Ill: If you feel severe pain, discomfort, shortness of breath
Unique Symptoms Of Sepsis: What To Know About Temperature
Your body temperature normally stays steady at about 98.6°F (37°C), with small changes based on activity, surroundings, and time of day. A reading of 100°F (37.7°C) or higher is considered a fever. During infection, the body often heats up to help fight germs. However, some people experience an unusual drop in temperature instead. Because of this, both a spike and a fall in temperature can be warning signs of sepsis.
Unique Symptoms of Sepsis: How To Know If You Have An Infection?
When an infection stays in one area, its symptoms usually match the site involved. A urinary tract infection may cause burning while urinating or frequent urges, pneumonia can bring cough and chest pain, and an infected cut may show redness or pus.
If the infection spreads through the body, broader symptoms like fever, tiredness, and body aches can appear. In some cases, an infection may not cause obvious symptoms at all. This is especially important to remember after surgery, medical procedures, skin injuries, or close contact with someone who is sick.
Unique Symptoms of Sepsis: What To Look Out For Mental Decline?
Sepsis can also alter how the brain functions. Some people, particularly older adults, may not develop the usual infection symptoms. Instead, they might suddenly become confused or show a sharp worsening of existing dementia. Marked drowsiness or unusual sleepiness is another common sign.
Unique Symptoms of Sepsis: Signs That You Are Extremely Ill
Many sepsis survivors recall feeling sicker than ever before. They describe overwhelming symptoms such as the most severe sore throat or abdominal pain they had experienced, along with a frightening sense that they might not survive.
Unique Symptoms Of Sepsis In Children
| A Child Who | Child under 5 (Infant) Who |
| Feels abnormally cold to touch | Is not eating |
| Looks mottled, bluish or has very pale skin | Is vomiting repeatedly |
| Has a rash that does not fade when you press it | Has not urinated in 12 hours |
| Is breathing very fast | |
| Has a convulsion | |
| Is very lethargic or is facing difficulty in waking up |
Unique Symptoms Of Sepsis In Adults
- High blood cell count
- Immature white blood cells in circulation
- Elevated plasma C-reactive protein
- Elevated procalctonin (PCT)
- Low blood pressue
- Low central venous or mixed venous oxygen saturation
- High cardiac index
- Low oxygen level
- Low urine output
- High creatinine in the blood
- Coagulation or clotting abnormalities
- Absent bowel sounds
- Low platelets in blood
- High bilirubin levels
- High lactate in blood
- Decreased capillary filling or mottling
Woman Lost Weight On Mounjaro But Her Breasts Didn't Stop Growing, This Is Why...

Credits: SWNS (Tianna Moon)
Mounjaro, a popular weight loss drug that helped many lose weight, however, in this one case, a woman, who was on the same drug noticed something different. While she lost weight, she noticed that her breasts continued to grow. The 30-year-old Tianna Moon of East Anglia, a region in eastern England first realized something was not normal with her chest in 2024. This was when she started to use Mounjaro.
She was losing weight, but her breasts continued to grow. This is when Moon's doctor diagnosed her with a rare disease call gigantomastia, which causes breast tissue to grow rapidly and in excess.
Also Read: 15 States Sue Trump Administration Over Revised Vaccine Schedule
Woman Lost Weight On Mounjaro But Her Breasts Didn't Stop Growing: What Happened To Her?
Moon said that the doctors had thought that she had macromastia, a less severe, however, a similar condition. "But when I broke down medical history, the weight loss on Mounjaro and the increased growth and side effects, he was point-blank like, 'This is gigantomastia'," she said.
Moon also told that her breasts currently weight 39 lbs, which is approximately 20 per cent of her overall body weight.
Moon also said that while her large breasts are "normal" at this point in her life, she said the rare condition still comes with challenges.
"The side effects are having numb arms quite a lot and having quite severe indentations on my shoulders. I have some light scarring under my breasts where bras have rubbed and ripped the skin open."
She also said that laying on her back is something she cannot do for a long time, as it restricts the amount of airflow she can get in. She also said that when she goes out she tries to make her breasts look smaller than they are and strap them up. "I [still] get stares and double takes."
Also Read: Wegovy And Ozempic Will Cost Less In 2027, Novo Nordisk Slashes Weight Loss Drugs Prices By Half
Woman Lost Weight On Mounjaro But Her Breasts Didn't Stop Growing: What Is Gigantomastia?
