- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
What Causes Bipolar Disorder? These 36 Genes Hold The Answer

Image Credit: Health and me
Bipolar disorder is a chronic mental illness that affects an individual by experiencing extreme mood fluctuations, such as episodes of depression and mania or hypomania (an elevated or irritable mood state). The impact on daily life, relationships, and productivity can be quite devastating for the person suffering from it, if not treated. Though the prevalence is 40 to 50 million worldwide, it remains undiagnosed for years in most patients due to its complex presentation and often being misdiagnosed as depression.
This condition is thought to have substantial genetic contributions, with estimated heritability of between 60 and 80%. However, for a long time, the challenge has been to isolate specific genes that play a role in its development as a result of a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors.
For the first time ever, researchers, publishing in Nature, have discovered 36 genes whose presence is a strong indicator for bipolar disorder development. This significant, international, multi-center investigation was the biggest study of its kind to date, and helped shine a spotlight on the genetics behind bipolar disorder. Bipolar disorder is one of the more common mental health diseases and affects millions worldwide.
The study was conducted by the Bipolar Disorder Working Group under the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium, which comprises more than 800 researchers from 40 countries. Among them were professionals from leading institutions such as IDIBAPS-Hospital Clínic and Hospital Vall d'Hebron in Spain.
The researchers used information from genome-wide association studies for a meta-analysis involving more than 158,000 patients suffering from bipolar disorder and 2.8 million control subjects, free of this condition. All six inhabited continents were represented with this dataset-an unprecedented size-owing to which significant insights into bipolar disorder's genetics architecture could finally be obtained.
The results provided 337 genome-wide significant (GWS) variants which are grouped into 298 distinct regions of the genome. This is four times the number reported so far in any previous study. Further advanced genetic mapping provided the researchers an opportunity to better narrow these variants down to about 36 genes that are strongly associated with the disorder.
One of the most striking findings was the genetic difference between the two main subtypes of bipolar disorder—type 1 and type 2. Type 1 bipolar disorder, with more severe manic episodes, showed a stronger genetic correlation with schizophrenia. In contrast, type 2 bipolar disorder, with less severe manic episodes (hypomania), showed a closer genetic relationship with major depressive disorder (MDD) and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Brain plasticity and signal transduction related variations were also seen to influence changes in neural circuitry as experienced in the development of the bipolar disorder; neurotransmitter signaling, notably in dopamine and serotonin, influences regulation of mood-which might directly be a player in these varied manifestations of this disorder.
This research involved participants of various ethnic and geographical backgrounds, thereby making the results more universally applicable than in most previous studies that were characterized by demographic homogeneity.
What Implications Does this Have with Bipolar Disorder Treatment?
"This study is a significant step forward in our knowledge of the genetic underpinnings of bipolar disorder," said Dr. Eduard Vieta, head of the Psychiatry Service at Hospital Clínic and a key author on the paper. "Over time, these findings will open up the possibility of developing new treatments and deepening our understanding of the mechanisms of the disorder."
The identification of such genes and markers may be helpful in making leaps in personalized medicine. Targeting those genes, it may be possible to develop therapy that is both more effective and matched to the patient's genetic makeup. Moreover, knowledge of genetic differences between the subtypes may help in making diagnoses more accurate and subtype-specific intervention.
Facts and Misconceptions About Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a medical condition caused by biological imbalances, particularly involving genetic and neurochemical factors. It involves the limbic system of the brain, the site of emotional regulation. People suffering from the condition experience these functions to become abnormal and then suddenly change with no apparent environmental stimuli. Bipolar Disorder:
Despite its seriousness, myths abound. Bipolar disorder is not just a personality flaw, nor is it equivalent to dangerous or violent behavior. It is not a transient problem; rather, it requires life-long management through pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapies.
Even though the disorder is based on biology, environmental and psychological factors can also be triggers for episodes. Intriguingly, both good and bad events in life-such as promotions or personal losses- can trigger episodes, indicating how complex the relationship between biology and external circumstances might be.
The identification of these 36 genes is the crucial step toward unlocking the mystery of bipolar disorder. With a deeper understanding of its genetic structure, researchers are paving the way for novel treatments that could change the face of the therapy.
Further, the attention mental health is gaining around the world is why researches such as this one are of paramount importance to address public health challenges through genetic research. This discovery, in due course of time and more research, can bring about a future where bipolar disorder will not only be better understood but also more effectively managed to improve the lives of millions across the globe.
The discovery of 36 genes associated with bipolar disorder is another milestone for mental health research. This kind of study bridges the gap between genetic findings and clinical applications, making hope real in terms of more targeted treatments and a deeper understanding of the condition. As science progresses, so does the potential to transform the landscape of mental health care, reducing stigma and improving outcomes for those living with bipolar disorder.
