- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
Can Measles Be Deadly? Everything You Need To Know About The Measles Outbreak
Image Credit: Canva
Measles can be a disease of the past, but its recent resurgence is evidence to the contrary. The outbreak, which started spreading in late January, has resulted in multiple hospitalizations, with at least nine confirmed cases and three probable cases as of early February. Health officials caution that at least one in five infected individuals will have to be hospitalized, highlighting the severity of the situation.
The first measles case in a Chicagoan since 2019 has recently been confirmed, again emphasizing the persistent risk—particularly in populations with low levels of vaccination. Although the disease was all but eliminated from the United States after the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine became available in 1963, it is still occurring because there are missed opportunities in immunization coverage.
Extremely contagious and potentially fatal, measles is still a worldwide health issue. Although some who get the disease recover without incident, the fact is that measles can kill, especially in children, pregnant women, and people with compromised immune systems.
How Measles Spreads and Why It's Dangerous?
Measles is the most infectious viral illness known. It is transmitted by airborne respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing and can remain in the air for as long as two hours after an infected individual has vacated the area. This results in nine out of ten unimmunized individuals exposed to the virus becoming infected. The illness can also be imported into the U.S. by travelers arriving from areas where measles remains prevalent.
Severe Medical Complications of Measles
Although measles may appear to be a normal childhood disease to some, its complications can be serious and even life-threatening. Some of the most frequent problems are:
Pneumonia: The major killer in measles, especially among children.
Encephalitis: A serious inflammation of the brain that may result in permanent brain damage.
Severe dehydration: From chronic diarrhea and vomiting.
Compromised immune system: Measles has the effect of erasing immune memory, and thus the survivors remain exposed to other pathogens for several months.
More than half of measles-infected children in the region of Europe in 2023 were hospitalized according to the World Health Organization (WHO), showing just how critical the illness could be.
Who is at Most Risk During Measles Outbreak?
Infants under the age of five are especially susceptible to measles and its complications. Their immature immune systems predispose them to serious infection. An estimated 136,000 individuals worldwide die from measles each year, and most are children. Prior to mass vaccination, the yearly death rate was much higher, with an estimated 761,000 deaths in children in 2000.
Can You Get Measles During Pregnancy?
Pregnant women who get infected with measles are at risk of severe health complications. The virus poses the risk of:
Pneumonia: Occurs in approximately 18 out of 100 pregnant women infected with measles.
Maternal mortality: Four out of 100 pregnant women with measles die.
Premature delivery: In approximately 13 out of 100 measles-infected pregnancies.
Since pregnant women are not administered the MMR vaccine, it is important for people to vaccinate themselves long before getting pregnant.
Why Vaccination is the Best Defense Against Measles
Measles is a vaccine-preventable illness. The MMR vaccine is extremely effective, with long-lasting immunity:
- A single dose covers 95% of vaccinees.
- Two doses cover 99% of vaccinees.
With such strong protection rates, mass vaccination campaigns have significantly decreased deaths from measles. But reduced vaccination levels in some regions have resulted in renewed outbreaks of the disease. Parents avoid vaccinating their children because of misinformation regarding vaccine safety, but there is overwhelming research proving that the MMR vaccine is safe and effective.
Why Are Measles Outbreaks on the Rise?
Increased measles cases are the result of declining vaccination rates. The main reasons include:
Vaccine hesitancy: There is misinformation surrounding vaccines, causing parents to hesitate or refuse vaccination.
Travel and exposure: Travelers to places where there is an active outbreak bring measles into the U.S.
Weakened herd immunity: As vaccination rates decline, the virus becomes easier to spread, putting more at risk.
What to Do If Exposed to Measles
If you or your child have come into contact with someone who has measles, do the following immediately:
Check vaccination records: If you or your child are already vaccinated, the chances of getting infected are very low.
Get the vaccine if not immunized: The MMR vaccine may still offer some protection if administered within 72 hours of exposure.
Watch for symptoms: Symptoms occur 7-14 days after infection and are fever, cough, runny nose, and rash.
Stay home if infected: People with measles must remain home to avoid infecting others.
Can the Measles Vaccine Cause the Disease?
MMR vaccine includes a weakened virus that allows the body to become immune without actually causing measles. In healthy children, it does not lead to infection. But severe immune deficiencies may develop a condition similar to measles and should not receive the vaccine.
How Long Is Measles Contagious?
Individuals with measles can be contagious before they even notice they are ill. The period of contagiousness is from four days prior to the onset of the rash through four days afterwards. Since the virus remains present in the air for hours, even a short exposure is very risky for those who have not been immunized.
Is it Possible to Prevent Measles?
Mass vaccination is the most effective strategy for preventing the outbreak of measles. The United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advises:
- The initial vaccine dose of the MMR during infancy at age 12-15 months.
- A second one at age 4-6 years.
- One extra dose among high-risk subjects in case of an outbreak.
Infants under the age of one year, who are not yet vaccine-age-appropriate, are protected by herd immunity. This is why it is important that the rest of the community is vaccinated to avoid spreading to the entire community.