As per Cleveland Clinic, it is a rare condition where your breasts become excessively large. It can also cause pain, infection, discomfort and issues with body image. It is also known as breast hypertrophy where one experiences rapid and disproportionate breast growth. The speed with which the breasts grow could vary depending on the person. It could take a few weeks to over several years. The tissue is almost never benign.
Gigantomastia is characterized by:
- Breasts that have an excess of at least 5 pounds of breast tissue.
- Extra breast tissue that equals more than 3% of your total body weight.
There are different types of gigastomastia:
- Juvenile gigantomastia: This type happens during puberty.
- Gestational gigantomastia: This is when gigantomastia occurs during pregnancy.
- Drug-induced gigantomastia (or medication-induced): This happens after taking certain drugs.
- Idiopathic gigantomastia: This is when the cause of gigantomastia is unknown or can't be determined. Idiopathic gigantomastia is the most common type.
Moon is now considering a breast reduction surgery. She has for now set up an account on OnlyFans. “I might as well try and reap the benefits of my medical condition rather than the negatives," she said.
Indigenous Td Vaccine Rollout In India To Boost Immunity In Children, Adults, Say Experts

Credit: X
The recent launch of the indigenous Td vaccine in India by Union Health Minister JP Nadda will boost immunity and reduce the risk of tetanus and diphtheria in children and adults, said health experts.
Union Health Minister JP Nadda formally launched the indigenously manufactured Td vaccine in Himachal Pradesh last week.
With the launch, the Tetanus Toxoid (TT) vaccine has been replaced with the Tetanus and adult diphtheria (Td) vaccine in India’s immunization program for all age groups, including pregnant women.
The move comes amid increasing numbers of cases of diphtheria amongst older age groups. Tetanus and diphtheria can lead to hospitalizations or even cause death. The Td vaccine will help to decrease diphtheria outbreaks.
“In keeping with global practice, India has shifted from TT, which covers for tetanus, to Td, which covers for both tetanus and diphtheria. This vaccine is indigenously manufactured and is expected to significantly reduce the risk of both these diseases in older children as well as adults,” Dr. Rajeev Jayadevan, Ex-President of IMA Cochin and Convener of the Research Cell, Kerala, told HealthandMe.
What Is The Td Vaccine?
The Td vaccine, indigenously manufactured at the Central Research Institute (CRI), Kasauli in Himachal Pradesh, is a combination of tetanus and diphtheria with a lower concentration of diphtheria antigen (d), and is recommended for older children and adults.
The use of Td, instead of TT, is recommended during pregnancy to protect against maternal and neonatal tetanus and diphtheria during prenatal care.
Vaccination during pregnancy also serves to boost immunity and increase the duration of protection in pregnant women who have not received the full set of recommended booster doses.
The Td is a safe vaccine, and 133 countries are currently using it.
The Health Ministry, in a statement, said that the Central Research Institute will supply 55 lakh doses to the UIP by April 2026, with production expected to scale up progressively in subsequent years to further strengthen the Universal Immunization Program in India.
“India’s indigenous Td vaccine rollout marks a significant milestone in strengthening the nation’s immunization program by enhancing self-reliance, affordability, and supply stability,” Dr. Neha Rastogi, Senior Consultant - Infectious Diseases, Fortis Gurugram, told HealthandMe.
“Locally produced vaccines reduce dependency on imports, ensuring uninterrupted protection for adolescents and adults against tetanus and diphtheria. This initiative supports wider coverage, faster distribution to remote regions, and improved public health preparedness,” she added.
Tetanus And Diphtheria: Disease burden In India
As per the National Health Profile 2022, India has reported 1,586 cases and 22 deaths due to diphtheria in 2020, and 3,677 cases and 47 deaths in 2021.
Around 10 Indian states report the majority (84 per cent) of the cases.
As of 21 June 2024, Orissa has also reported six deaths and 21 suspected diphtheria cases. There has been more than 90 percent coverage of diphtheria vaccination in birth cohorts since 2014, but gaps in booster dose coverage are widely prevalent.
Plugging of gaps in the routine immunization, coupled with inclusion of booster doses in the national data on diphtheria vaccination, is the need of the hour.
“Diphtheria is one of the most dangerous infectious diseases known to man; it spreads easily through the respiratory route. It can cause death due to the bacterial toxin affecting the heart (Myocarditis). It is vaccine-preventable, but the immunity fades over time,” Dr. Jayadevan said.
Therefore, the Td booster shots at ages 10 and 16 are essential to maintain protection. Similarly, pregnant women should receive two doses to protect both mother and child.
Given the recent outbreaks of diphtheria in India and elsewhere, this transition is a public health priority, the expert said.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