Genomics yields biological and phenotypic insights into bipolar disorder. Nature. 2025
Brain Eating Amoeba Cases Surge In Kerala: All You Need to Know About This Infection
Credits: Canva
Amoebic meningoencephalitis, a rare and often deadly brain infection caused by the free-living amoeba Naegleria fowleri, has recently raised alarms in Kerala. The state confirmed a new case involving a 17-year-old boy from Thiruvananthapuram, intensifying concerns amid the ongoing 2025 outbreak. Known as the “brain-eating amoeba,” this infection enters the body through the nose and attacks the brain, causing rapid health deterioration and a high risk of death.
The boy is believed to have contracted the infection while bathing in a pool with friends. Following the diagnosis, the Kerala health department has closed the swimming pool at Akkulam Tourist Village and sent water samples for testing.
Brain-Eating Amoeba: What Is This Brain Infection?Brain-eating amoeba is a type of amoeba that usually lives in warm freshwater or unclean, untreated water. When it enters the human body, it causes a deadly infection that inflames and destroys brain tissue. Medically, this condition is called primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM).
You can only contract this infection if water contaminated with the amoeba enters your nose. While Naegleria exists in several species, only Naegleria fowleri is responsible for causing PAM.
ALSO READ: Panic In Kerala As Brain-Eating Amoeba Claims 5 Lives In A Month, 11 Under Watch
Where Can You Find Brain-Eating Amoebas?
Brain-eating amoebas thrive in warm, untreated water, making it an ideal environment for Naegleria fowleri. They can survive in water as hot as 115°F. According to the World Health Organization, these amoebas are commonly found in:- Warm ponds, lakes, and rock formations
- Mud holes
- Rivers with warm currents, especially those with low water levels
- Spas and swimming pools with untreated water
- Untreated municipal or well water
- Geothermal water sources, including hot springs
- Thermally contaminated water, like aquarium runoff from power plants
- Water play areas for children
- Aquatic parks
Brain-Eating Amoeba Cases Surge in Kerala
Kerala has reported 67 confirmed cases of amoebic meningoencephalitis this year, including 18 deaths, seven of which occurred in September alone. Clusters of cases have been observed in districts such as Thiruvananthapuram, Kozhikode, and Malappuram. In response, the state health minister, Veena George, has intensified awareness campaigns to educate the public on prevention and early symptom recognition.ALSO READ: ICMR Flags Misuse Of Critical Drugs, Suggests New Antibiotics Be Sold Only In Hospitals
“We urge people to avoid swimming in unchlorinated or stagnant water and to maintain strict hygiene when using water bodies for bathing,” she said. The government has also acted swiftly by closing the implicated swimming pool and enhancing water safety testing protocols.
Prevention remains the most effective protection. Experts recommend:
- Avoid swimming or diving in warm, stagnant freshwater
- Use nose clips when swimming in lakes or rivers
- Avoid putting your head underwater in hot springs or untreated water
- Ensure swimming pools are properly cleaned and chlorinated
- Avoid water-related activities
To tackle waterborne diseases, Kerala has launched the comprehensive ‘Water is Life’ campaign under the Haritha Keralam Mission. This statewide effort emphasises chlorinating wells, cleaning public water sources, and running awareness programmes in schools and local communities.
Congo Ebola Outbreak Caused By The Zaire Strain So Far Has 28 Deaths, Confirms WHO
(Credit- Canva)
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has officially declared a new Ebola outbreak in its Kasai Province. The virus responsible is the highly dangerous Zaire strain. As per the World Health Organization (WHO), the "virus is believed to have jumped from an animal to a human". The first known case was a 34-year-old pregnant woman who died on August 25, reports WHO. Two healthcare workers who cared for her also became infected and passed away. As of September 15 WHO has confirmed a total of 81 cases and 28 deaths, including four healthcare workers.
How Fatal Is Zaire Strain of Ebola?
According to 1983 The Journal of Infectious Diseases study, this strain of Ebola is different and far more deadly than the Sudan strain which caused an outbreak in Uganda as recently as January 2025.
- In the study, the Zaire strain killed 90% of those infected.
- The Sudan strain was also very dangerous, but less so, killing between 55% and 65% of people.
How Ebola Spreads and Its Symptoms
The WHO explains that the Ebola was first discovered in 1976. Scientists believe it originally comes from fruit bats. From there, it can spread to humans who come into contact with other infected animals, like monkeys. Once a person is infected, the virus spreads to others mainly through direct contact with their blood or other body fluids and is a deadly zoonotic disease (World Organization for Animal Health)
Symptoms can show up anywhere from 2 to 21 days after exposure and often start very suddenly. Early signs include a high fever, extreme tiredness, and muscle pain. As the disease gets worse, it can cause vomiting, diarrhea, and internal or external bleeding. Without fast medical care, the death rate can be as high as 50% to 90%. Ebola can spread quickly in crowded places like hospitals and during funerals, where people might touch the body of someone who died from the virus.
