- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Walking Dead Actress Kelley Mack Dies At 33 After Battling Glioma

Credits: Instagram
Walking Dead famed actress Kelley Mack has passed away at the age of 33 on Saturday at her birthplace of Cincinnati. Her demise was confirmed by a social media post by her sister, who mentioned, "It is with indelible sadness that we are announcing the passing of our dear Kelley. Such a bright, fervent light has transitioned to the beyond, where we all eventually must go."
As per Deadline, the actress was battling with glioma of the central nervous system. She had also posted her health update battling the same, and shared how her radiation therapy had been going.
What Is Glioma?
As per the Johns Hopkins Medicine, glioma is a common type of tumor originating in the brain. About 33% of all brain tumors are gliomas, which originate n the glial cells that surround and support neurons in the brains, including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and ependymal cells.
Gliomas are called intra-axial brain tumors because they grow within the substance of the brain and often mix with normal brain tissue.
Types Of Glioma
Astrocytomas: Astrocytomas are tumors that form in glial cells, specifically from connective tissue cells called astrocytes. They are the most common type of primary intra-axial brain tumor, making up almost half of all primary brain tumors. These tumors are most often found in the cerebrum, the large outer part of the brain, but they can also occur in the cerebellum, located at the base of the brain.
Astrocytomas can affect both children and adults. In children, low-grade astrocytomas, known as pilocytic astrocytomas, are typically found in the cerebellum. In adults, these tumors are more commonly located in the cerebrum. The most aggressive form of astrocytoma is glioblastoma multiforme, a high-grade tumor that is considered the most malignant of all brain tumors. Its symptoms are often similar to those seen with other types of gliomas.
Brain stem gliomas: Brain stem gliomas, also known as diffuse infiltrating brainstem gliomas or DIPGs, are rare and usually found in the brain stem. Due to their location and the way they grow by blending into normal brain tissue, they are generally not removable by surgery. These tumors most often affect school-age children and are responsible for the highest number of childhood deaths from primary brain tumors.
Ependymomas: Ependymomas develop from ependymal cells, which line the brain’s ventricles or the spinal cord. Although they are rare, making up just 2 to 3 percent of primary brain tumors, they account for 8 to 10 percent of brain tumors in children, especially those younger than 10. In children, these tumors are usually found near the cerebellum, where they may block the flow of cerebrospinal fluid and lead to increased pressure in the skull. Ependymomas can also spread to other areas of the brain or spinal cord through spinal fluid, a process known as drop metastasis.
Mixed gliomas: Mixed gliomas, also called oligoastrocytomas, contain more than one type of glial cell. There is some debate over whether these tumors should be classified as a separate type, and genetic testing of tumor tissue is often used to clarify the diagnosis. These tumors usually occur in the cerebrum and are most common in adult men.
Oligodendrogliomas : Oligodendrogliomas form from oligodendrocytes, the supportive cells in the brain, and are usually located in the cerebrum. They make up about 2 to 4 percent of primary brain tumors and are more common in men, especially those in young to middle adulthood. Seizures are a frequent symptom, affecting up to 80 percent of patients, along with headaches, weakness, or speech problems. Oligodendrogliomas tend to have a better prognosis than many other gliomas.
Optic pathway gliomas: Optic pathway gliomas are low-grade tumors found in the optic nerve or optic chiasm. These tumors often affect people with neurofibromatosis and can lead to vision loss and hormone-related problems, especially since they tend to grow at the base of the brain, near areas responsible for hormone control. When these tumors impact hormone function, they may be referred to as hypothalamic gliomas.
What Are The Symptoms of Glioma?
- Headaches
- Seizures
- Personality changes
- Weakness in the arms, face or legs
- Numbness
- Problems with speech
- Nausea and vomiting
- Vision loss
- Dizziness
Ahmedabad Toddler Swallows Hulk Toy, Showed X-Ray, Doctors Remove It Via Endoscopy
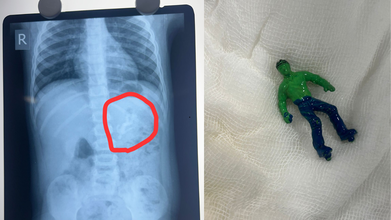
Credits: X
Ahmedabad toddler, one-and-a-half-year-old boy swallowed a 'Hulk' toy, which is based on a popular comic superhero. The toy was stuck in his stomach when his parents took him to the Civil Hospital. According to reports by News18, the child is identified as Vansh who showed the signs of discomfort and began vomiting. This is what alarmed the parents.
