- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Why 1 In 6 U.S. Parents Are Rejecting Vaccine Recommendations

Credits: Canva
A new Washington Post–KFF poll has found that one in six U.S. parents have skipped or delayed routine childhood vaccinations, not including flu or coronavirus shots, for their children. While the vast majority of parents continue to follow recommended schedules, the survey highlights a concerning rise in vaccine hesitancy driven largely by distrust in government institutions and concerns about safety.
According to the poll, conducted between July 18 and August 4, 2025, among 2,716 U.S. parents and guardians, 16 percent reported delaying or skipping at least one vaccine for their child. Even more troubling, 9 percent admitted skipping highly critical immunizations such as the polio or measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccines.
Public health experts warn that skipping such vaccines risks large-scale outbreaks of diseases once thought to be under control.
Also Read: Dan Marino Shares What Helped Him Treat His Liver Disease, Details Inside
“This survey gives us the clearest picture yet of what is fueling hesitation,” said Liz Hamel, KFF’s vice president and director of public opinion and survey research, as reported by the Washington Post. “We still have strong support for vaccines among parents in this country, but we’re also seeing cracks in confidence, especially among younger parents. The big question is whether those cracks will deepen.”
Who Is Skipping Shots?
The Post–KFF poll shows that vaccine avoidance is not evenly distributed. Instead, it is tied to specific demographics, political beliefs, and educational practices.
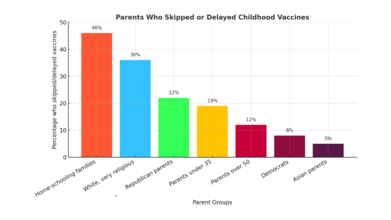
- Home-schooling families were the most likely to skip or delay shots, with 46 percent reporting they had done so.
- White, very religious parents had particularly high rates, with 36 percent reporting skipped or delayed vaccines, and 23 percent specifically skipping MMR or polio vaccines.
- Republican parents were also more likely to resist vaccines: 22 percent delayed or skipped a vaccine, compared with only 8 percent of Democrats.
- Age also played a role, with 19 percent of parents under 35 reporting skipped vaccines, compared with 12 percent of parents over 50.
- Democrats and Asian parents were among the least likely to delay or skip vaccines, with only 8 percent and 5 percent doing so, respectively.
Why Parents Say No
The reasons parents gave for vaccine hesitancy overwhelmingly related to safety fears and mistrust, rather than access or cost.
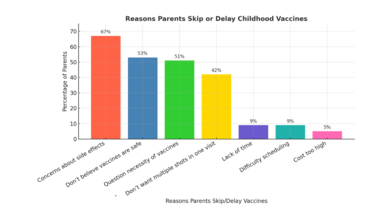
- 67 percent of hesitant parents cited concerns about side effects.
- 53 percent said they don’t believe vaccines are entirely safe.
- 51 percent questioned whether all recommended vaccines were even necessary.
- A smaller number, 42 percent, resisted because they didn’t want multiple shots given in one visit.
- By comparison, logistical barriers such as cost (5 percent), lack of time (9 percent), or difficulty scheduling appointments (9 percent) were rarely mentioned.
As one Arizona mother, Anna Hulkow, told The Post: “I don’t think my kids are worse off to get [chicken pox] firsthand.” Hulkow, who moved her family in part because of stricter school vaccine requirements in California, said she distrusts what she views as a profit-driven health care system.
Distrust of Federal Health Agencies
The survey underscores a sharp erosion of trust in federal institutions charged with vaccine safety. Just 49 percent of parents said they have confidence in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to ensure vaccine safety and effectiveness, while 51 percent expressed doubt.
Confidence was highly polarized along party lines:
- 60 percent of Democrats said they trust the agencies.
- 48 percent of independents expressed confidence.
- Only 41 percent of Republicans said the same.
This skepticism has grown since the coronavirus pandemic, which politicized public health guidance and created space for misinformation to spread widely online.
The Influence of Robert F. Kennedy Jr.
The appointment of Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr., a longtime critic of vaccines, has intensified debates. While Kennedy’s claims linking vaccines to autism have been repeatedly debunked by dozens of studies, the Post–KFF poll found that at least four in ten parents say they don’t know whether such claims are true or false.
Even without firm belief in Kennedy’s most controversial assertions, many parents expressed trust in his broader critique of federal vaccine policy. Among Republicans, 54 percent said they trusted Kennedy to provide reliable information about vaccines. Among parents overall, 36 percent expressed similar trust.
