- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
Recent Report Reveals The Dire Condition Of Indian Jails, Inmates Not Given Proper Healthcare

(L to R) Central Prison in Viyyur, Kerala; Tihar Jail, Delhi; and District prison in Mandya district, Karnataka (Wikimedia Commons and Central Jail, Government of NCT of Delhi)
Jail time, like everyone knows, is of course not an ideal situation to be in. However, like all, even the inmates are to be granted their basic rights, which include medical facilities. However, as per the India Justice Report 2025, inmates in Indian jails cannot avail these facilities. Indian jails are overcrowded, and they lack medical and mental health professionals.
Why Are The Numbers Concerning?
The report reveals that the national average occupancy rate of Indian jails are more than 131%. This means that there is of course overcrowding, leading to hygiene concerns, which eventually puts health at risk. The report also noted that India's prison inmate population will reach 6.8 lakh by 2030, while the capacity is only likely to grow to accommodate 5.15 lakh inmates.
This does not stop at space, but to health staff too. For the entire nation's prisoners, there are only 25 psychologists. The report has clearly noted that mental illness cases have risen from 4,470 in 2012 to 9,084 in 2022. On the contrary, the vacancy for medical officers are at 43%.
The report titled the State of Public Health in India's Prison: India Justice Report 2025 - Finding on Gaps in Staffing & Medical Health Care also threw light on the model prison manual, 2016. This sets the benchmark for the prison to doctor ratio, which must be 300 prisoners to 1 doctor. However, the report notes, the national average "far exceeds that, standing at 775 prisoners per doctor."
There is also non-availability of health data on prisoners who enter jail with a disability or those who acquire disability during their time in the prison.
ALSO READ: BeerBiceps Opens Up On Latent Row's Impact On His Mental Health
How Are Inmates Health Impacted?
As aforementioned, overcrowding is also a source of communicable disease. Between 2012 to 2022, there has been a concerning upward shift in prison population. The report reads: "The total number of people incarcerated has gone up from 3.8 lakh to 5.7 lakh; national occupancy rates have spiked from 112% to 131%. Overall, the 27% increase in prison housing capacity between 2012 and 2022 (from 3.4 lakh to 4.3 lakh) has not kept pace with need. Levels of overcrowding have also escalated. For instance, in 2012, Maharashtra averaged a 99% occupancy rate but in 2022, this had increased to 161%,’’
As per the 2023 Lancet Public Health studies, incidence of TB in Indian prisons is 1,076 cases per 100,000 persons in prisons. One of the main reasons is overcrowding. Furthermore, another study published in the International Journal of Infectious Diseases in 2017, notes that diagnostic and treatment services for TB were available in 18% and 54% of prisons respectively. The study noted: "Only half of the prisons screened inmates for TB on entry, while nearly 60% practised periodic screening of inmates."
The study also noted: "Prisons are known to be a high risk environment for tuberculosis (TB) due to overcrowding, low levels of nutrition, poor infection control and lack of accessible healthcare services."
Another report from 2023, published in the Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine, titled Health Status of the Prisoners in a Central Jail of South India, noted "Health care in prisons is one of the neglected health areas in our country."
The study found that 9.6% of the inmates from that particular jail suffered from acute upper respiratory tract infections, 5% from acute lower respiratory tract infections and 18% had ascariasis. "Diseases of musculoskeletal system and connective tissue contributed to 26 (8.7%) of inmates. A total of 252 (84%) prisoners had anemia. In sociodemographic profile, it was found that rural people, unmarried, illiterates, lower socioeconomic status people were more likely to have committed the crime resulting in the conviction for life," the study read.
Another 2023 study published in the International Journal of Conflict and Violence, titled The State of Prisons in India During Covid-19: The Impact on Incarcerated Prisons, noted: "The Coronavirus created an alarming situation in Indian prisons, where overcrowding exacerbated the problems."
The study quoted The Commonwealth Human Rights Initiative (CHRI) report that in the second wave of the pandemic starting 1 March 2021, there were a total of 5,960 infected prisoners and 646 infected prison staff,
with 28 Covid-related deaths of prisoner and six deaths of prison staff. A total of 177,071 prisoners were vaccinated with the first dose and 85,443 had been given the second dose as on September 2021.