Measles is more than a rash and fever- it is a dangerous disease that can cause life-threatening complications. Although the U.S. has made great strides in preventing measles through vaccination, the recent surge in cases is a harsh reminder of the risks of vaccine hesitancy.
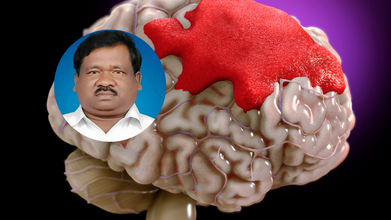
Jharkhand Education Minister Ramdas Soren Suffers Brain Hemorrhage, Airlifted To Delhi
Credits: Canva
Jharkhand Education Minister Ramdas Soren remains in critical condition after suffering a severe brain injury following a fall in the bathroom at his residence early Saturday morning.
According to officials, the minister was initially admitted to a hospital in Jamshedpur, where doctors detected a blood clot in his brain. He was later airlifted to a private hospital in Delhi for more advanced treatment.
Health Minister Irfan Ansari confirmed the incident and said that Soren’s condition deteriorated rapidly after the fall. “Ramdas Soren’s health suddenly declined. He suffered a serious brain injury and internal bleeding in the brain. I have been in constant touch with his family and am monitoring the situation closely,” Ansari said.
Airlifted to Delhi for Advanced Care
After initial treatment in Jamshedpur, the decision was made to transfer the minister to Delhi for more specialized care. Former Union Minister and senior BJP leader Arjun Munda, who was present at Sonari Airport during the airlift, said, “I have spoken to the director of Delhi Apollo Hospital, and he has assured that treatment will begin as soon as the minister reaches. The doctors have diagnosed a brain hemorrhage due to a sudden increase in pressure. His condition is critical, but we are hopeful.”
On Saturday evening, the Delhi hospital issued a statement confirming that the minister was on life support and under the care of a multidisciplinary team of senior specialists. “A close watch is being kept on all vital parameters,” a spokesperson for the hospital said.
Understanding Brain Hemorrhage: What Happened to Ramdas Soren?
A brain hemorrhage, commonly known as a brain bleed, occurs when there is bleeding either inside the brain tissue or in the space between the brain and the skull. It is a medical emergency that can cause damage by increasing pressure on the brain, reducing oxygen supply, and killing brain cells.
Doctors categorize brain hemorrhages based on where the bleeding occurs:
Bleeding Outside Brain Tissue (Within Skull)
Epidural Hemorrhage: Occurs between the skull and the outer membrane (dura mater)
Subdural Hemorrhage: Bleeding between the dura mater and the arachnoid membrane
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Bleeding between the arachnoid and the innermost membrane (pia mater)
Bleeding Inside Brain Tissue
Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Bleeding within the brain’s tissues
Intraventricular Hemorrhage: Bleeding into the brain’s internal cavities that hold cerebrospinal fluid
In Soren’s case, doctors suspect a form of intracerebral or subdural hemorrhage, given the mention of clotting and pressure build-up.
Symptoms and Risks
Brain bleeds can come on suddenly and include symptoms like severe headache, nausea, vomiting, confusion, weakness or numbness (especially on one side of the body), vision problems, dizziness, seizures, slurred speech, and even coma. A particular warning sign is the so-called “thunderclap headache”, a sudden, intense pain that can signal a subarachnoid hemorrhage.
When not treated immediately, such bleeds can be fatal or lead to long-term neurological complications. In some cases, surgery is required to relieve pressure and remove clots.
What’s Next?
As of Saturday night, Ramdas Soren continues to remain on life support. No additional medical bulletins have been released since his transfer to Delhi, but officials have indicated that his condition is still being evaluated. “We are hoping for positive progress, but his condition remains critical,” said Arjun Munda.
Family members and close colleagues are at the hospital, and the Jharkhand government has said it will provide all necessary support for his treatment.
The political and public community has expressed concern and extended wishes for the minister’s speedy recovery. Further updates are awaited from the hospital and health authorities.
FDA Escalates Recall Of 64,800 Lbs. of Butter Over Undeclared Allergen

Credits: Canva
In a growing food safety alert, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has escalated a butter recall to a Class II risk level following concerns over undeclared allergens. The product in question, European Style Butter Blend manufactured by Bunge North America Inc., was found to contain milk that was not listed on the packaging label.
Class II Recall Indicates Moderate Health Risk
The risk reclassification, issued on Wednesday, July 30, places the product under the FDA’s second-highest warning level. According to the FDA, a Class II recall involves “a situation in which use of or exposure to a violative product may cause temporary or medically reversible adverse health consequences or where the probability of serious adverse health consequences is remote.”
While no illnesses or allergic reactions have been reported so far, the undeclared presence of milk poses a potential health hazard to people with dairy allergies or lactose intolerance.
Initial Voluntary Recall Announced in Mid-July
The recall began as a voluntary measure by Bunge on July 14, when the company announced it was pulling approximately 64,800 pounds, or 1,800 cases, of its one-pound butter blocks from shelves. The recalled butter was packed in white paperboard cases, each containing 36 one-pound blocks.
