- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
Whooping Cough Kills Two Infants In Louisiana As Vaccination Rates Drop
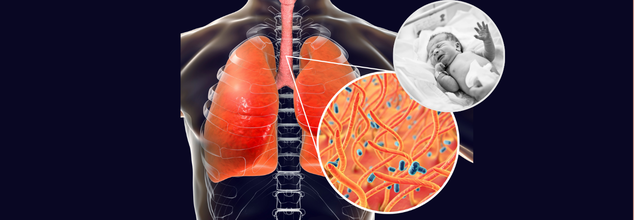
Whooping cough is making an alarming comeback in the United States, with cases spiking to their highest level in over a decade. As of mid-December, preliminary data from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reveals more than 32,000 cases of pertussis reported nationwide—nearly six times higher than the same period last year. The outbreak is causing alarm among health authorities as the highly contagious bacterial disease, once largely subdued by vaccination, returns with vigor.
Often mistaken in its early phases for a common cold, whooping cough may progress to bout after bout of violent coughing that induces vomiting, broken ribs, and an iconic gasping "whoop" for air. The illness can persist for weeks or even months, and sometimes individuals unknowingly spread it. With rising transmission and infants being particularly susceptible, the surge is also triggering new concerns about vaccine resistance and routine immunization coverage gaps.
Two infants in Louisiana have died of pertussis—also known as whooping cough—making it the first such deaths in the state since 2018. These fatalities are part of an overall national increase in cases of pertussis, triggering fresh alarm among pediatric professionals and public health officials about declining rates of vaccination and waning immunity.
Pertussis is a highly infectious respiratory infection caused by the Bordetella pertussis bacterium. It is identified by persistent fits of coughing that usually culminate in a characteristic "whooping" sound as the patient struggles to catch his or her breath. Though the disease infects individuals of all ages, it is particularly hazardous for babies too young to be vaccinated.
For babies, it's actually pretty scary," CNN quoted Dr. John Schieffelin, Associate Professor of Pediatrics at Tulane University.
“They’re just coughing so much, they can’t eat, they can’t drink, and they often get pneumonia, which means we have to put them on a ventilator… they just never stop coughing.” With two decades of experience in pediatric infectious diseases, Dr. Schieffelin asserts that no other illness compares to the suffering pertussis causes in the youngest patients. Surging Numbers: The Return of a Supposedly Controlled Disease
Louisiana reported 110 cases of pertussis through the first quarter of 2025 alone, almost reaching the total 154 cases for the entire year 2024. National trends have an even more ominous course. In 2024, the United States had more than 35,000 cases of pertussis—its highest rate in more than a decade—that resulted in 10 deaths, six of whom were infants younger than one year.
This year, 2025, is looking to be even worse, with already 6,600 cases reported—almost four times the number reported at this time last year.
The United States previously reported over 200,000 cases of whooping cough per year prior to the availability of the pertussis vaccine. As the DTaP vaccine (diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis) became widespread during the late 1940s, illness plummeted. Pertussis started seeping back into the United States in the 1980s due to enhanced surveillance and declining vaccine-induced immunity.
The CDC advises a five-dose series of the DTaP vaccine in children, starting at two months of age and continuing up to age six. Teenagers should have a booster (Tdap) between ages 11 and 12, and adults are encouraged to receive a Tdap booster every 10 years.
For newborns too young to be vaccinated, maternal immunization during the third trimester of pregnancy is crucial. This practice offers passive immunity to the infant, avertinh 78% of cases and decreasing the hazard of hospitalization by 91%, states the CDC. A second protective method is "cocooning," in which all members of the household are vaccinated to protect the infant from transmission.
The increase in cases of pertussis has come at the same time as a troubling drop in childhood vaccination coverage. The rate of US kindergartners vaccinated with the DTaP series has fallen steadily over the last five years, leaving thousands at risk.
In Louisiana, where the latest infant deaths occurred, access to healthcare is another pressing challenge. “Especially in a state like Louisiana, we’ve got a lot of poverty. We’ve got a lot of rural populations, and not everyone has access to regular medical care,” said Dr. Jennifer Herricks, founder of the nonprofit Louisiana Families for Vaccines.