One Las Vegas mother, Imani Schaade, told The Post she believes vaccines contributed to her daughters’ autism and allergic reactions. While she ultimately vaccinated her son for school entry, she said Kennedy “created a wave of people coming out and being able to speak out about [vaccines], and people have an opinion.”
The “Mushy Middle”
While a small percentage of parents identify as explicitly anti-vaccine (6 percent), nearly half fall into what The Post calls a “mushy middle”, parents who vaccinate but express skepticism. These parents may agree to vaccines like MMR and polio but express doubt about flu or COVID-19 shots, or delay doses because they are wary of multiple shots in a single appointment.
In fact, 52 percent of parents did not vaccinate their children against the flu last year, even though flu shots have been widely recommended since 2010. And only 13 percent of eligible children received last year’s coronavirus vaccine, according to federal estimates.
Also Read: Unique Symptoms Of Flu In 2025 And How Long The Infection Lasts
What Public Health Experts Say
Public health organizations, including the CDC and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), continue to stress that recommended childhood vaccines are safe, effective, and extensively tested before approval.
“Delaying or spreading out vaccine doses leaves your child unprotected during the time when they need vaccine protection the most,” the CDC warns.
The AAP has also emphasized that natural infection, such as allowing children to contract chicken pox, carries risks far more serious than those posed by vaccines. Before the chicken pox vaccine was introduced, the disease killed between 100 and 150 Americans annually and hospitalized thousands more.
The Political Tension
While vaccine hesitancy is more common among Republicans, the poll found 77 percent of Republican parents still follow vaccine recommendations, including 84 percent who vaccinate against measles and polio.
That strong baseline of support has made vaccine mandates politically sensitive. A conservative polling firm recently warned GOP lawmakers that aggressively rolling back school vaccine requirements could be politically damaging, given that most Trump voters still believe vaccines save lives.
The Post–KFF poll found that 81 percent of all parents believe public schools should require measles and polio vaccines, with exceptions only for medical or religious reasons.
Parents Who Still Believe
Some parents told The Post they felt increasingly isolated in their communities for supporting vaccines.
Elizabeth Stratford, a retired ICU nurse and Republican mother of six in Utah, described her frustration:
“I’ve taken care of people with polio and with rubella and with measles in my 35 years of nursing, and I don’t know why anybody would ever want those diseases,” Stratford said. “If people knew what these diseases were about, they would probably be more responsible.”
What Comes Next
The Washington Post–KFF poll paints a mixed picture: strong support for foundational vaccines like MMR and polio, but waning trust overall, especially around flu and COVID-19 shots. Younger parents, white religious conservatives, and home-schooling families are leading the resistance.
Public health experts fear that if vaccine skepticism continues to spread, and if federal leadership amplifies misinformation, the United States could see the return of once-eradicated diseases.
But for now, most parents are still vaccinating, even if they have questions. The challenge for policymakers and health professionals will be to rebuild trust, counter misinformation, and remind parents of what’s at stake.
India AI Summit: Union Health Minister Nadda Launches SAHI And BODH Initiatives To Boost AI In Healthcare

The Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare, JP Nadda, today launched two key national initiatives -- the Strategy for Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare for India (SAHI) and the Benchmarking Open Data Platform for Health AI (BODH) to boost the role of AI in the country's healthcare ecosystem.
The initiatives, launched at the India AI Summit at Bharat Mandapam, in the national capital, are aimed at promoting safe, transparent, and accountable AI in healthcare. It will also help strengthen the digital health ecosystem for equitable healthcare access.
What is SAHI and BODH?
SAHI is a national guidance framework to enable the safe, ethical, evidence-based, and inclusive adoption of AI across India’s healthcare system.
It aims to provide strategic direction on governance, data stewardship, validation, deployment, and monitoring of AI solutions, while supporting States and institutions in responsible adoption aligned with public health priorities.
"SAHI is not merely a technology strategy but a governance framework, policy compass, and national roadmap for the responsible use of AI in healthcare,” said Nadda.
He stated that SAHI will guide India in leveraging AI in a manner that is ethical, transparent, accountable, and people-centric. Nadda also emphasized that SAHI provides a structured framework for collaboration, ensuring that innovation flourishes while public interest remains paramount.
The second initiative, BODH, was developed by the Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur in collaboration with the National Health Authority. It is a privacy-preserving benchmarking platform that enables rigorous evaluation of AI models using diverse, real-world health data without sharing underlying datasets.