"Overcrowding and lack of sanitation and health facilities acted as catalysts in the spread of the virus in prisons," the study pointed out.
Mental Health Of Inmates Stay Ignored
The India Justice Report also pointed out that as of 2022, no State or Union Territory met the benchmark of one psychologist per 500 inmates. Only 69 sanctioned posts for psychologists and psychiatrists are there to cater across India's 1,330 prisons and 5.7 lakh inmates. Not even half of these positions were filled.
Valay Singh, who is the lead author of the India Justice Report said, "The data records the presence of only 25 or one for every 22,929 prisoners. Twenty-five States/ Union Territories make no provision for a psychologist or psychiatrist within their cohort of correctional staff."
Madonna Reveals Sepsis Ordeal, Says She Was Unconscious For Four Days- All You Need To Know About The Infection

Credits: Canva
Madonna has opened up about her frightening 2023 health scare while she was on tour. In a recent conversation with Jay Shetty on his On Purpose podcast, aired Monday, Sept. 29, the 67-year-old pop icon revealed how she battled sepsis, spending four days unconscious in the hospital after what doctors called a “serious bacterial infection.” She also shared how her faith and practice of Kabbalah played a role in her recovery.
Madonna’s Sepsis Ordeal
The singer was first hospitalized in June 2023, later telling fans at a Brooklyn show that December that she had been placed in an induced coma for 48 hours. Speaking with Shetty, she recalled how suddenly her condition escalated: “I was rehearsing for my tour, and I got a bacterial infection. One minute I was alive and dancing around, and the next I was in the ICU, waking up after being unconscious for four days.”
Reflecting on the experience, Madonna noted, “There’s no way we’re going to escape suffering. Even if you grow up with wealth and privilege, challenges and pain come to you in different ways.”
What Is Sepsis?
Sepsis occurs when the body has an extreme reaction to an infection. Instead of fighting only the infection, the immune response spirals, damaging healthy tissues and organs. In severe cases, sepsis can progress to septic shock, where blood pressure drops dangerously low and vital organs like the lungs, kidneys, and liver can fail. If untreated, it can be fatal, according to the Mayo Clinic.
Sepsis: Signs and Symptoms
Warning signs of sepsis can include:
- Sudden confusion or altered mental state
- Rapid, shallow breathing
- Unexplained sweating
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Chills and shivering
Because these symptoms are often vague and vary from person to person, sepsis can be difficult to recognize, and it may present differently in children compared to adults.
Who Is Most at Risk?
While sepsis can affect anyone with an infection, injury, or underlying illness, certain groups face higher risk. According to the World Health Organization, these include:
- Older adults
- Pregnant or recently pregnant women
- Newborns
- Hospitalized or ICU patients
- People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV or cancer
- Individuals with chronic conditions like kidney disease or cirrhosis
Sepsis is a medical emergency, and early treatment is critical to improving survival and recovery. Even healthy individuals can go from feeling fine to critically ill in a matter of hours. Experts stress the importance of recognizing early warning signs and seeking immediate medical attention, as timely intervention can make the difference between life and death.
Selma Blair Opens Up on Living With Multiple Sclerosis in Remission; Here’s How MS Affects Your Body

Credits: Canva
The world first learned about Selma Blair’s multiple sclerosis (MS) diagnosis nearly seven years ago, but the chronic autoimmune condition has affected her for much of her life. The 52-year-old “Cruel Intentions” star traces early signs of the disease back to her childhood, though she says doctors ignored the warning signs for decades. As Blair shares her journey with MS, we explain what the condition is, its symptoms, and how it can impact the body.
Selma Blair Opens Up on Her Multiple Sclerosis Journey
Selma Blair recently spoke about the impact of MS, revealing how the disease once left her unable to walk or speak properly. On ‘This Morning’ show, she described the decades-long struggle with the condition, including being misdiagnosed for 30 years. Blair, known for roles in films like Cruel Intentions and Legally Blonde, and more recent projects such as American Crime Story, is now sharing her health story to encourage others to seek proper diagnosis and care.She first publicly revealed her diagnosis in 2018, later telling The Guardian that her doctors had advised her to keep it private to avoid losing work. During her first pregnancy, she felt unusually well, unaware that MS can enter remission, masking her symptoms. After giving birth, her symptoms returned, initially being mistaken for post-partum depression. An MRI, her first after years of asking, finally confirmed the diagnosis.
