- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Ebola Outbreak Update: Vaccines Continue To Arrive As Congo Yet Again Becomes Disease Hotspot

Credits: Canva
Just 10 days after the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) declared an Ebola virus outbreak in Kasai province, health authorities have rolled out a vaccination drive targeting frontline workers and contacts of patients, the World Health Organization (WHO) confirmed in its latest update.
First Vaccines Arrive in Bulape
The first consignment of 400 doses of Ervebo (VSV-EBOV) was dispatched to Bulape health zone from a national stockpile of 2,000 doses stored in Kinshasa. Some frontline health workers in the capital had already received the vaccine. The WHO said additional shipments are expected in the coming days to sustain the response effort.
Health teams are deploying a “ring vaccination” strategy, which prioritizes those at the highest risk of infection, including patient contacts and health workers directly exposed to cases.
Also Read: What Is Babesia That Could Block Your Lyme Disease Recovery?
Global Support for Vaccine Supply
To ensure adequate coverage, the International Coordinating Group on Vaccine Provision has approved an additional 45,000 doses to be sent to the DRC. The WHO is assisting the Ministry of Health in formalizing a request for these doses and has also worked with partners to draw up a detailed immunization plan. Training sessions for vaccination teams are underway to streamline the rollout.
Alongside vaccines, treatment options are being reinforced. Courses of the monoclonal antibody therapy MAb114 (ansuvimab-zykl, commercially known as Ebanga) have already been dispatched to treatment centers in Bulape to support patient care.
Rising Case Numbers and Death Toll
Despite these interventions, the outbreak continues to grow. At a meeting of the provincial Ebola emergency committee on September 13, officials reported a sharp increase in infections and fatalities. According to the DRC’s National Public Health Laboratory (INRB), total cases have now risen to 81, with 28 deaths recorded, marking a case-fatality rate of 34.6%.
The latest figures represent a significant jump from a few days earlier, when authorities reported 68 suspected cases (including 20 confirmed) and 16 deaths.
Also Read: Congo Ebola Outbreak Caused By The Zaire Strain So Far Has 28 Deaths, Confirms WHO
Of seven new suspected cases detected in the Bulape health zone, five have been confirmed through laboratory testing. This highlights both the rapid spread of the virus and the crucial role of diagnostic capacity in containing the outbreak.
Expanding Contact Tracing
Efforts to trace and monitor contacts are also being scaled up. Health officials identified 58 new contacts in recent days, bringing the total to 716. Contact tracing is a cornerstone of the response, enabling teams to vaccinate and monitor individuals most likely to have been exposed.
In a further boost to local capacity, another 360 vaccine doses have arrived in Tshikapa, the provincial capital of Kasai. This shipment is expected to support wider vaccination efforts in neighboring areas.
With Ebola continuing to claim lives in Kasai, health authorities in the DRC and their global partners are racing to contain the outbreak. Vaccines, therapeutic drugs, and intensive contact tracing remain at the heart of the strategy. However, the rising case count underscores the urgent need to maintain momentum and secure sufficient supplies before the virus spreads further.
Nipah Virus Survivor Speaks Out, Calls for More Awareness

Credit: Canva
The Nipah virus outbreak began in West Bengal, India with two hospital nurses at AIIMS, Kolkata, testing positive for the infection and being quarantined, prompting widespread testing. Soon after, five cases, including a doctor and a staff member, were confirmed and over 100 people were quarantined.
However, one of the nurses, a 25-year-old unidentified man has now made a recovery and revealed his experience with the virus, claiming that despite irritation in the throat and uncertainty about what lay ahead, he had faith in his doctors and fellow nurses.
In an interview with the Metro, he said: “After I was taken off ventilation and regained consciousness, I came to know that I have Nipah. I still had the tube in my mouth, and there was irritation. Despite the irritation and my fear, I had faith in the doctors and nurses.
“I have suffered and I know the symptoms. I will tell people when they should get checked for the Nipah virus. I want to raise awareness about the virus and its symptoms.
“I am not sure how I came in contact with the deadly virus. Maybe it was while treating a patient. But I will continue to work as a nurse. I am waiting to rejoin the hospital,” he added.