Can Ebola Be Cured?
While there isn't a single cure, there are effective treatments. The Ervebo vaccine is a powerful tool being used to contain the current outbreak. This vaccine is highly effective against the Zaire strain of Ebola—the one in this outbreak—and has a 100% success rate when given right after someone has been exposed.
Also Read: Weatherman Geoff Fox Announces To Enter Hospice Care For The Recurrent Cancer Treatment
Why Is This Ebola Outbreak A Cause of Concern
The Ebola virus has caused a big wave of concern in the country. The DRC is already dealing with other major health crises, like mpox, cholera, and measles, which are stretching its limited resources. The country is also facing armed conflict, making it hard to get medical supplies and staff to remote communities.
Even though the affected area, Kasai Province, is somewhat isolated, it's close to a major city and the border of Angola. This raises the risk that the virus could spread to new areas as people travel for work and trade.
To stop the spread, health officials are using a strategy called "ring vaccination." This means they're vaccinating not only people who are infected but also everyone they've been in contact with, as well as frontline healthcare workers. Other key actions include quickly separating sick people from healthy ones and tracing their contacts. The WHO and its partners have sent 48 experts to the region and provided special medication called Mab114 to treat patients. They are also helping neighboring countries prepare in case the virus crosses borders.
How Was Early Detection Possible For Ebola?
Modern technology is helping to spot outbreaks faster than ever before. An AI platform called EPIWATCH noticed a sharp increase in reports of illness in the DRC in early September, even before the outbreak was officially confirmed. This early warning can give authorities a crucial head start in their response, especially in areas with limited medical testing.
The WHO believes that if the outbreak is contained quickly, its impact will likely stay local. The risk is currently assessed as high for the DRC, moderate for the surrounding region, and low globally.
Why 1 In 6 U.S. Parents Are Rejecting Vaccine Recommendations

Credits: Canva
A new Washington Post–KFF poll has found that one in six U.S. parents have skipped or delayed routine childhood vaccinations, not including flu or coronavirus shots, for their children. While the vast majority of parents continue to follow recommended schedules, the survey highlights a concerning rise in vaccine hesitancy driven largely by distrust in government institutions and concerns about safety.
According to the poll, conducted between July 18 and August 4, 2025, among 2,716 U.S. parents and guardians, 16 percent reported delaying or skipping at least one vaccine for their child. Even more troubling, 9 percent admitted skipping highly critical immunizations such as the polio or measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccines.
Public health experts warn that skipping such vaccines risks large-scale outbreaks of diseases once thought to be under control.
Also Read: Dan Marino Shares What Helped Him Treat His Liver Disease, Details Inside
“This survey gives us the clearest picture yet of what is fueling hesitation,” said Liz Hamel, KFF’s vice president and director of public opinion and survey research, as reported by the Washington Post. “We still have strong support for vaccines among parents in this country, but we’re also seeing cracks in confidence, especially among younger parents. The big question is whether those cracks will deepen.”
Who Is Skipping Shots?
The Post–KFF poll shows that vaccine avoidance is not evenly distributed. Instead, it is tied to specific demographics, political beliefs, and educational practices.
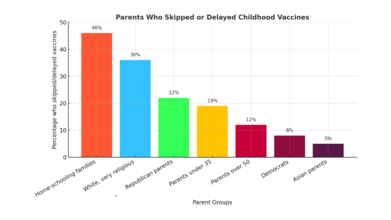
- Home-schooling families were the most likely to skip or delay shots, with 46 percent reporting they had done so.
- White, very religious parents had particularly high rates, with 36 percent reporting skipped or delayed vaccines, and 23 percent specifically skipping MMR or polio vaccines.
- Republican parents were also more likely to resist vaccines: 22 percent delayed or skipped a vaccine, compared with only 8 percent of Democrats.
- Age also played a role, with 19 percent of parents under 35 reporting skipped vaccines, compared with 12 percent of parents over 50.
- Democrats and Asian parents were among the least likely to delay or skip vaccines, with only 8 percent and 5 percent doing so, respectively.
Why Parents Say No
The reasons parents gave for vaccine hesitancy overwhelmingly related to safety fears and mistrust, rather than access or cost.
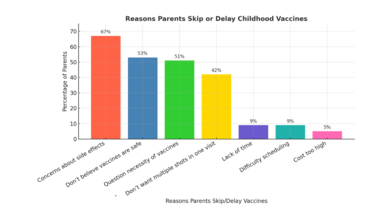
- 67 percent of hesitant parents cited concerns about side effects.
