- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Scientists Behind Life-Changing Cystic Fibrosis Treatment That Extends Life By Decades Win Medical ‘Nobel’ Prize

Three scientists whose groundbreaking work redefined the future of cystic fibrosis (CF) care have been awarded one of the world’s most prestigious honors in medicine: the Lasker-DeBakey Clinical Medical Research Award. Often referred to as the “American Nobel,” the award recognizes contributions that radically improve human health. This year, it went to Dr. Michael Welsh of the University of Iowa, Paul Negulescu of Vertex Pharmaceuticals, and Jesús (Tito) González, now of Integro Theranostics.
Together, their decades of research led to the creation of Trikafta, a therapy that has extended the lifespan of cystic fibrosis patients by decades and fundamentally reshaped what it means to live with the disease.
When cystic fibrosis was first described in the 1930s, it was considered a fatal childhood condition. Patients rarely survived past elementary school. Even as late as the 2010s, before Trikafta’s approval in 2019, half of patients with CF died before the age of 40.
Today, the outlook is dramatically different. Children born with CF between 2020 and 2024 who have access to Trikafta now face a median survival age of 65 years — nearly indistinguishable from the general population.
As Dr. Eric Sorscher of Emory University explained in The New England Journal of Medicine, “Available projections suggest that health and longevity may increase further as modulators begin to be administered at younger ages.”
This shift marks one of the most profound turnarounds in modern medicine.
The Role of the CFTR Gene
Cystic fibrosis is caused by mutations in a single gene: CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator). The gene is critical for regulating the movement of ions across cell membranes, which in turn ensures proper water balance in tissues.
In healthy cells, CFTR forms channels that allow ions to flow freely. But in CF, the mutated gene produces faulty channels. The result is thick, sticky mucus that clogs the lungs and digestive system, fuels recurrent infections, and damages organs over time.
Dr. Michael Welsh, a pulmonologist and molecular biologist, helped illuminate the exact ways the most common CF mutation, delta-F508, disrupts cell function. He discovered two problems: the defective protein often gets “trapped” inside cells before reaching the surface, and even when it does reach the surface, it underperforms.
In a pivotal experiment, Welsh showed that simply lowering the temperature of cells allowed the trapped protein to move correctly. “That meant it was not totally broken,” he later recalled — a crucial realization that opened the door to correcting the defect.
Meanwhile, as a postdoctoral researcher in Nobel laureate Roger Tsien’s lab, Jesús (Tito) González developed a real-time system to track ion movement across membranes. Initially designed to study neurons, this tool proved invaluable for testing whether new drugs could restore CFTR function.
Negulescu and the Push to Find a Therapy
At Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Paul Negulescu helped drive the systematic search for compounds that could repair CFTR defects. Guided by Welsh’s molecular insights and González’s imaging system, the team screened thousands of molecules. The result was Trikafta, a triple-drug therapy that addressed the underlying cause of CF for most patients.
'Trikafta' Of Game-Changer in CF Treatment
Approved by the FDA in 2019, Trikafta combines three drugs — elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor — that work synergistically to help defective CFTR proteins fold correctly, reach the cell surface, and function effectively. The impact has been extraordinary. Since its introduction:
- Hospitalizations for lung infections have plummeted.
- The need for lung transplants has declined.
- Patients report stronger lung function, weight gain, and dramatically improved quality of life.
- For many families, the treatment has meant that milestones once unimaginable — graduating college, starting families, living into retirement — are now within reach.
Recognition at the “American Nobels”
The Lasker Awards, founded in 1945, celebrate biomedical achievements that shape the future of health. They are considered one of the highest honors in science, often predicting future Nobel Prizes.
The recognition of Welsh, González, and Negulescu underscores the profound impact of their work. The $250,000 prize, while symbolic compared to the billions Trikafta has generated, highlights the ethical and humanitarian dimension of their achievement: turning a once uniformly fatal disease into a chronic, manageable condition.
What CF Treatment Means for Medicine?
