- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Not Just COVID-19, Or Hepatitis B, Kennedy's New Vaccine Committee Plans To Change Chickenpox, Measles, Mumps And Rubella Shots

RF Kennedy Jr, Health Secretary, Source: AP
The future of childhood vaccinations in the U.S. is suddenly in question. Health Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr.’s newly restructured vaccine advisory committee is set to vote this week in Atlanta on whether to alter long-standing recommendations for several critical vaccines, including shots against chickenpox, measles, mumps, rubella, hepatitis B, and COVID-19.
The committee, known as the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), plays a powerful role: its recommendations guide pediatricians nationwide and determine which shots are covered by the government-funded Vaccines for Children (VFC) program, a safety net for low-income families.
While some experts say the agenda looks like a routine review, others worry it could open the door to unnecessary confusion, weaken trust, and reduce access to vaccines that have long protected children from serious disease.
Also Read: Unique Symptoms Of Covid In 2025 And How Long Infection Now Last
Chickenpox and the MMRV Vaccine Debate
Before the chickenpox vaccine was licensed in 1995, nearly every American child contracted the disease. While often dismissed as a rite of passage with itchy rashes and mild fevers, chickenpox could also lead to severe complications like pneumonia, skin infections, brain swelling, and in rare cases, death. The virus, varicella, also lingers in the body and can resurface decades later as shingles, a painful nerve condition.
The introduction of the vaccine dramatically reduced cases and hospitalizations. In 2005, regulators approved a combination shot called MMRV, which bundled measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella vaccines into a single injection. Initially, health officials recommended the combo as the preferred option for the first dose in toddlers.
However, studies soon revealed a catch: children who received the MMRV shot were more likely to develop fevers, rashes, and in rare instances, febrile seizures compared with those who got separate MMR and varicella injections.
In response, the ACIP in 2009 updated its guidance, recommending separate shots for the first dose (typically given between ages 12–15 months) but allowing the combo shot for the second dose in preschool years.
Today, most pediatricians follow that approach. Still, the evidence hasn’t changed in over a decade. That raises eyebrows about why the Kennedy-led committee is reopening the debate now.
Public health experts caution that limiting the combined shot could make vaccination less convenient for families and potentially reduce uptake. Pediatric advisors warn that even small barriers, like two shots instead of one, can mean some kids fall behind.
Why Measles, Mumps, and Rubella Still Matter
While much of the attention is on chickenpox, the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine remains equally critical. Each of these viruses was once a common threat in childhood:
- Measles can lead to pneumonia, brain swelling, and death.
- Mumps can cause meningitis and, in boys, permanent infertility.
- Rubella is especially dangerous for pregnant women, sometimes causing miscarriage or severe birth defects.
Before widespread vaccination began in the 1970s, hundreds of thousands of children in the U.S. contracted these diseases every year. Outbreaks have returned in recent years when vaccination rates dip, underscoring the importance of reliable and consistent recommendations.
Revisiting guidance without new evidence, experts say, risks fueling skepticism among parents already facing a flood of misinformation online.
The COVID-19 Vaccine Question
The COVID-19 shots are also on the table. Typically, ACIP renews recommendations annually for vaccines against respiratory viruses such as flu. But this June, Kennedy’s panel endorsed flu vaccines while staying silent on COVID-19.
Also Read: US Health Officials To Examine Covid Vaccine Effects In Pregnant Women And Kids
That silence matters. Earlier, Kennedy had already removed COVID-19 shots from CDC recommendations for healthy children and pregnant women, sparking lawsuits from pediatric groups who said the move endangered kids’ health.
The FDA recently narrowed the authorization of updated COVID-19 vaccines, limiting use for certain younger groups. If ACIP mirrors that without clarification, millions of children could lose federally funded access through the Vaccines for Children program. Experts warn this could leave families confused, especially since COVID-19 formulations update yearly, much like flu shots.
Revisiting Hepatitis B Vaccinations
Hepatitis B presents a different set of challenges. The virus can cause chronic liver infection, cirrhosis, and cancer. While adults often acquire it through sexual contact or sharing needles, newborns face the highest lifelong risk if exposed at birth.
Since 2005, U.S. guidance has recommended that infants receive their first hepatitis B shot within 24 hours of birth. This approach significantly reduced cases of mother-to-child transmission, which often slipped through maternal screening programs. Studies show the newborn shot is safe and highly effective, preventing 85–95% of chronic infections.
Yet Kennedy’s committee has floated the idea of revisiting this recommendation, though experts note there is no new evidence suggesting safety concerns. Critics argue that questioning the birth dose now could reverse decades of progress.
Why the Stakes Are So High
Beyond the science, the politics surrounding these deliberations are unusual. Kennedy, once one of the nation’s most vocal vaccine skeptics, dismissed the 17-member ACIP earlier this year and replaced it with a panel that includes several anti-vaccine voices.