As per the News18 report, his mother Bhavika was suspicious when she noticed that one of his toys was missing. The child was rushed to the hospital and an X-ray revealed that he had swallowed the entire plastic toy. The toy was not broken.
Hindustan Times reported that Dr Rakesh Joshi, Head of the Department of Pediatric Surgery removed the toy through upper GI endoscopy. "Had it been a little late, the toy could have moved further from the stomach and got stuck in the intestines. In that case, there would have been a risk of intestinal blockage and even rupture," the senior doctor said.
"There is a natural valve between the esophagus and the stomach. The biggest challenge was to take out a whole toy through this valve. When we tried to grab it with the endoscope, the toy kept slipping because of the air in the stomach. Pulling the toy by its hand or foot raised the possibility of it getting stuck in the valve and causing it permanent damage," he said.
The doctor noted that if the toy had further slipped down, it would have increased the risk of intestine rupturing.
Ahmedabad Toddler Swallows Hulk Toy: What Parents Must Keep In Their Mind
Under the Toys (Quality Control) Order, 2020 issued by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, toy safety in India was brought under mandatory BIS certification from September 1, 2020. The move aims to ensure safer toys for children while also supporting the government’s policy of curbing non-essential imports.
Industry sources estimate that more than 85 percent of toys sold in India are imported. Officials say the Toys Quality Control Order is a key step in preventing the entry of cheap and substandard toys into the domestic market, many of which fail to meet basic safety requirements.
Ahmedabad Toddler Swallows Hulk Toy: Standards for Electric and Non-Electric Toys
The quality control order clearly defines safety standards based on the type of toy. Non-electric toys such as dolls, rattles, puzzles, and board games must comply with IS 9873 (Part 1):2019. These toys do not rely on electricity for any of their functions.
Electric toys, which include at least one function powered by electricity, are required to meet the standards outlined under IS 15644:2006. Compliance with these standards is mandatory before such toys can be sold in the Indian market.
Ahmedabad Toddler Swallows Hulk Toy: Risks Linked to Untested Toys
Toys that are not tested by NABL-accredited toy testing laboratories can pose serious health risks to children. Sharp edges and poorly finished parts can cause cuts and injuries. PVC toys may contain phthalates, which are considered harmful chemicals.
Many low-quality toys have also been found to contain lead, a substance known to be particularly damaging to brain development in children. Soft toys with fur or hair can trigger allergies or become choking hazards. In some cases, small body parts can get stuck in gaps or holes, increasing the risk of injury.
Testing by NABL-accredited laboratories ensures that toys are safe, durable, and suitable for specific age groups. Parents are advised to check for IS marks on toys before purchasing, as this indicates compliance with Indian safety standards.
Ahmedabad Toddler Swallows Hulk Toy: What Parents Should Check Before Buying Toys
Experts recommend avoiding toys with small detachable parts for toddlers and young children, as they are more likely to put objects in their mouths. Toys should always match the child’s age, skill level, and interests.
Parents are also urged to look for IS marks, which confirm that the toy has been tested and certified. Loud toys should be avoided, as prolonged exposure to sounds above 85 decibels can harm a child’s hearing.
Electric toys with heating elements should be used with caution or avoided altogether due to burn risks. Finally, toys with sharp edges or shooting components should be carefully examined to prevent cuts and injuries.
Nipah Virus Outbreak In India: Myanmar Airport Tightens Health Screenings

Credits: iStock
Nipah virus outbreak in India triggered airport screenings of travelers, including in Myanmar. Many reports claim that passengers are being checked in similar ways as they were during the COVID-19 virus spread. Health and Me reported how in Thailand the health screenings of foreign travelers were taken seriously, a similar case is seen in Myanmar.
Nipah Virus Outbreak In India: How Are Travelers Screened In Myanmar?
Myanmar has tightened its health screenings and surveillance at Yangon International Airport to prevent any possible entry of Nipah virus case, reported The Global New Light of Myanmar. Travelers who are arriving from India, especially West Bengal are given special attention to check for any fever or other Nipah-related symptoms, read the report by the Ministry of Health.
The ministry also noted that health screening of passengers arriving from abroad is being conducted in line with the established guidelines for infectious diseases that could give rise to public health emergencies, Xinhua news agency reported.