The CF breakthrough is not just about one disease. It represents a paradigm shift in genetic medicine. By targeting the root molecular defect rather than simply managing symptoms, Trikafta has become a model for other genetic conditions, from sickle cell disease to rare metabolic disorders.
It also illustrates the power of partnerships between academic researchers, biotech innovators, and patient foundations. The Cystic Fibrosis Foundation’s early investments in research were critical to advancing the work that ultimately led to Trikafta’s approval.
While Trikafta has transformed care in wealthy countries, challenges remain. The therapy is expensive — with an annual price tag of over $300,000 in the U.S. — putting it out of reach for many patients globally.
Furthermore, a subset of CF patients with rare genetic mutations still do not benefit from the drug, leaving an urgent need for alternative therapies. And as with all long-term treatments, researchers must continue monitoring for side effects and resistance.
Roughly 100,000 people worldwide live with cystic fibrosis. For decades, their lives were defined by daily medical regimens, frequent hospitalizations, and shortened lifespans. Today, thanks to the pioneering work of Welsh, González, and Negulescu, those same patients are looking toward futures filled with possibility.
Delhi Kidnappings Were False Fear Mongering, Officials Confirm

Days after it emerged that over 800 people had gone missing in Delhi during the first 27 days of 2026 and officials requested people to remain calm, Delhi Police has revealed this is false and such claims are being "pushed through paid promotion".
In a statement released on X today morning: "After following a few leads, we discovered that the hype around the surge in missing girls in Delhi is being pushed through paid promotion. Creating panic for monetary gains won't be tolerated, and we'll take strict action against such individuals."
Authorities across the capital claim that dispensing false information about life-altering information such as kidnappings and death through paid promotion can cause as well as amplify fear among the general public, which can massively ruin mental health and cause long-term damage to overall wellbeing.
Dr Kunal Bahrani, Chairman and Group Director, Neurology at Yatharth Hospitals, explained to Healthandme: "Incidents like this highlight how quickly fear can spread in today’s hyperconnected world and how deeply false news can impact mental wellbeing. When people are exposed to alarming information, especially involving safety and crime, the brain’s threat system switches on almost instantly. Stress hormones such as cortisol surge, increasing anxiety, restlessness, sleep disturbances and even physical symptoms like headaches or heart palpitations.
"Repeated exposure to frightening but unverified news can also condition the brain to remain in a constant state of alert, making individuals more irritable, emotionally overwhelmed and prone to panic. For children, elderly people and those already struggling with anxiety or depression, the psychological impact can be far more intense and long-lasting."
However, while many wonder how this form of promotion came into being, Reddit users are already pointing towards Rani Mukerji's Mardaani-3, a movie based on the kidnapping of minor girls as the source for this chaos.
How Does Fear Mongering Ruin Mental Wellbeing?
Fear-mongering severely impacts mental health by triggering chronic stress, anxiety, and depression, often overloading the brain’s threat response system (amygdala) and leading to long-term damage.
Over time, constant exposure to exaggerated, alarming narratives fuels irrational fears and cognitive distortions such as catastrophizing. This constant state of fear can also lead to avoidance behaviors, hopelessness, and physical symptoms like headaches, poor sleep and a weakened immune system.
Dr Neetu Tiwari, MD Psychiatry Senior Resident, NIIMS Medical College & Hospital also told Healthandme: "When things like this happen around us, it creates a sense of panic and fear amongst parents and children. Our brain usually reacts as if the danger is real. The body then becomes alert, our heart beats faster than it should, and our mind stays at tense. Even if the news is proven to be false, this fear that has set in often takes time to settle down.
"Now this in turn causes a lot of trouble. It makes people feel unsafe, so people avoid going out, they worry more about loved ones, or may also keep checking their phones repeatedly for updates. This behavior can lead to anxiety, panic, disturbed sleep, and constant overthinking. Even when the news is fake, fear travels very quickly. And once fear enters our mind, calming down takes time.
"This is why sharing unverified information can unknowingly harm others especially children as it can lead them in feeling scared even to go to school, or sleep alone, or even step outside. In fact in some children this may even cause nightmares or these children become unusually clingy to parents or guardians which further leads to problem in social development and confidence.
