- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
You Cannot Fool Your Doctor About These 7 Things

(Credit-Canva)
Visiting a doctor can be a daunting task for many people. While health is a concern for many, people often worry about how they look to the doctor. Going about our day-to-day life, we often do things that we know are not good for our bodies. Whether it is smoking or eating unhealthy foods, and when asked about it at the doctor's office, many people chose to lie.
While we all want to be healthy and have the best care, the nervousness we experience at the doctors can sometimes stumble us into a harmless fib. But what most of us do not know is that doctors can usually tell when we are telling a lie. A 2020 survey done by the BCMJ revealed the number of people who lie and what they lie about.
The Pollfish survey revealed that 43% of those who admitted to lying did so about their exercise routines, with smoking being the most common lie at 46%. Older patients (35+) were more prone to misrepresenting their exercise habits, while younger patients (<35) were more likely to lie about smoking.
Common Lies Doctor Knows We’re Telling
While the doctors understand why one would choose to lie about certain things, they also urge their patients to answer them truthfully as at the end of the day it will help them give you the best treatment possible
"I Only Drink Occasionally"
The lie is saying you drink less alcohol than you really do. Doctors know many people don't tell the truth about this. Drinking too much can cause big problems like liver damage and heart disease. If you're honest, your doctor can give you the right advice. If you're not honest, they might miss problems or give you medicine that doesn't mix well with alcohol.
"I Don't Smoke"
It may seem like a harmless fib, but doctors can tell when someone is not telling the truth about these things. Smoking is very bad for your health and can cause cancer and hurt your lungs. Also, smoking can change how your medicine works. If you tell the truth, your doctor can help you quit and lower your risk of getting sick. If you lie, you might miss out on help and get very sick.
"I Went to the Doctor Pretty Recently"
You may think that lying about this is ok as it does not affect your current medical crisis, but that is not true. Your doctor needs to know your full health history to give you the best care. If you lie, they might miss important screenings or not find problems early. This can lead to delays in getting the right treatment.
"I Rarely Eat Junk Food"
We all know junk food is bad for us, yet we cannot keep ourselves from having some time to time. What you eat affects your weight, test results, and how your medicine works. If you're honest, your doctor can help you with diet problems. If you lie, your diabetes or cholesterol might get worse, and your medicine might not work right.
"I Don't Know My Family's Health History"
Your family history is crucial for your health, while you may think your health is separate, it give your doctor much needed information. Familial history reveals risks for hereditary diseases, making accurate information vital for preventative care. Lying about this can lead to missed opportunities for early detection and prevention of potentially life-altering conditions.
"I've Only Had X Number of Sexual Partners"
It may be embarrassing to tell, but being truthful about your sexual history can help your doctor give you the right advice and also give important context. When you speak truthfully, your doctor will help you safeguard against things like sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and HIV. Dishonesty can result in untreated or poorly managed STIs and other health issues, potentially leading to long-term complications.
"I Take My Medication Regularly"
You may think you can be dishonest about whether you took the medication regularly or not, but it can lead to negative consequences. Your doctor could assign you an incorrect does, which could lead to ineffective treatment, unwanted side effects, and further health problems. Honesty ensures proper medication management, reducing the risk of drug interactions and preventing the worsening of your underlying condition.
What Really Happens In Your Brain During Deep Sleep

Credits: CANVA
Sleep takes up nearly one-third of a person’s life, yet many still wonder what really happens while we rest. Until the mid-20th century, scientists believed sleep was simply a time when the body and brain shut down.
Research now shows that sleep is far from passive, it’s an active, restorative process essential for mental and physical health. As Johns Hopkins neurologist and sleep expert Dr. Mark Wu explains, the brain remains deeply engaged during sleep, performing vital tasks that influence memory, mood, and overall well-being.
The Stages of Sleep
Experts say the human sleep cycle has four main stages that repeat throughout the night. The first three make up non-rapid eye movement (non-REM) sleep, while the fourth is REM sleep, the stage most closely linked with dreaming.
In the first stage of non-REM sleep, the brain and body begin to shift from wakefulness to rest. Brain activity slows, muscles relax, and it is common to experience small, sudden twitches.
During the second stage, the body’s temperature drops slightly, and breathing and heart rate slow. Brainwaves continue to decelerate, though quick bursts of activity may still appear as the brain processes and stores information.