Historically, ACIP’s recommendations are based on careful review by subcommittees made up of pediatricians, infectious disease experts, pharmacists, and public health officials. Those subgroups sift through peer-reviewed studies, track outbreaks, and balance risks against benefits. But this time, critics say the process appears less about science and more about ideology.
Even if the committee doesn’t overturn long-standing guidance, simply reopening settled debates may erode confidence. Parents who hear that vaccines are “under review” might delay or decline shots, leaving children vulnerable.
Perhaps most worrisome: a restrictive vote could block coverage of these vaccines under the Vaccines for Children program, which supplies nearly half of all childhood shots in the U.S. Without it, low-income families could lose access, widening gaps in protection.
What Lies Ahead?
The stakes of this week’s ACIP votes go far beyond the meeting room in Atlanta. At issue is not just whether a child gets one shot or two, but whether the nation maintains decades of progress against diseases once considered inevitable.
Chickenpox, measles, mumps, rubella, hepatitis B, and COVID-19 vaccines have all proven their worth in protecting children from dangerous, sometimes deadly illnesses. Experts say undermining trust or restricting access now could reopen the door to outbreaks that public health worked so hard to shut.
Measles In DC: Health Officials Warn of Possible Exposure After National March for Life Events
Credits: Canva
Health officials in Washington, D.C. are warning that confirmed cases of measles may have spread during this year’s National March for Life rally and related events held in the capital late January. The annual anti-abortion gathering drew thousands of people to the National Mall and surrounding areas, raising concerns about potential large-scale exposure.
The D.C. Department of Health said it is actively working to identify individuals who may be at risk after learning that several people who later tested positive for measles were present in the city while contagious.
“DC Health was notified of multiple confirmed cases of measles whose carriers visited multiple locations in the District while contagious,” the agency said in a statement on Sunday. Officials are now contacting people who were at those locations during the exposure window.
Measles In DC: Transit Hubs and Campuses Among Exposure Sites
According to DC Health, potential exposure sites span a wide range of busy public locations between January 21 and February 2. These include Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport, Union Station, an Amtrak Northeast Regional train, and multiple stops within the city’s Metro subway system.
Health officials also flagged visits to the Basilica of the National Shrine of the Immaculate Conception and Catholic University as part of the exposure timeline. Given the volume of visitors moving through these spaces daily, authorities say the risk of wider spread cannot be ruled out.
Measles In DC: Hospital Issues Public Health Notice
Children’s National Hospital has also issued a public health notice after a confirmed measles patient from Virginia visited its Emergency Department on February 2 while infectious. The hospital said it is coordinating with public health authorities to identify and notify anyone who may have been exposed during that time.
Measles is highly contagious and can remain airborne for up to two hours after an infected person leaves an area, making hospital settings particularly vulnerable.
Measles In DC: Surge Across the United States
The situation in Washington comes as the United States faces its largest measles outbreak in decades. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 733 confirmed cases have been reported across 20 states so far this year. The CDC says about 95 percent of those cases involve people who were unvaccinated or whose vaccination status is unknown.
South Carolina remains one of the hardest-hit states. Its outbreak began in October 2025 and has now surpassed earlier outbreaks elsewhere in the country. State health officials reported 44 new cases on Friday, bringing the total to 920. While the pace of new cases has slowed slightly, officials continue to warn of possible exposure at public places such as a Target store in Taylors and a Social Security Administration office in Spartanburg, where the outbreak is centered.
Measles In DC: Vaccination Urged Amid Global Concern
Speaking on CNN’s State of the Union, Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Administrator Mehmet Oz urged Americans to get vaccinated against measles. While recent federal policy changes have rolled back recommendations for some vaccines, guidance on measles immunization remains unchanged.
International health authorities are also watching closely. The World Health Organization’s Pan American Health Organization has invited U.S. officials to a meeting in April to review the country’s measles elimination status, which is now under threat.
D.C. health officials are urging anyone who may have been exposed and is not fully vaccinated, pregnant, or immunocompromised to contact a healthcare provider immediately.
Epstein Files: A Chat With Urologist Shows Stendra Was Prescribed To Jeffery Epstein; Why Did This Name Come Up?

Credits: DOJ, Canva, AI-generated and modified
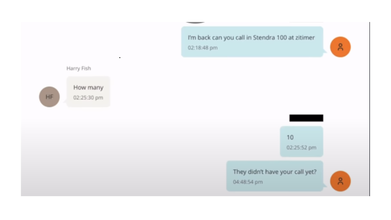
The latest release by Department of Justice (DOJ) on Epstein Files show a chat between the late sex offender and financer Jeffery Epstein and Harry Fisch, a urologist. The message from Epstein reads: "I am back can you call in Stendra 100 at zitimer".
Epstein Files: What Is Stendra Used For?
Stendra, which is a common brand name for avanafil, is a commonly used medicine for erectile dysfunction. This is a condition where a man has trouble getting or keeping an erection. It can also be used for other conditions as determined by a healthcare provider.
It works by blocking an enzyme in the body called PDE5, which helps relax certain blood vessels. This also increases blood flow to the penis when aroused, and makes it easier to get and keep an erection.