Dr. Rajiv Mehta, senior consultant psychologist, Sir Gangaram Hospital added: "The society at large is very gullible and anxiety prone, as we have seen the rise in mental illnesses. The people who are already anxious will get more anxious, the people who are not anxious will get anxious and that will increase the mental instability in the persons.
"And what they and parents are going to do is take a lot of precautions towards their young kids by not allowing them to go outside, to play with the children and go out of society buildings. They will be very fearful and when children will be home bound, then they will spend more time on screens or will have altercations with their parents.
"People should not resort to such kind of things only for the sake of their own materialistic monetary benefit. That is highly condemnable if it has occurred because of these kind of reasons that movie is going to release and they are sensationalizing these things."
Are The Delhi Kidnappings False?
Data obtained from Press Trust of India suggests that a total of 807 people went missing between January 1 and 15, with an average of 54 people going missing every day. Of these, 509 were women and girls, and 298 were men. Among the total reported missing, 191 were minors and 616 were adults.
In an official statement, the police said that, while the data was recorded, January 2026 saw a "decline in the number of missing persons reports when compared with the corresponding period of previous years."
Officials had previously further clarified that no organized gang or criminal network has been found involved in cases of missing or abducted children in Delhi so far.
"Recent public discourse has raised concerns about the welfare of children in Delhi. We appeal to the citizens not to fall prey to the rumours about the spurt in the cases of missing children.
While denying such claims, we also warn rumour mongers of strict legal action for creating unnecessary panic and fear by misrepresenting data.
The safety of every child is of paramount importance to Delhi Police.
"Delhi Police is committed to serve 24x7 and making all out efforts to trace all missing persons and reunite them with distraught family members, at the earliest," they said in a statement released yesterday.
Cheaper Copy Of Wegovy Pill By Hims & Hers Now Available For 49, Novo Nordisk Says It Will Take Legal Actions

Credits: iStock
Cheaper copy of Wegovy by Hims & Hers for $49 has drawn tensions, with Novo Nordisk now approaching to take legal actions. The pill by Novo Nordisk is sold for $149. In a statement, Novo said, "The action by Hims & Hers is illegal mass compounding that poses a significant risk to patient safety. Novo Nordisk confirmed that the company will take legal and regulatory actions to protect patients.
“Novo Nordisk will take legal and regulatory action to protect patients, our intellectual property and the integrity of the US gold-standard drug approval framework. This is another example of Hims & Hers’ historic behaviour of duping the American public with knock-off GLP-1 products, and the FDA has previously warned them about their deceptive advertising of GLP-1 knock-offs,” the statement said.
Read: Wegovy Pills Now Available At Your Pharmacies, Here's What To Know About Its Usage
Cheaper Copy Of Wegovy Pill: What Unveiled Afterwards?
After the cheaper copy of the pill was launched by Hims & Hers, shares of Novo Nordisk and rival Eli Lilly fell by 7%. Whereas, stock for Hims & Hers initially spiked after the announcement, but pared gains after Novo said that it would fight the rollout.
Hims & Hers was previously offering compounded semaglutide, the active ingredient in Novo Nordisk's popular weight loss drug Ozempic and Wegovy, in injectable format. The company has now extended to offer the oral version.
Cheaper Copy Of Wegovy Pill: How Much Does This Cost?
Hims & Hers said that the Wegovy copy pill cost $49 for the first month and $99 with a 5-month plan. While semaglutide's patent is protected in the US until 2032, however, Hims & Hers claim that the copies are 'personalized' and therefore legal.
“This compounded product uses a different formulation and delivery system than FDA-approved oral semaglutide,” Hims & Hers said. “This once-a-day pill has the same active ingredient as Wegovy and empowers providers to tailor treatment plans specifically for those who prefer to avoid needles or need smaller doses to help to balance side-effects,” it said.
Cheaper Copy of Wegovy Pill: Novo Nordisk Rejects Hims & Hers Claims
Novo Nordisk however, highlighted that it manufactures Wegovy pill by using SNAC technology. This technology helps in absorption when administered orally. Therefore, it is not clear how Hims & Hers copy formula could match that level of absorption.