The third stage marks deep sleep, which is the most restorative phase. Here, the body fully relaxes, and the heart rate, breathing, and brain activity reach their lowest levels. This stage is crucial for waking up feeling refreshed and for healing and repair processes throughout the body.
The final stage is REM sleep, which begins about 90 minutes after you fall asleep. It starts short, roughly 10 minutes, but lasts longer with each cycle. During REM, the eyes move rapidly beneath the eyelids, breathing quickens, and heart rate and blood pressure rise to near waking levels. This is when most dreaming occurs. Interestingly, as people age, the amount of REM sleep they experience gradually decreases.
How The Body Regulates Sleep
According to Dr. Wu, two main forces govern sleep: the circadian rhythm and the body’s sleep drive.
The circadian rhythm acts as the body’s internal clock, controlled by a cluster of brain cells that respond to light and darkness. This rhythm triggers the release of melatonin at night and halts it when morning light appears. People who are completely blind often struggle with sleep because their brains can’t register these light cues properly, as per the John Hopkins Study.
The sleep drive works much like hunger. The longer you stay awake, the stronger your urge to sleep becomes. Unlike hunger, though, your body can override your willpower, if exhaustion sets in, it can force sleep to happen, even during daily activities or while driving. In extreme fatigue, brief “microsleep” moments lasting just a few seconds can occur without a person realizing it. However, taking long naps later in the day can reduce this natural sleep pressure, making it harder to fall asleep at night.
Why Sleep Matters For Your Brain
Anyone who has felt mentally sluggish after a sleepless night knows how strongly rest affects the brain. Adequate sleep is key to brain plasticity—the ability to learn, adapt, and form memories. Without it, the brain struggles to retain new information and perform cognitive tasks. Scientists also believe that deep sleep allows the brain to clear out toxins that build up during waking hours, improving long-term brain health.
Sleep impacts far more than the mind. Poor sleep can worsen conditions like depression, high blood pressure, migraines, and even seizures. It weakens the immune system, leaving the body more vulnerable to infection. Metabolism also suffers, as just one night without enough rest can temporarily throw the body into a prediabetic state.
As Dr. Wu explains, “There are countless ways sleep supports health.” From mental clarity to physical repair, the hours we spend asleep are some of the most important for keeping the body and brain functioning at their best.
Can A Rash Be A Sign Of COVID-19? Here’s Everything You Should Know
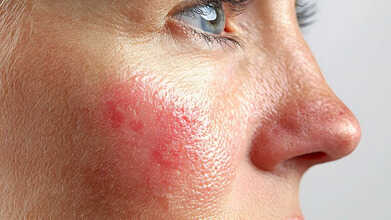
Credits: canva
When COVID-19 first emerged, it was largely seen as a respiratory illness. Over time, doctors discovered that the virus can affect nearly every major organ, including the heart, kidneys, liver, and skin. While cough, fever, and fatigue remain common signs, some people also develop unusual skin reactions. So, can COVID-19 actually lead to rashes? Here’s what experts have found.
Can COVID-19 Really Cause Rashes?
When COVID-19 first emerged, it was largely seen as a respiratory illness. Over time, doctors discovered that the virus can affect nearly every major organ, including the heart, kidneys, liver, and skin. While cough, fever, and fatigue remain common signs, some people also develop unusual skin reactions. So, can COVID-19 actually lead to rashes? Here’s what experts have found.
What Do COVID-19 Rashes Look Like?
Skin changes linked to COVID-19 are not among the most common symptoms, but they do occur. These rashes may appear on the neck, mouth, or toes and are often caused by inflammation in the body, as per Health website. They can look like flat or raised patches, small round spots, or itchy bumps. In some people, these rashes appear while they’re infected; in others, they show up weeks later.
Why Do These Rashes Occur?
Researchers believe COVID-related rashes are connected to how the virus interacts with the body’s ACE2 receptors, which are found in the skin. When the virus attaches to these receptors, it can trigger the release of inflammatory proteins called cytokines. This inflammation may lead to skin irritation, itchiness, or lesions.
Common Types of COVID-19 Rashes
1. COVID Toes
One of the most recognized skin signs of the virus, “COVID toes,” resembles chilblains, which are cold-weather sores. They appear as pink, red, or purple patches, sometimes with swelling or blistering. This condition is seen more often in younger people and may occur even after other symptoms fade.
2. Hives (Urticaria)
Hives tend to appear suddenly and can spread across any part of the body. They’re itchy, raised, and may come and go within hours or days.