The unidentified healthcare professional remains very weak physically and is undergoing physiotherapy to regain his strength. “I was bedridden for over a month. I am still very weak and have an unstable gait. So, I am undergoing physiotherapy,” he said.
The other nurse, a woman, remains in a coma but has been taken off ventilation support, a hospital official confirmed this week. .
Nipah Virus: What Is It And What Are Its Symptoms?
According to WHO, Nipah virus is a zoonotic illness which means it is mostly transmitted from animals to humans through bats. However, it can also spread through fruits that have been contaminated by the saliva, urine or droppings of infected bats. Human-to-human transmission can also occur through close contact with an infected person or their bodily fluids.
The illness has a 75 percent fatality rate and there are no vaccines to protect the public.
The virus was first identified in 1998 during an outbreak among pig farmers in Malaysia and soon made its way to India and Bangladesh in 2001 with cases often involving family members or caregivers tending to infected patient.
READ MORE: Nipah Virus Outbreak In India: Myanmar Airport Tightens Health Screenings
Although Nipah virus has caused only a few known outbreaks in Asia, it infects a wide range of animals and causes severe disease and death in people. Some of its common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Breathing difficulties
- Cough and sore throat
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Muscle pain and severe weakness
Samples collected from the patient’s home and workplaces, including pets and partially eaten fruits dropped by bats, all tested negative for the virus, and the exact source of the infection could not be identified.
What Does WHO Say?
The World Health Organization has declared it is unlikely India's deadly Nipah Virus outbreak will cross borders and reach other nations, noting that countries do not need to set any travel restrictions in place.
In an email to Reuters, officials said: "The WHO considers the risk of further spread of infection from these two cases is low". adding that India has the capacity to contain such outbreaks.
"There is no evidence yet of increased human to human transmission," it said, adding that it has coordinated with Indian health authorities.
While health officials state it is nearly impossible for the virus to transmit across countries and unlikely to cause an international outbreak, countries including Australia, Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia and Singapore continue to remain on high alert and have begun airport screenings.
Ahmedabad Toddler Swallows Hulk Toy, Showed X-Ray, Doctors Remove It Via Endoscopy
Credits: X
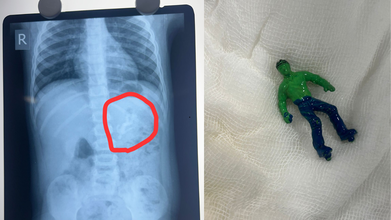
Ahmedabad toddler, one-and-a-half-year-old boy swallowed a 'Hulk' toy, which is based on a popular comic superhero. The toy was stuck in his stomach when his parents took him to the Civil Hospital. According to reports by News18, the child is identified as Vansh who showed the signs of discomfort and began vomiting. This is what alarmed the parents.
As per the News18 report, his mother Bhavika was suspicious when she noticed that one of his toys was missing. The child was rushed to the hospital and an X-ray revealed that he had swallowed the entire plastic toy. The toy was not broken.
Hindustan Times reported that Dr Rakesh Joshi, Head of the Department of Pediatric Surgery removed the toy through upper GI endoscopy. "Had it been a little late, the toy could have moved further from the stomach and got stuck in the intestines. In that case, there would have been a risk of intestinal blockage and even rupture," the senior doctor said.
"There is a natural valve between the esophagus and the stomach. The biggest challenge was to take out a whole toy through this valve. When we tried to grab it with the endoscope, the toy kept slipping because of the air in the stomach. Pulling the toy by its hand or foot raised the possibility of it getting stuck in the valve and causing it permanent damage," he said.
The doctor noted that if the toy had further slipped down, it would have increased the risk of intestine rupturing.
Ahmedabad Toddler Swallows Hulk Toy: What Parents Must Keep In Their Mind
Under the Toys (Quality Control) Order, 2020 issued by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, toy safety in India was brought under mandatory BIS certification from September 1, 2020. The move aims to ensure safer toys for children while also supporting the government’s policy of curbing non-essential imports.
Industry sources estimate that more than 85 percent of toys sold in India are imported. Officials say the Toys Quality Control Order is a key step in preventing the entry of cheap and substandard toys into the domestic market, many of which fail to meet basic safety requirements.