- 53 percent said they don’t believe vaccines are entirely safe.
- 51 percent questioned whether all recommended vaccines were even necessary.
- A smaller number, 42 percent, resisted because they didn’t want multiple shots given in one visit.
- By comparison, logistical barriers such as cost (5 percent), lack of time (9 percent), or difficulty scheduling appointments (9 percent) were rarely mentioned.
As one Arizona mother, Anna Hulkow, told The Post: “I don’t think my kids are worse off to get [chicken pox] firsthand.” Hulkow, who moved her family in part because of stricter school vaccine requirements in California, said she distrusts what she views as a profit-driven health care system.
Distrust of Federal Health Agencies
The survey underscores a sharp erosion of trust in federal institutions charged with vaccine safety. Just 49 percent of parents said they have confidence in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to ensure vaccine safety and effectiveness, while 51 percent expressed doubt.
Confidence was highly polarized along party lines:
- 60 percent of Democrats said they trust the agencies.
- 48 percent of independents expressed confidence.
- Only 41 percent of Republicans said the same.
This skepticism has grown since the coronavirus pandemic, which politicized public health guidance and created space for misinformation to spread widely online.
The Influence of Robert F. Kennedy Jr.
The appointment of Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr., a longtime critic of vaccines, has intensified debates. While Kennedy’s claims linking vaccines to autism have been repeatedly debunked by dozens of studies, the Post–KFF poll found that at least four in ten parents say they don’t know whether such claims are true or false.
Even without firm belief in Kennedy’s most controversial assertions, many parents expressed trust in his broader critique of federal vaccine policy. Among Republicans, 54 percent said they trusted Kennedy to provide reliable information about vaccines. Among parents overall, 36 percent expressed similar trust.
One Las Vegas mother, Imani Schaade, told The Post she believes vaccines contributed to her daughters’ autism and allergic reactions. While she ultimately vaccinated her son for school entry, she said Kennedy “created a wave of people coming out and being able to speak out about [vaccines], and people have an opinion.”
The “Mushy Middle”
While a small percentage of parents identify as explicitly anti-vaccine (6 percent), nearly half fall into what The Post calls a “mushy middle”, parents who vaccinate but express skepticism. These parents may agree to vaccines like MMR and polio but express doubt about flu or COVID-19 shots, or delay doses because they are wary of multiple shots in a single appointment.
In fact, 52 percent of parents did not vaccinate their children against the flu last year, even though flu shots have been widely recommended since 2010. And only 13 percent of eligible children received last year’s coronavirus vaccine, according to federal estimates.
Also Read: Unique Symptoms Of Flu In 2025 And How Long The Infection Lasts
What Public Health Experts Say
Public health organizations, including the CDC and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), continue to stress that recommended childhood vaccines are safe, effective, and extensively tested before approval.
“Delaying or spreading out vaccine doses leaves your child unprotected during the time when they need vaccine protection the most,” the CDC warns.
The AAP has also emphasized that natural infection, such as allowing children to contract chicken pox, carries risks far more serious than those posed by vaccines. Before the chicken pox vaccine was introduced, the disease killed between 100 and 150 Americans annually and hospitalized thousands more.
The Political Tension
While vaccine hesitancy is more common among Republicans, the poll found 77 percent of Republican parents still follow vaccine recommendations, including 84 percent who vaccinate against measles and polio.
That strong baseline of support has made vaccine mandates politically sensitive. A conservative polling firm recently warned GOP lawmakers that aggressively rolling back school vaccine requirements could be politically damaging, given that most Trump voters still believe vaccines save lives.
The Post–KFF poll found that 81 percent of all parents believe public schools should require measles and polio vaccines, with exceptions only for medical or religious reasons.
Parents Who Still Believe
Some parents told The Post they felt increasingly isolated in their communities for supporting vaccines.
Elizabeth Stratford, a retired ICU nurse and Republican mother of six in Utah, described her frustration:
“I’ve taken care of people with polio and with rubella and with measles in my 35 years of nursing, and I don’t know why anybody would ever want those diseases,” Stratford said. “If people knew what these diseases were about, they would probably be more responsible.”
What Comes Next
The Washington Post–KFF poll paints a mixed picture: strong support for foundational vaccines like MMR and polio, but waning trust overall, especially around flu and COVID-19 shots. Younger parents, white religious conservatives, and home-schooling families are leading the resistance.
Public health experts fear that if vaccine skepticism continues to spread, and if federal leadership amplifies misinformation, the United States could see the return of once-eradicated diseases.
But for now, most parents are still vaccinating, even if they have questions. The challenge for policymakers and health professionals will be to rebuild trust, counter misinformation, and remind parents of what’s at stake.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