The affected products carry the lot code 5064036503 and were shipped to 12 distribution centers across the United States and one in the Dominican Republic.
Why the Undeclared Milk Is a Serious Concern
Milk is one of the nine major food allergens identified by the FDA, alongside eggs, fish, crustacean shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soybeans, and sesame. The FDA mandates clear labeling of such allergens because exposure, even in small amounts, can cause a range of reactions, from mild discomfort to life-threatening symptoms.
Food-related allergic reactions may include hives, facial swelling, vomiting, coughing, and skin irritation. More severe responses can result in anaphylaxis, a rapid-onset, whole-body allergic reaction that may lead to shock and, in extreme cases, death.
According to the Mayo Clinic, anaphylaxis occurs when the immune system floods the body with chemicals in response to an allergen. This can cause a sudden drop in blood pressure, narrowing of the airways, and potential organ failure if not treated immediately.
FDA Reiterates Importance of Allergen Labeling
In light of the recall, the FDA has emphasized the importance of allergen labeling and said it continues to enforce regulations requiring companies to clearly list all ingredients and potential allergens on packaging.
“More specific labeling requirements exist for foods that can cause allergies or other hypersensitivity reactions,” the agency stated. “These rules are designed to prevent accidental consumption of allergens and to protect consumers with dietary restrictions.”
The FDA also advised that anyone who experiences symptoms of an allergic reaction after consuming the recalled butter should “stop eating the food immediately, evaluate the need to use emergency medication (such as epinephrine), and seek medical attention.”
Company Yet to Comment
As of August 2, Bunge North America has not issued an updated public statement in response to the FDA’s reclassification and did not respond to a request for comment.
Food Safety Under Scrutiny Amid Other Recent Recalls
This butter recall follows a string of other high-profile food safety incidents this year. In recent weeks, more than 110,000 cases of popular chocolate ice cream bars were recalled across 23 states. Target-branded baby food was also pulled from shelves for containing “elevated levels of lead.”
Could This New Alzheimer’s Drug Buy Patients Four More Good Years? Here Is What We Know

Not forever, but what if you could press pause on Alzheimer’s just long enough to enjoy a few more good years? That is the tantalising promise behind a new drug called lecanemab, hailed as a game-changer in the fight against dementia.
The drug has already been licensed for use in the UK after trials showed it could slow the pace of decline in people with early-stage Alzheimer’s. But new long-term findings are turning cautious hope into something stronger: patients who stayed on lecanemab for four years experienced a noticeable delay in the disease's progression. Some even showed no decline at all.
How It Works
Alzheimer’s is known for its slow but relentless grip on memory and cognition, typically marked by the build-up of sticky proteins in the brain. Lecanemab targets tau, a protein that increases as the disease worsens.In the initial 18-month trial, the drug delayed Alzheimer’s progression by just under six months. That might not sound like much, but it’s the long game that matters here. Among 478 patients who remained on the drug for four years, the average delay before their disease advanced to the next stage stretched to almost 11 months.
Even more striking: 69 per cent of those with low levels of tau saw no decline at all over the four years. And over half in that same group actually improved their cognitive scores.
A Slow Slide Instead of a Steep Drop
Typically, people with mild Alzheimer’s see their scores on memory and function tests worsen by one or two points each year. But for those taking lecanemab, the total decline across four years was just 1.75 points. That’s a major shift in the rhythm of the disease, changing it from a downhill tumble to a slow shuffle.
Professor Christopher Van Dyck, who led the study at Yale School of Medicine, puts it simply: “You will get worse over time, but it will take longer to get there.” That extra time could mean more independence, more connection with loved ones, and more living.
Why Early Treatment is Key
The benefits weren’t evenly distributed. Patients who had less evidence of Alzheimer’s pathology, that is, fewer early changes in the brain, showed the most striking outcomes. In other words, the earlier you start treatment, the better your odds of preserving function.This makes a strong case for early diagnosis and intervention, which could shift the way we approach Alzheimer’s care. No longer is it just about managing symptoms; it’s about changing the trajectory of the disease.
Not a Cure, But a Clear Step Forward
Lecanemab isn’t a miracle cure. It doesn’t reverse Alzheimer’s, and it’s not suitable for all patients. But experts say it’s a major milestone. Reportedly, this is the first wave of disease-modifying treatments and there’s still plenty to understand.
Other Contenders in the Ring
Lecanemab isn’t the only drug showing promise. A similar treatment called donanemab was tested over a three-year period, though it was only administered for 18 months. Still, the results were encouraging: patients on the drug gained an extra six to 12 months before their disease progressed.
That might not sound earth-shattering, but in a condition where time is everything, even a few more months of clarity and connection can be priceless.
The research is still evolving, but the signs are encouraging. With continued trials, this could be the start of a new chapter in dementia treatment, one where patients and families have more time to prepare, more time to enjoy life, and more hope than ever before.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