Dr. Herricks and other health advocates contend that such systemic obstacles, combined with increasing vaccine reluctance, render state efforts to encourage immunization all the more vital. But in a contentious decision, the Louisiana Department of Health recently stated it would no longer encourage mass vaccination at community events and health fairs.
In a memo, Louisiana Surgeon General Dr. Ralph Abraham made clear that although the state still supports routine childhood immunizations, it will no longer encourage seasonal vaccines like COVID-19 and flu at mass clinics. But some local health officials are concerned this change in approach sends a confusing message.
"When you cast dispersions or make a question regarding the safety and effectiveness of a single vaccine, I think that it actually ends up having this ripple effect across all vaccines," said Dr. Jennifer Avegno, Health Department Director for New Orleans. Although she lauded the recent messaging by the Department of Health regarding pertussis, she wondered if outreach was sufficient. "It's perhaps too little, too late."
While the country grapples with this comeback, experts emphasize that vaccination is the best means to avoid pertussis outbreaks and save lives—particularly among the most vulnerable. Beyond early childhood immunizations, adult booster doses and maternal vaccination during pregnancy are key measures.
Dr. Schieffelin stresses the importance of communities coming together to work toward the protection of infants. "We have to think not just about ourselves, but about the people around us—particularly babies who can't yet get vaccinated. That's what community immunity is all about."
With over 6,000 cases already this year and numbers rising, the stakes are high. Public health officials, parents, and policymakers all must move quickly to rebuild trust in vaccines, increase access to care, and protect future generations from this preventable and fatal disease.
Jenny Mollen Ends Up In ER After Microdosing GLP1 Medication
Credits: Instagram and Canva
US TV Star, the 46-year-old Jenny Mollen was rushed to the Emergency Room due to a reaction that happened after she consumed the weight-loss drug, GLP1 or the glucagon-like peptide-1 medication.
In an Instagram story on June 26, she wrote, “I just posted a follow-up to my piece about Tirzepatide and microdosing. I had a lot of unanswered questions about it [that] just ironically got answered for me in the form of a trip to the ER two nights ago … I’m in such a f***ing haze. It’s been a crazy 48 hours.”
She also revealed that she lost one-fourth of her blood as she ended up in the hospital.
What Is Tirzepatide?
Before we understand what is tirzepatide, it is important to understand how GLP1 medications work. It is a hormone naturally produced in the body that plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels and appetite. GLP-1 receptor agonists are a class of medications that mimic the effects of this hormone, used to treat type 2 diabetes and, increasingly, for weight management.
Tirzepatide, on the other hand is a GLP1, like Ozempic or Wegovy. It regulates a person's blood sugar, appetite, and digestion. These medications are usually used to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity.
What Happened To Mollen?
Mollen, who is the wife of Jason Biggs, also wrote an essay, published on Substack, where she expressed her "growing concerns" about how the medication was affecting her “mentally.”
In her essay, she wrote: “I do think that in the coming years, we will hear more about how GLP1s cause depression, ruin marriages and rob us of our capacity for feeling joy. These drugs bind to our neurotransmitters, affecting levels of dopamine and serotonin. They change our relationship with food. And I believe they also change our relationship with people and ourselves.”
She also noted that why others may have a desire to use it, however, she expressed her concerns over how it could have a negative impact on individual’s mental health, as she also has her own first-hand experience.
She further noted: “When I started Tirzepatide, the first thing I noticed was that I was crying more frequently. I couldn’t control the tears that would pour out of me when talking about subjects ranging from kids to open-faced tuna melts. I also noticed this underlying anxiety that would, without warning, after no more than one cup of espresso, take over my body and have me pacing in the kitchen like I’d just snorted an eightball of cocaine.”
She also noted that she would get irritated much quickly and she was “more easily offended and quicker to react” while she was on GLP1.
She wrote: “I also began to sense that the joy and gratitude I once experienced, those moments of peak happiness, weren’t quite as intense as they used to be. I could feel the joy simmering beneath the surface, but it never reached the pinnacle it once had internally. Even on a rollercoaster, my sense of euphoria was dampened. I couldn’t feel the highs and lows. Satisfaction, personally and professionally, was just out of reach.”