Informational leaflets too are being distributed among travelers to be aware of the symptoms. Posters are also displayed at the airport. Along with all that, disease prevention and control measures are also being carried out in the airport.
Screening measures are also enhanced and implemented at Mandalay International Airport.
Nipah Virus Outbreak In India: What Is It?
As per the World Health Organization (WHO), Nipah virus infection is a zoonotic illness that is transmitted to people from animals, and can also be transmitted through contaminated food or directly from person to person.
In infected people, it causes a range of illnesses from asymptomatic (subclinical) infection to acute respiratory illness and fatal encephalitis. The virus can also cause severe disease in animals such as pigs, resulting in significant economic losses for farmers.
Although Nipah virus has caused only a few known outbreaks in Asia, it infects a wide range of animals and causes severe disease and death in people.
Nipah virus is infectious and can spread from animals like bats and pigs to humans through bodily fluids or contaminated food. It can also pass between people through close contact, especially in caregiving settings. While it can spread via respiratory droplets in enclosed spaces, it is not considered highly airborne and usually requires close, prolonged contact for transmission. Common routes include direct exposure to infected animals or their fluids, consuming contaminated fruits or date palm sap, and contact with bodily fluids such as saliva, urine, or blood from an infected person.
Nipah Virus Outbreak In India: What Are The Common Symptoms?
- Fever
- Headache
- Breathing difficulties
- Cough and sore throat
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Muscle pain and severe weakness
Measles Outbreak In Disneyland: An International Traveler Gets Infected

Credits: iStock
Measles Outbreak in Disneyland: Health officials in Orange County sounded alarmed after they confirmed a recent measles case in a child who visited Disneyland last week. The Orange County Health Care Agency said on Saturday that the child was an international traveler who arrived at Los Angeles International Airport (LAX). The child then went to Disneyland on Wednesday and that is what became the potential exposure window.
As per the health authorities there could be two possibilities of getting the disease:
- Goofy’s Kitchen in Disneyland Hotel, 10:30 a.m. to 1:30 p.m. on Wednesday
- Disneyland Park and Disney California Adventure Park, 12:30 p.m. to closing on Wednesday.
Health authorities said they are coordinating with Disneyland to contact employees who may have been exposed to measles. According to Orange County health officials, visitors present at the theme park during the identified period could develop symptoms between seven and 21 days after exposure.
Measles Spreads Easily, Experts Warn
Dr Danielle Curitore, a pediatrician at St Joseph Heritage Providence, explained NBC Los Angeles that measles is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets.
“Very similar to these respiratory viruses, but even more so because it can be in a close setting and if that person with measles sneezes or coughs and transmits some respiratory droplets, you are exposed,” she said. “And that room that they’ve been in is also contagious for at least two hours after they left.”
Measles Outbreak In Disneyland: Vaccination Remains The Strongest Protection
Doctors emphasize that individuals who have received the measles vaccine, particularly the recommended two doses, are generally well protected against the disease. Those who have not been vaccinated face a significantly higher risk of infection.
Read: Measles Elimination Status In The US Is ‘Not Really’ At Risk, CDC Says As Cases Surge
“Your best protection is to be vaccinated, so if you’ve been vaccinated against measles and you’ve received your two doses of measles vaccine at any point, those are usually given in childhood but you do continue to be immune as you get older,” Dr Curitore added.
New Measles Cases Reported In Southern California
Health officials have confirmed at least five new measles cases in Southern California, prompting renewed warnings and surveillance. Authorities are closely monitoring the situation to limit further spread and identify potential exposure chains.
What Is Measles?
Measles, also known as rubeola, is an extremely contagious viral illness that typically causes high fever, cough, runny nose, red and watery eyes, and a characteristic rash that begins on the face and spreads downward across the body. It spreads through respiratory droplets and can lead to severe and sometimes fatal complications, including pneumonia and inflammation of the brain known as encephalitis.
Although it is preventable through the safe and effective MMR vaccine, measles remains a serious threat in many regions. There is no specific cure, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
Measles Outbreak In Disneyland: Common Symptoms To Watch For
Experts say measles symptoms often begin with signs similar to a common cold, including cough, congestion, and high fever. Some patients may also develop conjunctivitis.
“Sometimes it just starts out like the common cold cough congestion: high fever sometimes conjunctivitis can be part of it,” Dr Curitore said. “Then day three to five, you get that very classic measles rash, which usually starts on the face, center of the body.”
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