On the show, Blair reflected on how the experience has changed her, noting that while an MS diagnosis is daunting, it also offers opportunities to learn more about oneself. She urges anyone noticing similar symptoms to consult a doctor, as early detection can make a significant difference.
What Is Multiple Sclerosis?
Multiple sclerosis is a condition in which the protective covering around nerve fibers, called myelin, is damaged. This breakdown interferes with communication between the brain and the rest of the body. The disease can lead to numbness, weakness, vision changes, and difficulty walking, among other symptoms. According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders, MS occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks myelin, eventually causing lasting damage to the nerves.
How Multiple Sclerosis Affects the Body
MS affects the body by triggering the immune system to attack the myelin sheath surrounding nerve fibers in the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. When myelin is damaged, a process called demyelination, in which nerve signals are disrupted, leads to a wide range of possible symptoms, including vision issues, numbness, muscle weakness, balance problems, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties. Symptoms can vary greatly between individuals and may change over time, making MS unpredictable.
Life with MS can be challenging, but early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Anyone experiencing similar warning signs should speak with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
Clade 1 Mpox Virus Detected in US Wastewater; How High Is the Risk of Catching The Virus?
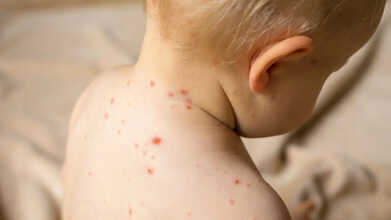
Credits: Canva
The Washington State Department of Health, along with the University of Washington, identified the virus in wastewater samples on September 24, 2025. Following this, the Tacoma-Pierce County Health Department began working closely with the CDC and state officials to expand testing. So far, no human cases have been reported in Pierce County, though six travel-related cases have been confirmed in other parts of the country.
How Does Mpox Spread?
Mpox can spread to humans either from animals or through direct human-to-human contact. There are two main types: Clade 1, which is more severe and linked to higher death rates, and Clade 2, which is typically milder. While Clade 2 circulates mostly in West Africa, Clade 1 is common in Central Africa.
Transmission of Mpox can occur through:
- Direct contact with rashes, scabs, or body fluids of an infected person
- Close physical interactions, including intimate or sexual contact
- Sharing contaminated items such as bedding, clothing, or towels
- Contact with infected animals through bites, scratches, or exposure to their fluids and waste
Common Symptoms of Mpox
According to the World Health Organization, the symptoms often begin with fever, body aches, joint pain, swollen lymph nodes, chills, and fatigue. Within a few days, a rash typically develops, which might start from your face before spreading to other areas, including the genitals and mouth. The rash may look like blisters, spots, or ulcers, sometimes numbering in the thousands.
How High Is the Risk Of Catching A Mpox Virus?
At present, experts believe the risk of widespread infection remains low. Mpox does not spread as easily as viruses like influenza or COVID-19. Close, prolonged contact with a symptomatic individual is usually required for transmission. While Clade 1 may have a higher potential for spread and severity, there is limited evidence so far on its transmissibility in community settings outside Africa.
Is There A Mpox Vaccine?
Yes, vaccines are available that can help prevent mpox and lessen the severity of symptoms. Each vaccine works a little differently, and who can receive them also varies.
The main vaccines in use are:
- MVA-BN (also called Imvamune, Imvanex, or Jynneos): This is usually given as a shot under the skin. In some cases, it may be given just between the skin layers, which allows a smaller “fractional dose” to be used while still being effective, as per World Health Organnization.
- LC16m8 (also known as LC16-KMB): This is given using a special bifurcated needle that lightly pricks the skin several times, delivering the vaccine just beneath the surface.
Both of these vaccines contain a weakened form of the vaccinia virus, which is related to smallpox. The weakened virus triggers the immune system to build protection against mpox.
In addition, according to World Health Organization, there is also ACAM2000, a vaccine currently licensed in the United States for mpox prevention. However, because it may cause side effects in certain people, its use is limited.
The finding of Clade 1 mpox in wastewater highlights why continued monitoring is so important. For now, health officials stress that awareness and precautions, especially avoiding close contact with anyone showing symptoms remain the best protection.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

