- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
Invasive Meningococcal Disease Confirmed In Maldives; What Are The Symptoms Of This Bacterial Infection?
Credits: Health and me
Health authorities in the Maldives have confirmed a case of invasive meningococcal disease, triggering immediate precautionary measures to prevent further spread and protect public health. With the Maldives Health Protection Agency's (HPA) announcement of a confirmed case of invasive meningococcal disease (IMD) on the night of June 7, prompt public health response was initiated. Contact tracing, prophylactic treatment, and increased surveillance are now in motion. The case signifies the need for heightened global awareness of the uncommon—but potentially fatal—bacterial infection.
Whereas meningococcal disease in the Maldives is rare and usually the result of travel outside the country, the case here is particularly concerning since it indicates local transmission. In the past, the archipelago has experienced only isolated cases and these have usually been traced to pilgrims who have come back from Hajj pilgrimages in Saudi Arabia.
Invasive meningococcal disease stems from the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis, a Gram-negative diplococcus that typically resides harmlessly in the nose and throat of up to 10% of people. Occasionally, it breaches the body’s defenses, causing:
Meningococcal meningitis – inflammation of the brain and spinal cord linings.
Meningococcal septicemia (meningococcemia) – a bloodstream infection that damages blood vessels and can result in hemorrhaging in skin and organs.
If not treated immediately, IMD is lethal within hours—a stark fact testified to by CDC information on fatality rates of 10–15%, with treatment, jumping to 18% in a few U.S. epidemics.
How Does Meningococcal Disease Spread?
Meningococcal bacteria are transmitted through respiratory droplets—by coughing, sneezing, kissing, or sharing food and drinks. The greatest risk occurs between people with extended, close contact, such as family members and sexual partners. Prolonged riding in enclosed vehicles—buses, planes—with the infected person also increases risk greatly.
CDC states that infants below one year, adolescents 16–23 years old, immunocompromised patients, and residents of communal environments are at greatest risk.
Early Symptoms of Meningococcal Disease
IMD at first presents a nonspecific viral illness but can worsen suddenly. Parents and caregivers must be aware of the following signs:
- Fever, headache, stiff neck – classic symptoms of meningitis
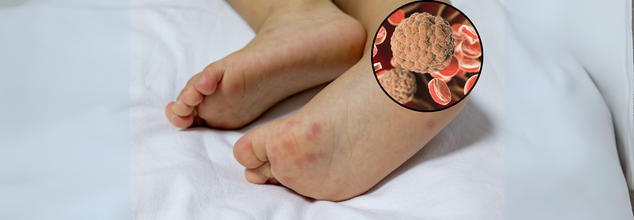
- Red spots or rash – typically seen as pinpricks or larger bruise-like patches, a sign of blood vessel involvement
- Nausea, vomiting, photophobia (light sensitivity)
- Confusion, lethargy, rapid breathing, seizures – signs of severe progression
- Neck stiffness and changed mental status, usually with fever
In the most severe cases, sepsis, exhaustion, coldness of extremities, and coma may ensue—all necessitating immediate medical intervention. Shockingly, worsening can happen within 6–12 hours of the onset of symptoms .
The HPA, falling under the Ministry of Health, immediately initiated tracing and gave prophylactic antibiotics—usually rifampin, ciprofloxacin, or ceftriaxone—to high-risk contacts This is in line with CDC recommendations to prevent nasopharyngeal carriage and interrupt further spread.
Relaying precise definitions of "close contact," the HPA's reach encompasses family members, travel mates, and those exposed to respiratory secretions of the patient.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Meningococcal Disease
The gold-standard diagnosis for invasive meningococcal disease involves a combination of blood cultures and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis obtained through lumbar puncture. However, in cases where increased intracranial pressure is suspected, performing a lumbar puncture may need to be delayed to avoid complications. Additionally, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing plays a crucial role in rapidly identifying the infection, particularly when prior antibiotic treatment may interfere with traditional culture results.
IMD survivors develop severe complications: hearing loss, neurological injury, kidney failure, or limb amputation by necrosis. Unfortunately, natural infection does not offer absolute lifelong immunity; recurrence, although infrequent, can occur, warranting immune deficiency assessments.
Is the Disease Preventable by Vaccination?
Vaccination is the best protection. Vaccines protect against several serogroups (A, B, C, W, Y, X) and are universally advised—particularly among adolescents, travelers, and those at risk.
In Maldives, HPA advises unvaccinated persons—particularly Hajj pilgrims who departed within 14 days of booster doses—to see health practitioners promptly.
Fox News Anchor John Roberts Diagnosed with Malaria – How To Identify The First Symptom

(Credit- FOX News Channel)
John Roberts, a 68-year-old anchor for Fox News, is currently in the hospital battling a serious case of malaria. Roberts shared with PEOPLE magazine that he was diagnosed on Monday, August 25. He believes he contracted the illness during a vacation in Indonesia.