As a digital public good under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, it is designed to strengthen trust, transparency, and quality assurance in Health AI deployment.
"The collaboration between Government and academia has led to the development of BODH -- the Benchmarking Open Data Platform for Health AI -- which provides a structured mechanism for testing and validating AI solutions before deployment at scale,” said Nadda.
Nadda reiterated that AI solutions must be rigorously evaluated for performance, reliability, and real-world readiness. Together, SAHI and BODH represent India’s commitment to building a trustworthy, inclusive, and globally competitive health AI ecosystem grounded in innovation, responsibility, and public trust.
AI An Indispensable Enabler to Viksit Bharat
Earlier, delivering the keynote address at a session themed “Innovation to Impact: AI as a Public Health Game-Changer”, at the Summit, Anupriya Patel, Union Minister of State for Health and Family Welfare, highlighted AI as an "All-Inclusive Intelligence".
She also emphasized AI's potential in addressing "health inequities across the country".
Patel called technology -- particularly AI "an indispensable enabler" in India's race towards the vision of a Viksit Bharat by 2047.
She highlighted the potential role of AI on India’s vast and diverse population, the rural–urban divide, and the dual burden of communicable and non-communicable diseases, which present unique challenges.
She also noted that AI has been integrated across the entire continuum of healthcare -- from disease surveillance and prevention to diagnosis and treatment.
H3N2 Not Just Common Cold, Experts Say Do Not Self-Medicate

Credit: Canva
While the national capital is seeing a significant rise in H3N2 Influenza A cases, experts explained that it's not just the common cold and people must not try to self-medicate.
Speaking to Health And Me, multiple experts stressed the need to treat the virus properly, as its symptoms can last longer and potentially lead to pneumonia.
What Is The H3N2 Virus?
H3N2 is a subtype of the Influenza A virus that causes seasonal flu. The symptoms are often stronger and more persistent, with many patients reporting prolonged fatigue, cough, breathing difficulty, and slower recovery.
It is highly contagious, spreading via respiratory droplets (coughing/sneezing) and contaminated surfaces. The symptoms usually last 5–7 days, with treatment focusing on rest and symptom management.
Dr. Mohit Saran, Consultant - Internal Medicine and Diabetologist, Manipal Hospital, Gurugram, told this publication: “H3N2 is not just a common cold. While symptoms may not appear instantly, they can lead to high fever, constant cough, body pain, and breathing issues. In some people, this can also increase the risk of pneumonia or the need for hospitalization if not managed early.”
The experts attributed the surge in the disease to factors such as changing weather, fluctuating temperatures and reduced immunity.
Who Is At The Highest Risk For H3N2?
Children, youngsters, senior citizens, pregnant women and people with low immunity or with conditions such as asthma, diabetes, or heart problems are more vulnerable to H3N2. Health care professionals and people who are exposed to crowded places may also be affected by this disease.
Dr. Atul Gogia, Head of Infectious Diseases, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, told Health and Me that the H3N2 virus "predominantly affects elderly people and those who have comorbid illnesses".
"We need to be especially careful because this illness predominantly affects individuals with comorbid conditions, the elderly, and those who are more vulnerable to developing complications that may require hospitalization,” he said.
Why Does H3N2 Last Longer Than The Common Flu?
Symptoms of H3N2 infection can last for two to three weeks, with a lingering dry cough and fatigue being common.
The virus often affects the lower respiratory tract, leading to more intense coughing and breathing discomfort. Young children, older adults, and individuals with chronic health conditions are at higher risk of complications.
"H3N2 is considered more infectious because of its ability to mutate quickly and adapt to the human host. This high mutation rate allows the virus to evade the immune system more effectively and can lead to more severe outbreaks. It spreads easily through respiratory droplets, direct contact, and contaminated surfaces,” explained Dr. Manisha Arora, Director - Internal Medicine at the CK Birla Hospital(R), Delhi told HealthandMe
"Frequent changes in its surface proteins, a process known as antigenic drift, make it harder for the body to recognize and fight the virus, which can result in more hospitalizations and, in severe cases, increased mortality,”
How Can The Disease Be Prevented?
H3N2 can be prevented through regular handwashing, wearing masks in crowded places, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, and avoiding self-medicating. Flu vaccination, timely medical consultation for long-term fever, and adequate rest help reduce the risk and further spread of the condition.