Scientists Find Over 20 New Bat Viruses In China, Warn Of “Critical Implications”
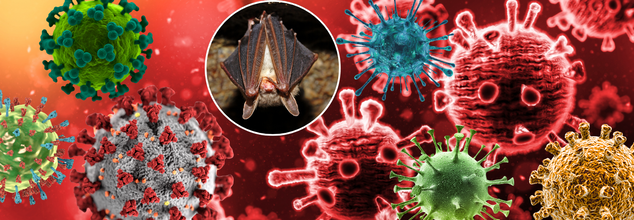
The most deadly viruses in the world may be quietly fermenting in fruit orchards—literally over your head? You got it. In a finding that is generating high-profile buzz throughout the international scientific community, scientists in China have discovered over 20 novel bat viruses, some of which have close relatives to Hendra and Nipah—diseases with skull-chilling mortality rates and a track record of crossing over from animals to humans.
So what does this all mean to you, me, and the rest of the world? A new science study issued a warning to the global health community: scientists have found over 20 previously unknown viruses in Chinese Yunnan province bats. Two newly discovered henipaviruses closely related to the lethal Hendra and Nipah viruses are causing special concern because of their likely ability to cause human and animal disease. Health professionals caution that these discoveries have "critical implications" for global public health, highlighting an urgent need for increased surveillance and biosecurity protocols.
The discovery, reported in the journal PLOS Pathogens, has been sending shockwaves across the world's scientific and medical circles, with scientists alerting that the newly discovered viruses may have "critical implications" for global public health.
The Two Viruses That Have Experts Particularly on Edge
Two of the 22 viruses identified were particularly concerning: henipaviruses—a class of viruses with a reputation for being lethal. These were discovered in fruit bats that inhabit the vicinity of orchards and human habitations, a configuration that duplicates earlier outbreaks of Hendra virus in Australia. Among the viruses discovered in the study is the closest-known relative of the Hendra and Nipah viruses, which carry mortality rates of 40% to 80% in humans and are responsible for causing severe respiratory disease and brain inflammation.
What is more alarming is the transmission mode: both Hendra and Nipah viruses can also be transmitted via bat urine. In farming areas where bats scavenge in fruit farms, infected fruit can be used as a bridge for spillover into livestock—or humans.
"Academically, this is not a concern," replied Associate Professor Vinod Balasubramaniam, a virologist at Monash University's Malaysian campus. "This has practical implications, particularly for nations such as Australia where the ecology is shockingly similar."
Why Bats Are A Matter of Concern?
Bats have long been known to be the main hosts of viruses that are able to leap onto humans and animals, sometimes with catastrophic consequences. From Ebola to SARS, MERS, and most recently, the coronavirus causing COVID-19, bats are often suspected to be responsible for the appearance of new infectious diseases. Their own biology—long lifespan, social roosting habits, and strong immune systems—tends to make them perfect reservoirs for a vast range of viruses.
The emphasis of the new study on the kidneys is important. While most research to date has focused on bat saliva, feces, or blood, the kidneys might be important in viral shedding, especially by way of urine. This is particularly important for henipaviruses, which have been found to be excreted in bat urine and can infect fruit or surfaces and cause spillover to humans and animals.
The Henipavirus Threat
Of all the viruses that have been found, the two new henipaviruses in fruit bats are of most concern to researchers. One of them is now known to be the closest-known relative of the Hendra and Nipah viruses—both of which have caused fatal outbreaks among humans and animals.
Hendra and Nipah viruses have the notorious reputation for high mortality rates, ranging from 40% to 80%. They induce severe brain inflammation (encephalitis) and respiratory illness, and can spread efficiently within populations of both humans and animals. In Australia alone, Hendra virus has caused 66 recorded outbreaks since 1994, killing four individuals and scores of horses. Nipah virus, on the other hand, has produced recurrent outbreaks in South and Southeast Asia, frequently associated with the consumption of fruit or fruit products contaminated by urine from bats.
The detection of henipaviruses closely related to each other in Yunnan's fruit bats—particularly those that inhabit orchards and villages—heightens the possibility of future spillover incidents. As Associate Professor Vinod Balasubramaniam of the Malaysian campus of Monash University points out, "The proximity between the Australian rural setting and Yunnan's orchards close to human dwellings emphasizes the need for heightened surveillance and biosecurity efforts."