Epstein Files: Did Jeffery Epstein Have An STI?
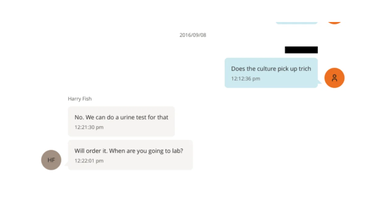
Another chat thread between the two reveal that Epstein was worried if he had caught 'trich' or trichomoniasis. The chat from Epstein reads: "Does the culture pick up trich", to this Harry replies: "No. We can do a urine test for that".
Trichomoniasis or trich is a common, curable sexually transmitted infection in men caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. While many men are asymptomatic, they can still transmit the infection.
Common symptoms of trich are:
- Burning after urination
- Burning after ejaculation
- Itching
- Penile discharge
In another screenshot of the chat, Harry responded that he had ordered a Trich urine test and the test was negative on 9/6/16.
However, based of the DOJ documents and report by The Times, a blood test in 2016 reported Epstein had tested positive for gonococcus (GC), or gonorrhea.
Epstein Files: What More Do These Documents Reveal About His Health?
Epstein had 'very low' testosterone levels, and appeared to have cryogenically frozen his sperm, reported The Times, based on the medical records released by DOJ.
A urology test also showed that his testosterone levels were well-below normal levels in 2016. On this, Epstein noted that it had been the "same for ten years".
His reported levels ranged between 65 and 150 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL), far below the normal range of about 350 to 1,000 ng/dL, and warrant prompt medical consultation to identify the underlying cause, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
In a 3am email dated April 24, 2015, Epstein, who was 62 at the time, wrote to one of his doctors, Dr Bruce Moskowitz: “As you can see from the time stamp my sleep pattern is not wonderful. I am hesitant to start a regimen of hormones. my low testosterone has been there for 15 years. mechanic view is that it has caught up to me?”
Among the several doctors he consulted, one advised Epstein to use testosterone replacement therapy along with Clomid, a drug that blocks estrogen receptors in the brain and stimulates the body to produce more testosterone. In a 2016 email to Dr Peter Attia, Epstein said he had stopped taking Clomid, calling it a “giant mistake.” “Stopped the clomid the water retention and fat around the waist made it as if i was pregnant,” he wrote.
California Mushroom Poisoning: 4 Dead, 3 Receive Liver Transplant

Credits: Canva
California mushrooms poisoning has led to four deaths and three people who required liver transplant. This happened after people consumed the death cap mushroom that is proliferating in California following a rainy winter.
The California Department of Public Health has urged people to avoid mushroom foraging altogether as death cap mushrooms could easily be confused with the safe and edible ones.
California Mushroom Poisoning: How Many Cases So Far?
Since November 18, 2025, there have been more than three dozens cases of death cap poisoning. This included three people getting liver transplants, confirmed the health department. Among the cases, four were also reported to be dead. Some of whom sought medical attention suffered from rapidly evolving acute liver injury and liver failure. Other patients were required to be admitted in intensive care units. The patients age ranged from 19 months to 67 years old.
California Mushroom Poisoning: What Is The Death Cap Mushroom?
The death cap mushroom is the most poisonous mushrooms in the world. It is part of a small group of mushrooms that contain amatoxins, which are highly potent compounds and cause 90% of fatal mushroom poisoning globally. They could be found in city parks, forests, and often under oak trees.
Dr Craig Smollin, medical director for the San Francisco Division of the California Poison Control System tells PBS News that in a year, there are between two to five death cap poisonings.
"The main thing this year is just the magnitude, the number of people ingesting this mushroom," Smollin said. "Having almost 40 is very unusual."
With warm temperature along with early rains, a 'super bloom' of death caps in California could be seen.
Experts point out that eating even a small amount could be fatal. The confusing part is that the color is usually not a reliable way to detect toxicity. Furthermore, whether the mushroom is consumed raw, dried or cooked, does not make a difference.
California Mushroom Poisoning: A Case Study
Speaking to San Francisco Chronicle, Laura Marcelino, 36, said that her family in the Northern California town of Salinas gathered mushrooms that looks like the ones she and her husband used to forage in their native Oaxaca. "We thought it was safe".
However, the next day, her husband felt dizzy, but Marcelino was fine. They ate the mushrooms again, heating them up in a soup with tortillas. Her kids do not like mushrooms, so they were safe, as they did not have any. The next day, she and her husband became ill with vomiting, and stayed home form work.
Marcelino spent five days in a hospital, while her husband underwent a liver transplant.
In an email response to The Associated Press, the US Poison Centers said that the cases of mushroom exposure have increased, and not just the death cap. This increase was noted from September through January by 40% from the same period in the previous year. Exposure do not always result in illness or poisoning.
California Mushroom Poisoning: Common Symptoms
- Cramping
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
Experts point out that early symptoms could go away within a day, but serious to fatal liver damage can still develop within 2 to 3 days
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