According to the Center of Disease Control and Prevention, US reports 2000 malaria cases a year with an average of 7 deaths per year since 2007-2022. What’s surprising is that 95% of these cases happen to be people who did not take malaria prevention medication.
What Symptoms Did John Roberts Experience?
Roberts described his symptoms as starting about 10 days after he returned from his trip. He felt pain all over his body, as he explained “from head to toe” and experienced uncontrollable shivering while on air. Initially, he thought it was just the flu, but knew it was serious when blood tests showed his white blood cells and platelets were very low.
Upon being officially diagnosed in the emergency room, Roberts admitted he was "a little scared," recognizing that malaria can be deadly if not treated. He said he has never felt this sick in his life.
What Is The First Symptom Of Malaria?
Stanford University explains that In the beginning, malaria can feel a lot like the flu. Symptoms might not seem unique, as they are similar to many other common illnesses. The most typical symptoms of malaria include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Headache
- Sweating
- Fatigue or feeling very tired
- Nausea and vomiting
- Body aches
- A general feeling of being sick
How severe these symptoms are can depend on your age, overall health, and the type of malaria parasite you have. In some cases, people who have been infected many times might have few or even no symptoms at all.
While most people recover, in rare cases, malaria can become very serious. It can lead to problems with the brain or spinal cord, seizures, or a loss of consciousness. The most severe types of malaria can even be deadly.
How Long Does It Take For Malaria Symptoms To Appear?
Symptoms usually show up anywhere from 7 to 30 days after you are infected. However, for some types of malaria, you might not feel sick for many months, and in rare cases, up to a year after being exposed. The time it takes for symptoms to appear can also be longer if you have taken medicine to prevent the infection. Additionally, if you have had malaria before, your symptoms might be less severe.
How Was John Roberts Treated?
Roberts has been treated with IV artesunate, a powerful medication used for severe cases of malaria. He describes his recovery as a series of "up and down" days, with his body temperature swinging from shivering cold to sweating.
Roberts is the only malaria patient in his hospital, and one of his doctors said it was the first case he had ever seen. A person’s malaria treatment depends on a few things like,
- Whether it's for prevention or to treat an active infection.
- Your health, age, and if you are pregnant.
- How sick you are.
- If the malaria parasite is resistant to certain medicines.
- The possible side effects of the medicine.
- People who need special care include pregnant women, children, the elderly, and those with other health problems.
How Is Severe Malaria Treated?
In very serious cases of malaria, a special procedure called an exchange blood transfusion may be used. This is the fastest way to get rid of the parasites. During this procedure, blood is taken from you while you receive new blood from a donor, along with malaria medicine.
If you are traveling to a remote area without easy access to medical care, your doctor might give you medicine to carry with you. You will get instructions on how to use it if you start showing malaria symptoms. This is a temporary solution, and you should still get to a doctor as soon as possible, ideally within 24 hours.
UK Children To Get Chickenpox Vaccine On NHS: Why It Is A Lifesaver Vaccine
Credits: Canva
From January next year, parents in England and Wales will have one less health worry on their checklist. The NHS is rolling out the chickenpox vaccine for free to all young children. Administered in two doses at 12 and 18 months, the jab will be paired with the existing MMR vaccine that already shields kids from measles, mumps and rubella.
The move also comes with a catch-up programme for slightly older children, ensuring no one misses out. It is a win not just for health but also for households and the economy, with chickenpox costing the UK around £24 million annually in lost workdays and productivity.
What is Chickenpox?
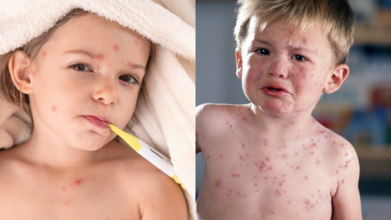
The virus behind it is the varicella-zoster, which spreads faster than playground gossip. It triggers an itchy rash, dotted with small blisters and often accompanied by fever, fatigue and general misery.
The rash, however, shows up 10 to 21 days after exposure and lasts about a week. And you can spread the virus even before the rash is evident and until every blister has dried out. That means kids can be carriers long before anyone realises.
Why the Vaccine is a Game-Changer
For most children, chickenpox is unpleasant but manageable. But in some cases, the virus does not play fair. Pregnant women, very young babies and adults are especially vulnerable. Complications can include pneumonia, encephalitis (brain swelling), bacterial infections, and in rare instances, even stroke. It sounds dramatic because it can be.
And let us not forget the dreaded shingles. Once you have had chickenpox, the virus hibernates in your nerve cells, waiting for years to reactivate. When it does, it emerges as shingles, a painful and sometimes long-lasting condition that haunts adults. By vaccinating children, the NHS is not just preventing itchy rashes; it is reducing future risks of shingles too.