3. Neck Eczema
Some people develop eczema-like rashes on the neck, chest, or trunk during or after COVID-19. The patches can be itchy and vary in color depending on skin tone—pink on lighter skin and brown, gray, or purple on darker skin.
4. Oral Rash
COVID can also cause soreness or peeling inside the mouth or on the lips. The area may feel dry, irritated, or scaly as it heals.
5. Vesicular and Papular Rash
These small, itchy bumps can be filled with fluid (vesicular) or solid (papular). They may appear anywhere on the body and are often linked with ongoing inflammation.
6. Pityriasis Rosea
This condition begins with a single large patch on the chest, back, or abdomen, followed by smaller spots that form a tree-like pattern. Though harmless, it can take several weeks or months to fade.
7. Purpuric or Vasculitic Rash
These rashes appear as dark, bruise-like spots caused by small blood vessel damage under the skin. The color may range from red and purple to brown or black, depending on skin tone.
How Long Do COVID Rashes Last?
The duration depends on the type of rash and the person’s immune response. Most clear up within 2 to 12 days, but some, especially in long COVID cases, may persist for weeks.
How Are COVID Rashes Treated?
Many rashes resolve without any special treatment. To relieve itching or pain, applying mild hydrocortisone cream can help. For more severe or persistent cases, doctors may recommend:
- Antihistamines to reduce itching
- Corticosteroids to lower inflammation
- Blood thinners if the rash is linked to blood vessel irritation
Your doctor will determine the safest treatment depending on the type of rash and overall health.
Disclaimer: This article is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before starting, stopping, or changing any medication, or if you experience any unusual symptoms or side effects.
Don't Ignore Your 'Winter Blues', This Is The Biological Reason Behind Winter Depression

(Credit-Canva)
It is a common theme for people to feel down and sad in winter. However, why do shorter, colder days often bring on feelings of loneliness and gloom? There is a biological reason behind it. As the days get shorter, many people feel a dip in energy or mood, but for millions, this signals Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD), which is a serious form of depression that shouldn't be ignored. Experts from West Virginia University (WVU) caution that SAD symptoms are very similar to major depressive disorder and must be taken seriously.
What Causes SAD?
SAD is much more than just feeling down when it gets dark. It's a genuine type of depression most often seen during the winter months, especially in places far north where daylight is scarce. The basic problem is simple: less natural light hits your eyes. This drop in sunlight confuses your brain's chemistry.
It messes with two vital brain chemicals: serotonin, which helps stabilize your mood, and melatonin, which controls when you sleep and wake up. This lack of light also throws off your body's internal clock, called the circadian rhythm. When all these elements get disrupted, it triggers feelings of low energy and depression.
What Are The Symptoms Of SAD?
SAD involves a cluster of symptoms that persist and significantly interfere with your daily life. The pattern is usually predictable: symptoms begin in the fall, peak in the winter, and disappear by spring. Symptoms often include:
- Feelings of hopelessness.
- Loss of interest in activities you once enjoyed.
- Significant changes in sleep (often sleeping more, or having disrupted sleep).
- Changes in appetite or increased food cravings.
- Difficulty concentrating and persistent fatigue.
The risk of SAD is higher among younger people, women, and those with a family history of mood disorders.
Can You Treat/Prevent Seasonal Affective Disorder?
Because Seasonal Affective Disorder is highly predictable, experts advise starting preventative treatments early in the fall. Seeing a healthcare provider is essential to determine the best plan and timing for treatment, rather than waiting for severe symptoms to appear later in winter.
Light Therapy
This involves sitting daily before a special light box emitting 10,000 lux of bright white light. Doing this for 30 to 60 minutes each morning is the most common and effective treatment for SAD, as it helps correct the imbalance caused by reduced sunlight exposure.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
This form of talk therapy teaches you practical skills to manage negative thinking patterns and behaviors linked to depression. CBT helps individuals reframe their outlook on winter and build effective coping mechanisms to reduce the impact of SAD symptoms.
Medication
In certain situations, a healthcare provider may prescribe antidepressant medication to help regulate mood-affecting brain chemicals like serotonin. This is often considered alongside light therapy or counseling, especially if symptoms of depression are severe or persistent.
Lifestyle Changes
Simple daily habits are powerful tools. Regular exercise boosts mood and energy, while maintaining a consistent sleep schedule keeps your body's internal clock stable. These practical steps offer significant support alongside clinical treatments.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