Ahmedabad Toddler Swallows Hulk Toy: Standards for Electric and Non-Electric Toys
The quality control order clearly defines safety standards based on the type of toy. Non-electric toys such as dolls, rattles, puzzles, and board games must comply with IS 9873 (Part 1):2019. These toys do not rely on electricity for any of their functions.
Electric toys, which include at least one function powered by electricity, are required to meet the standards outlined under IS 15644:2006. Compliance with these standards is mandatory before such toys can be sold in the Indian market.
Ahmedabad Toddler Swallows Hulk Toy: Risks Linked to Untested Toys
Toys that are not tested by NABL-accredited toy testing laboratories can pose serious health risks to children. Sharp edges and poorly finished parts can cause cuts and injuries. PVC toys may contain phthalates, which are considered harmful chemicals.
Many low-quality toys have also been found to contain lead, a substance known to be particularly damaging to brain development in children. Soft toys with fur or hair can trigger allergies or become choking hazards. In some cases, small body parts can get stuck in gaps or holes, increasing the risk of injury.
Testing by NABL-accredited laboratories ensures that toys are safe, durable, and suitable for specific age groups. Parents are advised to check for IS marks on toys before purchasing, as this indicates compliance with Indian safety standards.
Ahmedabad Toddler Swallows Hulk Toy: What Parents Should Check Before Buying Toys
Experts recommend avoiding toys with small detachable parts for toddlers and young children, as they are more likely to put objects in their mouths. Toys should always match the child’s age, skill level, and interests.
Parents are also urged to look for IS marks, which confirm that the toy has been tested and certified. Loud toys should be avoided, as prolonged exposure to sounds above 85 decibels can harm a child’s hearing.
Electric toys with heating elements should be used with caution or avoided altogether due to burn risks. Finally, toys with sharp edges or shooting components should be carefully examined to prevent cuts and injuries.
Nipah Virus Outbreak In India: Myanmar Airport Tightens Health Screenings

Credits: iStock
Nipah virus outbreak in India triggered airport screenings of travelers, including in Myanmar. Many reports claim that passengers are being checked in similar ways as they were during the COVID-19 virus spread. Health and Me reported how in Thailand the health screenings of foreign travelers were taken seriously, a similar case is seen in Myanmar.
Nipah Virus Outbreak In India: How Are Travelers Screened In Myanmar?
Myanmar has tightened its health screenings and surveillance at Yangon International Airport to prevent any possible entry of Nipah virus case, reported The Global New Light of Myanmar. Travelers who are arriving from India, especially West Bengal are given special attention to check for any fever or other Nipah-related symptoms, read the report by the Ministry of Health.
The ministry also noted that health screening of passengers arriving from abroad is being conducted in line with the established guidelines for infectious diseases that could give rise to public health emergencies, Xinhua news agency reported.
Informational leaflets too are being distributed among travelers to be aware of the symptoms. Posters are also displayed at the airport. Along with all that, disease prevention and control measures are also being carried out in the airport.
Screening measures are also enhanced and implemented at Mandalay International Airport.
Nipah Virus Outbreak In India: What Is It?
As per the World Health Organization (WHO), Nipah virus infection is a zoonotic illness that is transmitted to people from animals, and can also be transmitted through contaminated food or directly from person to person.
In infected people, it causes a range of illnesses from asymptomatic (subclinical) infection to acute respiratory illness and fatal encephalitis. The virus can also cause severe disease in animals such as pigs, resulting in significant economic losses for farmers.
Although Nipah virus has caused only a few known outbreaks in Asia, it infects a wide range of animals and causes severe disease and death in people.
Nipah virus is infectious and can spread from animals like bats and pigs to humans through bodily fluids or contaminated food. It can also pass between people through close contact, especially in caregiving settings. While it can spread via respiratory droplets in enclosed spaces, it is not considered highly airborne and usually requires close, prolonged contact for transmission. Common routes include direct exposure to infected animals or their fluids, consuming contaminated fruits or date palm sap, and contact with bodily fluids such as saliva, urine, or blood from an infected person.
Nipah Virus Outbreak In India: What Are The Common Symptoms?
- Fever
- Headache
- Breathing difficulties
- Cough and sore throat
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Muscle pain and severe weakness
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