Last year, Novo Nordisk and Hims & Hers partnered to offer weight loss jabs at a discounted price to telehealth company's customer. However, Novo Nordisk ended the collaboration just two months later, stating that Hims & Hers used 'deceptive' marketing that put patient safety at risk
Cheaper Copy of Wegovy Pill: Does Eli Lilly Have A Weight Loss Pill Yet?
While rival Eli Lilly does not have the weight loss pill yet, it is expected to launch orforglipron in the first half of this year. The pill is currently pending Food and Drug Administration approval.
Read: Eli Lilly Sends Weight-Loss Pill For Approval: Is Oral GLP-1 As Effective As The Injections?
“With the ... current legal backdrop, there is no reason why HIMS shouldn’t evaluate these launches for every subsequent weight loss product as the market continues to evolve,” Leerink analyst Michael Cherny said in a note to clients.
TrumpRx Is Live: How Is It Changing US Healthcare System? Explained

Credits: Wikimedia Commons and Canva
TrumpRx is live. President Donald Trump on Thursday announced the launch of TrumpRx, a direct-to-customer website that will lower prescription drug costs in the US.
As per the president, millions of Americans would save money through this platform. However, it is still unclear if all patients, especially those with insurance coverage will see more cost saving while using this website to buy their medicines.
TrumpRx is for people willing to pay cash and forgo insurance, which means people without or with limited coverage could benefit.
"You are going to save a fortune and this is also so good for overall health care," said Trump at the TrumpRx launching night on Thursday.
TrumpRx Is Live: How Does It Work?

TrumpRx does not sell drugs directly to American patients, rather acts as a central hub that points them to drugmakers who are offering discounts. For instance, Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk were already offering their popular weight loss drugs at hefty discounts, TrumpRx would further give them discount coupons and redirect them to their website.
This means if someone clicks on Eli Lilly's Zepbound offer, it will send them directly to the company's platform, where the person must submit prescription details.
TrumpRx Is Live: Which Drugs Are Now Cheaper?
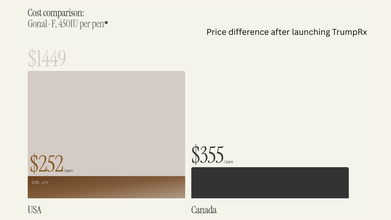
At launch, the site only featured medications from five companies, which are:
- AztraZeneca
- Lilly
- EMD Serono
- Novo Nordisk
- Pfizer
However, as per a White House fact sheet, TrumpRx will list drugs from other companies "in coming months".
TrumpRx marks the government’s latest attempt to curb soaring prescription drug prices in the US, which are on average two to three times higher than in other developed countries and can be up to 10 times costlier than in some nations, according to public policy think tank Rand Corp.
TrumpRx Is Live: Is It Really Beneficial?
TrumpRx “doesn’t appear to be a one-stop solution” to high drug costs for most Americans, said Juliette Cubanski, deputy director of the Program on Medicare Policy at KFF, a health policy research organization. While cash-pay options may offer better value for people without insurance, it remains unclear how many individuals would actually benefit from TrumpRx, she noted.
“If someone can already access a medication through their insurance with a relatively affordable copay, there isn’t much added advantage to using the TrumpRx website,” Cubanski said.
She also pointed out that insured consumers who purchase medicines through direct-to-consumer platforms may find those purchases do not count toward their insurance benefits, meaning they do not help meet deductibles or out-of-pocket maximums.
At the same time, Cubanski said TrumpRx could play a role in improving access to certain drugs at lower prices, especially medications that are not widely covered by insurance in the US, such as obesity treatments. Medicare is set to cover weight-loss drugs for the first time later this year under agreements struck by Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk with Trump, though many employers remain reluctant to include these medicines in their coverage.
However, she added that many other drugs expected to be offered on TrumpRx are already commonly covered by insurance, and several are also available as lower-cost generics from rival manufacturers.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