How Do These Viruses Spread?
Bats have come under closer scientific examination as natural reservoirs for most lethal viruses, including SARS, MERS, Ebola, and even SARS-CoV-2. This research is special because it targets the kidneys—a less often examined organ in virology studies.
Both Hendra and Nipah viruses can be spread by contact with bat urine. Fruit bats in agricultural environments tend to roost and feed in orchards near human habitation. When their urine gets onto fruit, the virus is consumed by livestock or human beings, paving the way for possible outbreaks.
This method of transmission is especially cause for alarm in areas where humans and animals are in close contact to bat habitats. As Dr. Alison Peel, a disease ecologist of wildlife at the University of Sydney, describes, these results indicate "potential opportunities for contact" with humans—particularly those in rural and peri-urban settings.
This research broadens our knowledge of the bat kidney infectome," scientists said. "It identifies the imperative zoonotic dangers lurking in plain sight and emphasizes the importance of complete-spectrum viral monitoring in understudied organs.
As per Dr. Yong Gao Peng, a virologist who participated in the research, "This finding does not mean an outbreak will be imminent. But it does show just how much we still don't know about the viral world within bats, and how important it is to chart it out comprehensively."
Why the World Should Pay Attention?
The detection of so many new bat viruses in a fairly small sample puts into perspective how much scientists actually still have yet to learn about the microbial universe borne by bats. As Dr. Yong Gao Peng, a virologist at Nias, cautions, "While the results are based on bat kidney samples and do not suggest impending outbreaks, they show how much we still don't know about the microbes bats carry."
In light of the past history of lethal outbreaks with bat-borne viruses, the stakes are obvious. Increased monitoring, particularly where bats and humans coexist in close proximity, is called for. The research also underscores the necessity of thorough investigations of hitherto less-studied organs—such as the kidneys—to fully evaluate the entire range of spillover threats.
"These viruses don't have to be pathogenic today," added Dr. Peel, "because viruses change. The take-home message here is the need for urgency in surveillance, especially in ecotones where humans, animals, and wildlife overlap."
Dr. Peng further contributes that the existence of such viruses, while localized to kidneys in this instance, is a sign from nature. "Most outbreaks are initiated by asymptomatic spillovers," he states. "Without timely detection and proper containment measures, they could quietly ferment into international crises."
This finding arrives as the globe is still fighting COVID-19 and wrestling with the advent of new infectious variants. Only 6% of Australian adults have been vaccinated with the new COVID-19 booster, as reported in national health figures. With the northern hemisphere preparing to face another winter surge, public health officials say complacency is not a choice.
India’s Drug Regulator Flags 186 Medicines For Failing Quality Test, Paracetamol And Diabetes Meds Included

In a significant development that highlights the increasing scrutiny over the safety of pharma products, India's Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) has identified 186 drugs and formulations as Not of Standard Quality (NSQ) in its surveillance report for May 2025. These identified drugs encompass widely prescribed drugs like paracetamol as well as diabetes drugs, triggering grave concerns over the safety of drugs in one of the world's largest pharmaceutical markets.
The action, the CDSCO says, is its part of regular regulatory vigilance aimed at detecting and eliminating unsafe drugs in the market so that patients are not inadvertently left consuming substandard or spurious medicines.
The list, published by the country's national drug regulator on 27 June, 2025, contains common drugs like paracetamol and insulin used to treat diabetes, prompting critical questions on drug safety, regulatory scrutiny, and public health in one of the biggest pharma markets in the world.
The CDSCO's recent warning follows central and state drug testing laboratories in India reporting scores of samples from pharmacies and distribution centers across the country. Of the total 186 failed quality test samples, 128 were detected by state drug testing laboratories, and 58 by central labs. All this aggressive monitoring forms part of CDSCO's constant vigilance to ensure the quality of drugs being sold to Indian consumers.
Of the 186 substandard drug samples, 128 were identified by state drug testing labs and 58 by central labs, as per the official notification. All these drugs failed one or more of the quality parameters such as potency, dissolution rate, microbial load, or content uniformity, and hence were not fit for use by patients.