The experts recommended that all adults above 18 consider annual flu vaccination ideally in August or September, unless they are currently experiencing flu-like symptoms.
Maintaining good hygiene, eating nutrient-rich foods, staying hydrated, and following healthy habits can help boost immunity.
Greater Noida Locals Contract Food Poisoning From Kuttu Flour, Here's Why

Credit: TOI
Over 70 residents in Supertech Ecovillage-3, Royal Court Society and Himalaya Pride Society, Greater Noida have contracted food poisoning after they consumed a specific batch of buckwheat (kuttu) flour during Mahashivratri this weekend.
The widespread outbreak has caused panic and triggered a police investigation. As a result, officials sealed Prashant General Store, a retail shop in Royal Court Society and HD Spices, a primary warehouse in Chipiyana Buzurg village suspected of selling the spoiled batch.
Moreover, four people including the warehouse owner have now been detained by the Bisrakh police. Assistant Commissioner of Food, Noida, Sarvesh Kumar said lab tests are yet to confirm whether the infection was due to bacterial contamination, fungal toxins or adulteration.
This incident adds to a troubling trend of food and water contamination in the area, a topic that has recently reached discussions in Parliament. Improper storage allows toxic molds like aflatoxins to grow, triggering rapid-onset vomiting and dehydration, especially on the empty stomachs of fasters.
This "Buckwheat flour poisoning" occurs because the flour's high natural oil content makes it highly perishable; when stored in humid or warm conditions, these oils oxidize, creating a breeding ground for toxic molds and bacteria.
Why Is Buckwheat (Kuttu) Flour Harmful For Your Health?
Despite its reputation as a "pure" fasting food, buckwheat flour carries a hidden risk: its high natural oil content. Unlike refined grains, these healthy fats are highly unstable; when exposed to heat or moisture, they oxidize and turn rancid.
This transformation from a nutrient-dense staple to a source of food poisoning commonly occurs when households treat it like a non-perishable grocery item rather than the sensitive, short-lived ingredient it actually is.
The real danger of buckwheat flour lies in storage. Because buckwheat flour is used sporadically, it often sits in pantries in unsealed packets, warm cupboards or humid environments for months and becomes a silent breeding ground for dangerous molds and bacteria over time
The degradation is often hard to spot; a faint bitter aroma or slightly clumpy texture can easily be hidden by the strong spices and oils used in traditional fasting recipes.
Along with this, expired or damp buckwheat flour can harbor aflatoxins and other toxic compounds beneath the surface. Once ingested, these irritants attack the stomach lining, triggering a rapid physical "rejection," usually within just a few hours.
What Is Buckwheat-Caused Food Poisoning?
If you suspect someone has consumed contaminated buckwheat flour, these are the primary symptoms to watch for:- Intense Nausea and Vomiting: Usually the first sign, as the body tries to expel the toxins.
- Acute Abdominal Pain: Sharp cramps or bloating in the stomach area.
- Fever and Chills: A sudden rise in body temperature as the immune system reacts.
- Diarrhea (Loose Motions): Frequent and watery stools.
- Extreme Weakness: Feeling dizzy, shaky, or completely drained of energy.
- Dehydration: Dry mouth and reduced urination due to fluid loss.
How To Safely Store Your Flour
- Buy Small, Buy Fresh: Purchase only the amount needed for the current fasting period. Avoid bulk buying buckwheat flour to store for the next season.
- Check the Date: Always look for the manufacturing date. If it’s more than two months old, it may already be turning rancid.
- Airtight & Cool: Transfer the flour to an airtight glass or metal container immediately. Store it in a cool, dry place, or better yet, refrigerate it to slow the oxidation of its natural oils.
- The "Sensory" Test: Before cooking, smell the flour. If it has a bitter, soapy, or musty aroma, throw it away. Fresh buckwheat flour should have a mild, nutty scent.
- Keep it Dry: Ensure your hands and measuring cups are completely dry before touching the flour, as moisture triggers fungal growth.
- Don't Mix Batches: Never mix new flour with old leftovers from a previous fast.
Who Is At The Highest Risk?
While anyone can get food poisoning, women, children and the elderly are at the highest risk. The practice of fasting can actually make the illness more dangerous. On an empty stomach, even a small amount of mold or bacteria can trigger an explosive physical response.
Furthermore, fasting usually involves lower water intake; once vomiting or diarrhea begins, the body loses its remaining fluid reserves instantly, leading to rapid, severe dehydration.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

