- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
FDA Greenlights Zevaskyn for Rare Genetic Skin Condition
Credits: Canva
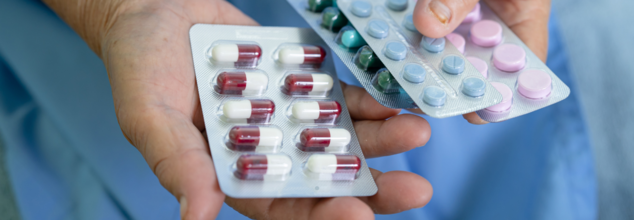
In a landmark development for patients who live with a rare and painful skin condition, the US Food and Drug Administration or the FDA has approved Zevaskyn (prademagene zamikeracel) for the treatment of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa or RDEB. This is an inherited disorder that causes the skin to be extremely fragile. I also leads to chronic wounds, bleeding, and tearing even from minor friction or trauma.
As per the 2015 study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, there are four major subtypes of the skin disorder, which comes from the heterogeneous group of inherited mechanobullous disorder hat is caused by mutation in genes that encode structural proteins in the skin. The overall condition is referred to as epidermolysis bullosa, and one of its type is RDEB, which further comes with two main subtypes of dystrophic EB.
Zevaskyn is now the first and only autologous cell-based gene therapy approved for both adult and pediatric patients living with this life-altering condition.
Why Is This A Breakthrough In Gene Therapy?
Zevaskyn represents a new era in wound care and gene therapy. Unlike traditional treatments that only manage symptoms, this one-time surgical application targets the underlying genetic mutation responsible for RDEB. The therapy uses the patient's own skin cells, which are genetically modified to produce a functional version of the missing COL7A1 gene, critical for anchoring skin layers together.
"Zevaskyn is not just a bandage—it’s a breakthrough that may help change the course of this disease for many," said Madhav Vasanthavada, Ph.D., Chief Commercial Officer at Abeona Therapeutics, the biopharmaceutical company behind the treatment.
How Was It Approved?
The FDA based its approval from the results of two clinical trials: a phase 1/2a study and the pivotal phase 3 VITAL study.
Phase 1/2a Trial: In this study, seven patients with 38 chronic wounds received a single Zevaskyn application. Researchers observed a significant and long lasting improvement at treated sites during the median follow-up of seven years.
Phase 3 VITAL Study: This was a larger study that included 43 patients with large unhealed or non healing wounds. After six months, 81% of those wounds treated by Zevaskyn, showed at least 50% healing, as compared to only 16% in the control group, who had received the standard care.
These outcomes were not only statistically significant but also clinically meaningful, especially for patients who have previously struggled with limited treatment options.
Zevaskyn also showed a favorable safety profile across both studies. No treatment-related serious adverse events were reported. The most common minor side effects were procedural pain and itching, affecting approximately 5% of participants.
"This therapy offers hope for patients and families who have lived too long without effective solutions," said Vasanthavada. “We’re confident in Zevaskyn’s ability to deliver long-term results and are committed to making it widely accessible.”
Access For Patients
To ensure access, Abeona Therapeutics plans to collaborate with both commercial insurers and government payers. The company aims to develop outcome-based agreements that reflect the long-term benefits of a single application of Zevaskyn, reducing the need for repeat procedures or ongoing wound care costs.
With FDA approval, Zevaskyn is set to be a game-changer in the treatment of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa—offering patients more than just relief, but a meaningful step toward healing.
Cancer Postcode Lottery: What Is It And Why Is UK Govt Putting An End To It?

Credits: Canva
Cancer Postcode Lottery will soon be put to an end by the UK Government. Reports say that it will enable the rural population access to cancer specialists and treatments. Before getting into how it will help the rural population and people living in coastal areas to find it easier to see a cancer doctor, let us first understand what postcode lottery means.
What Is Cancer Postcode Lottery?
The term cancer postcode lottery refers to a situation where a cancer patient’s access to the latest and most effective treatments depends on where they live or which hospital they are treated at, rather than purely on medical need.
Based on the information you shared, senior cancer doctors in England are warning that this is happening because of bureaucratic hurdles within the NHS. Even though cancer care is supposed to be equitable across the country, in practice, not all hospitals can easily offer the same treatments.
How Does This Postcode Lotter Work?
Doctors say that some cutting-edge cancer treatments such as advanced radiotherapy techniques and newer immunotherapy drugs require separate funding approvals. Individual cancer centers often have to apply to NHS England for permission and money to use these treatments.
Larger, better-funded hospitals with more administrative resources are often able to navigate this complex system more easily. Smaller or less well-resourced units may struggle, meaning patients treated there may not get access to the same options.
For instance, Stereotactic Ablative Body Radiotherapy (SABR). SABR is a highly precise form of radiotherapy that delivers strong radiation doses directly to small tumors in areas such as the lungs, liver, brain and lymph nodes. Although SABR is a well-established treatment and can be life-saving for certain patients, the Royal College of Radiologists (RCR) says some cancer units still have to apply for special funding to use it. This leads to situations where a patient in one area can receive SABR, while another patient with the same cancer elsewhere cannot.
What Is The Government Planning To Do With Postcode Lottery?
As per the official website of UK Government, this will allow people "living in rural and coastal communities will find it easier to see a cancer specialist as part of plans to tackle the current postcode lottery."
The website notes that most deprived parts of the country have fewer cancer consultants, which leaves patients waiting longer for essential care. These same areas also face highest economic inactivity, with long waits for diagnosis and treatment keeping people out of work and holding back local economies. This is why the government is now introducing "new training places targeted at trusts with biggest workforce gaps, prioritising rural and coastal areas".
Working with the Royal Colleges, the government will encourage more doctors to train in clinical and medical oncology to increase the number of cancer specialists in underserved areas.
These steps will be outlined in the upcoming National Cancer Plan, which aims to speed up diagnosis and treatment, reduce inequalities, and support the goal of making England a global leader in cancer survival, while building a future-ready NHS.
Could Red Light Therapy Help Protect Football Players From CTE