In a statement that released with the move, CDSCO sought to point out that one failed batch of drug is unique to that batch and does not always mean all batches of the same brand or product are unsafe. Still, the detection of even a single poor batch can have implications for public health, particularly in the case of life-saving and chronic disease drugs.
The CDSCO also established that two of the Bihar drug samples were spurious, i.e., produced by unauthorized parties with the brand name of a different licensed company. These results suggest counterfeit operations in India's huge and intricate drug distribution system.
The regulator has assured that the incidents are being investigated and action would be taken under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act and the accompanying rules.
This is not a one-off case. CDSCO reported 900 samples as substandard and 20 as spurious in the year 2024 alone, all of them selected from pharmacies, hospitals, and distribution outlets throughout the nation.
What Are "Not of Standard Quality" (NSQ) and Spurious Drugs?
CDSCO defines NSQ as an occurrence of failure to satisfy one or more of the stipulated quality parameters during laboratory testing. The parameters would involve potency, purity, dissolution, and contaminants or impurities. Significantly, the regulator points out that a failed batch does not necessarily incriminate all the products of the same brand or company.
Aside from NSQ medicines, the CDSCO also marked two samples from the state of Bihar as "spurious." These were discovered to have been produced by illegal manufacturers with the use of the brand name of another firm—a grave offense which is being investigated. Adulterated and spurious medicines are especially threatening since they can have the wrong or harmful ingredients and therefore directly threaten patient safety.
How India Monitors Drug Quality?
India's pharma industry is one of the biggest in the world, serving not just the domestic market but also exports to more than 200 nations. With such a huge market, maintaining drug safety is no small effort. The CDSCO, along with state regulators, regularly takes drug samples from sales and distribution points. The samples are tested thoroughly in the laboratory, and the findings are made available on the CDSCO portal on a monthly basis.
This openness achieves several functions: it warns medical professionals and the general public to possible danger, raises responsibility on manufacturers, and preserves the level of trust for the healthcare system. In the words of Dr. Rajeev Singh Raghuvanshi, India's Drugs Controller General, only roughly 1.5% of drugs tested in recent surveys turned out to be less effective, indicating that the overwhelming majority of medicines available are safe. Still, a small proportion can add up to potentially great public health threats in view of India's population and the magnitude of drug use.
Threats to Public Health and World Drug Supply
India has been commonly referred to as the "pharmacy of the world," exporting generic drugs to more than 200 nations. Any quality lapse not only impacts Indian consumers but also tarnishes world confidence in Indian pharmaceuticals. Paracetamol and anti-diabetics are consumed by millions — any compromise on their effectiveness or safety can be devastating health-wise.
Substandard or counterfeit drugs are one of the greatest dangers to contemporary medicine," an independent pharmacovigilance expert in New Delhi said. "They may not treat the disease, may worsen patient outcomes, or lead to antimicrobial resistance."
The public, clinicians, and policymakers need to address CDSCO notifications not as run-of-the-mill bureaucracy but as canary-in-the-coal-mines warnings of broader systemic problems in manufacturing regulation, supply chain integrity, and quality control procedures.
What Can Healthcare Providers and Patients Do?
Awareness is the best defense for patients. The CDSCO's medicine alert system seeks to inform consumers and healthcare providers about possible dangers of certain drugs. Patients must go see their doctors or pharmacists if they have issues with their medication and avoid buying drugs from unofficial sources.
Healthcare professionals, on their part, must remain up to date on the current CDSCO reports and advisories, particularly when dispensing or prescribing high-risk drugs. Keeping an eye on the CDSCO portal regularly and being subscribed to alerts can help ensure that patients receive only safe and effective medicines. Patients must:
- Inquire about the batch number and manufacturer prior to taking prescribed drugs.
- Immediately report any side effects.
- Do not buy drugs from illegal online pharmacies.
In addition, hospitals and states should institutionalize pharmacovigilance programs in order to identify adverse trends early.
The CDSCO's forward-looking attitude—constant vigilance, open reporting, and rapid enforcement against violators—is reflective of India's seriousness in protecting public health. Nevertheless, the challenge persists. As the pharmaceutical sector continues its expansion, so must regulatory capability, laboratory facilities, and public awareness.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