Symptoms Worth Spotting
Chickenpox has a very distinct three stages:
- Red bumps called papules make their debut.
- Those bumps turn into fluid-filled blisters, which eventually burst.
- Scabs form and healing begins.
To complicate matters, new spots appear over several days, so your child may look like they are juggling different skin stages at once.
Who is at Risk?
Anyone who has not had chickenpox or the vaccine is fair game. The risk is higher for people working in schools, nurseries or any place where germs travel in packs. The virus can spread through direct contact with the rash or even via droplets from a cough or sneeze.
But if you have been vaccinated and still catch chickenpox, the symptoms are typically much milder: fewer blisters, less fever and a quicker recovery.
Complications That Keep Doctors on Their Toes
While chickenpox is usually mild, the potential complications are no joke. These include:
- Infected skin or bloodstream
- Dehydration
- Pneumonia
- Encephalitis
- Toxic shock syndrome
- Reye’s syndrome (when children take aspirin during infection)
Such risks say why the vaccine is not just a convenience but a lifesaver.
Tackling Falling Vaccination Rates
The chickenpox announcement also comes at a crucial time. Uptake of existing childhood vaccines in England is slipping. In 2024/25, none hit the 95 per cent target, with MMR uptake hovering at 91.9 per cent among five-year-olds—the lowest since 2010/11. Adding chickenpox protection to the routine schedule could help remind parents of the importance of immunisation.
Why Parents Should Welcome This Move
Chickenpox may sound like a rite of passage, but in reality, it is an unpredictable infection that can disrupt households, put vulnerable people at risk and occasionally turn dangerous. With the vaccine, parents can skip the sleepless nights of itch relief lotions, the endless laundry of pus-stained sheets and the nervous waiting for complications to pass.
Shingles Vaccines Now Available For 18+ People With Weak Immune Systems - How Long Does The Vaccine Last?
(Credit-Canva)
Starting on September 1, 2025, the NHS in the UK is expanding who can get the shingles vaccine. The program now includes all adults aged 18 and older who have a very weak immune system. This change aims to protect about 300,000 more people from the painful and serious problems shingles can cause.
This decision came from a group of experts called the Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (JCVI). They found that younger adults with weak immune systems face a similar risk of getting so sick from shingles that they need to go to the hospital, just like older adults who were already getting the vaccine.
Dr. Amanda Doyle from NHS England says the vaccine is safe and works well. She explains that it greatly lowers the chance of getting shingles and becoming seriously ill. She encourages anyone who is now eligible to get vaccinated as soon as possible, even if they have had shingles before, since you can get it more than once.
Who Is Now Eligible for Shingles Vaccine?
Shingles is caused by the same virus as chickenpox, and it can cause a very painful rash. For most people, it's not a serious illness, but it can lead to problems like long-lasting nerve pain, eye issues, or even more serious infections like pneumonia.
The new group of people who can get the vaccine includes those with conditions like leukemia or lymphoma, or those going through chemotherapy. These individuals are at a much higher risk of getting very sick if they get shingles. The NHS will start contacting eligible patients soon, but you can also book an appointment through your doctor's office.
How Long Does Shingles Vaccine Work?
According to the Harvard Health, the Center of Disease Control and Prevention recommends that adults aged 50 and older get two doses of the Shingrix vaccine to prevent shingles. A 2024 study by Annals of Internal Medicine, looked at how well this vaccine works over time, and the results are very promising.
The study, which included almost two million people, found that the two-dose vaccine was still 73% effective at preventing shingles four years later. This shows that the vaccine provides long-lasting protection.
However, the study also highlighted the importance of getting both doses. People who only received one dose saw their protection drop quickly after the first year, with the vaccine being only 52% effective after three years. This makes it clear why getting the second shot is so important.
What If You're Late for the Second Shot?
If you miss the recommended two-to-six-month window for your second dose, don't worry—it's not too late. The study found that delaying the second dose beyond six months did not make the vaccine less effective. You should get your second dose as soon as you can to ensure you have full, long-lasting protection.
The study also found that the vaccine worked slightly better for people who got their shots before age 65 compared to those who were vaccinated later in life.
When Do You Need Shingles Shot?
Different countries have different guidelines, while CDC recommends people above 50 get vaccinated as well as adults aged 19 and older who have a weakened immune system should also get two doses to protect themselves.
In the UK, the shingles vaccine, called Shingrix, was previously given to people aged 65 to 79 and those with a very weak immune system who were 50 or older. However, following advice from a group of experts, this is changing.
Starting next week, all adults aged 18 and over with a very weak immune system will be able to get the vaccine. This is because the experts found that these younger adults face the same high risk of severe illness or long-lasting nerve pain from shingles as the groups who were already eligible.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