Credits: Canva
A treatment already popular in the US for skin care, pain relief, and faster healing may soon be known for something far more serious. A new study suggests red light therapy could help protect football players’ brains from chronic inflammation caused by repeated hits to the head.
Experts say the findings are early but promising, especially in the ongoing search for ways to reduce long term brain damage in contact sports.
What Is CTE?
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy, or CTE, is a degenerative brain disease linked to repeated head injuries. It is commonly found in former football players, boxers, and military personnel exposed to blast injuries. Over time, the condition can cause memory loss, confusion, mood changes, aggression, and eventually problems with movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing. There is currently no cure, and doctors still do not know how to slow its progression.
Why inflammation matters in CTE
For now, the only proven way to lower CTE risk is to reduce repeated brain trauma through better helmets, rule changes, and fewer hits to the head. But with more than 100 former NFL players diagnosed with CTE after death and many more suspected cases, experts agree that prevention tools alone are not enough.
Researchers believe chronic inflammation in the brain plays a major role in how CTE develops and worsens over time. If that inflammation can be reduced early, it could potentially limit long term damage.
Red light therapy, also known as photobiomodulation, has already been shown to reduce inflammation in other parts of the body. It works by stimulating energy production inside cells and improving blood flow, which helps tissues repair and recover.
Inside the football study
To see whether the therapy could help the brain, researchers at the University of Utah Health studied 26 collegiate football players during a full season. Half received active red light therapy using a light emitting headset and a small device placed inside the nose. The other half used an identical looking device that did not emit light.
Players completed three 20 minute sessions each week over 16 weeks. Brain scans were taken before and after the season.
Read: 21-year-old Billy Vigar Of Chichester City Dies Of Sustaining Brain Injury
The results were striking. MRI scans showed that players in the placebo group experienced a significant increase in brain inflammation by the end of the season. In contrast, those using red light therapy showed little to no increase, with protection seen across most brain regions.
Why experts are paying attention
Specialists who reviewed the findings say the results align with what scientists already understand about inflammation and brain injury. Reducing the inflammatory response after repeated impacts could help limit the damage that builds up over time.
Another advantage is that the therapy is non invasive and does not involve medication. Most users report no major side effects, which makes it especially appealing for athletes.
That said, experts caution against buying over the counter red light devices. The therapy requires very specific wavelengths that can penetrate skin and tissue effectively. Many consumer products do not meet those standards.
Researchers stress that more studies are needed to confirm long term safety and effectiveness. A large Department of Defense funded trial is already planned, involving 300 people with persistent concussion or traumatic brain injury symptoms, including veterans and first responders.
If future research continues to show benefits without harm, red light therapy could one day become part of how teams protect athletes’ brains, not just in football, but across many sports.
Nicole 'Snooki' Polizzi Says Doctors Found Cancerous Cells In Her Cervix

Credits: Wikimedia Commons
Nicole "Snooki" Polizzi opened up about a cancer scare. Now, 38, the Jersey Shore star, posted on her TikTok an emotional video, where she explained that she has been dealing with abnormal pap smear results. She said that it has been about four year since the precancerous cells were found. Because of that she had to undergo an "uncomfortable" colposcopy and biopsy.
She said that when the results came back, the doctor informed her that her cervix is "Not looking great". The doctor had found cancerous cells on the top of her cervix. She said that she would soon need a cone biopsy under anesthesia for further testing. "I am terrified. It is scary, but we have to get it done because cervical cancer is nothing to joke about."
She said, "But whatever to keep me healthy and safe to be here for my kids that I have now," referring to her three children with her husband Jionni LaValle.
In her TikTok video, she said that she is scared and freaking out. She also said that she hopes to find community on social media with other women who have been through the same.
She also agreed to delaying her routine examination because of fear. "I waited on my appointments because I knew I might not get great results but also because I didn't want to feel the pain. I didn't want to deal with the stress of having to deal with all of this," she said.
Talking about her TikTok video, she said, “Just making this video to spread awareness to make sure you get your pap smears. And if your doctor calls you to do it again, do it, Make sure you are fine and prevent all the bad things that could happen, like cervical cancer." She said she was nervous but also shared that she received a lot of support from her friends and family. "Being a woman is not easy and is definitely a scary thing. I know I am going to be fine. It is just scary."
Read: Oncologist Reveals 5 Subtle Cervical Cancer Signs That You May Miss
What Is Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer develops in a women's cervix (uterus opening) due to abnormal cell growth, primarily caused by persistent HPV infection, a common infection that's passed through sexual contact.
When exposed to HPV, the body's immune system typically prevents the virus from causing damage however, in a small percentage of people, the virus can survive for years and pave the way for some cervical cells to become cancerous.
Treatment involves surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, with early detection significantly improving outcomes, though it remains a major cancer in low-income countries. Cervical cancer can also be prevented through vaccination and regular screening (Pap/HPV tests).
Dr Ninad Katdare told News18: "In its early stages, it is often more of a whisper than a shout. As a cancer surgeon who has treated hundreds of women with gynaecological cancers, I can say with confidence that recognizing these subtle cues can lead to earlier diagnosis and significantly better outcomes."
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

