- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
6 Modern Lifestyle Habits That Are Keeping You Constipated- Here's How To Fix It

Image Credits: Health and me
Chronic constipation can be more than a passing annoyance—it can disrupt daily life, impacting mood, energy, and overall health. Occasional constipation is not uncommon, but chronic constipation is a recurring problem that could be a sign of an underlying medical condition. Some are relatively harmless and simple to treat, but others will need medical attention.
Chronic constipation is more than an occasional annoyance—it can have a profound effect on daily functioning and overall well-being. Knowing what causes it, making the needed lifestyle changes, and getting the right treatment can bring substantial relief.
What Is Chronic Constipation?
Chronic constipation is defined by less than three weekly bowel movements that are hard to pass or that take a long time, lasting more than several weeks. Symptoms of this condition include less than three weekly bowel movements, straining during bowel movements, hard stools, bloating, and the feeling of incomplete evacuation. Epidemiological studies have shown that as many as 63 million North Americans have diagnostic criteria for chronic constipation, with prevalence rising with advancing age and being higher in women than men.
Dr. Kishan, Consultant Proctologist & Gastro Surgeon, points out the pervasiveness of constipation: "Constipation affects 16 out of every 100 adults and despite its prevalence, many people overlook it, assuming it to be a minor inconvenience rather than recognizing it as a legitimate health concern."
If left untreated, chronic constipation can significantly affect an individual's quality of life and even result in complications like hemorrhoids, anal fissures, and fecal impaction.
Causes of Chronic Constipation
Causes of chronic constipation are very diverse and can be classified into structural, medical, medication-induced, and functional causes. Chronic constipation may at times be a manifestation of underlying medical conditions, which include:
- Conditions such as colon cancer, strictures, or narrowing of the intestine may prevent normal stool passage.
- Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, and spinal cord injuries may disrupt normal bowel function.
- Diabetes and hypothyroidism may slow down digestion and cause constipation.
- Hormonal changes and compression of the intestines may cause constipation.
Some medications may cause chronic constipation, including:
- Opioid pain medications (narcotics)
- Calcium channel blockers (for high blood pressure)
- Anti-seizure drugs
- Antidepressants
- Iron supplements
- Antispasmodics
When in such cases drug is the only cause, switching to another under medical guidance could relieve symptoms.
Constipation Without Any Underlying Condition
Functional constipation happens when there is no underlying medical or structural cause. Three are the leading types:
- Normal rate of passing stool through colon but hard in consistency and therefore difficult to pass.
- The colon absorbs too much water, resulting in hard, dry stools and slow bowel movements.
- A condition where pelvic floor muscles do not coordinate properly during bowel movements, leading to difficulty in passing stool.
Modern Lifestyle Habits Contributing to Chronic Constipation
Urban lifestyles of today contribute significantly to the rising incidence of chronic constipation. Lack of physical activity, irregular meal times, and stressful environments interfere with the natural functioning of the body. As per Dr Kishan, "Chronic constipation has a major effect on digestive health, is most commonly a direct consequence of modern lifestyle behaviors that interfere with the body's natural rhythm. The problems of chronic constipation reach far beyond mere physical discomfort, influencing overall well-being and quality of life."
There are a number of factors associated with modern-day lifestyles that add to the prevalence of chronic constipation, which are as follows:
Sedentary lifestyle: Physical inactivity makes it more difficult for the digestive system to work optimally.
Inadequate dietary fiber intake: Diets devoid of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains tend to provide low dietary fiber intake, which is necessary for good digestion.
Poor hydration: Most people do not drink enough water, and this makes the stools harder and more difficult to pass.
Processed and fast foods: Greater dependence on nutrient-deficient, high-fat, and low-fiber foods worsens digestive issues.
Stress and irregular routines: Elevated levels of stress and irregular eating times disrupt the body's inherent digestive rhythms.
Overuse of laxatives: Regular or long-term laxative use causes dependency, compromising the body to naturally control bowel movements.
Managing and Treating Chronic Constipation
A holistic treatment plan involves dietary changes, lifestyle adjustments, and, in certain situations, medical treatments.
1. Dietary Changes
Diet is one of the best methods for controlling chronic constipation.
Boost fiber – Eat more fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Hydrate – Drinking 8-10 glasses of water per day softens stools and facilitates bowel movements.
Add probiotics – Yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods support a healthy gut microbiome.
2. Physical Activity
Physical exercise is essential to digestive well-being.
Walking – A 20-30 minute daily walk keeps intestinal motility going.
Yoga and stretching – Specific yoga exercises assist in the relief of constipation.
Core strengthening exercises – Use abdominal muscles to help with digestion.
3. Stress Management
Severe levels of stress affect digestion. Ways to control stress include:
Meditation and deep breathing exercises
Adequate sleep – No rest causes interruption in digestion.
Mindful eating – Eating calmly enhances digestion.
4. Advanced Medical Treatments
For those that don't succeed with lifestyle adjustments, medical treatments can be the solution.
Colon Hydrotherapy – A non-surgical process that facilitates colon cleansing.
Biofeedback Therapy – Employed to retrain pelvic floor muscles in defecatory disorders.
Prescription Medications – Medicines like fiber supplements, stool softeners, and prokinetic agents can help bring relief.
Surgical Interventions – In a few instances when other treatment doesn't work, surgery can be suggested to correct structural problems.
It is crucial to visit the doctor if constipation is long-standing, along with bleeding from the rectum, sharp pain, unexplained weight loss, or if the symptoms are getting worse despite changing lifestyle.
Dr Kishan is a Consultant Proctologist & Gastro Surgeon at Healing Hands Clinic, Bengaluru in India
Breast Cancer Awareness Month: Nutritionist Reveals 6 Foods That May Lower Breast Cancer Risk

Credits: Canva
October is Breast Cancer Awareness Month, making it the perfect time to focus on habits that can help protect your health. While no single food can guarantee prevention, research shows that certain nutrients and antioxidants found in everyday foods may play a role in reducing the risk of breast cancer. For women, especially those with risk factors, incorporating these foods into your diet can be a meaningful step toward prevention.
Understanding Breast Cancer
Breast cancer occurs when breast cells start to grow abnormally and form tumours. If these tumours are not treated, they can spread to other parts of the body and become life-threatening. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), this disease claimed an estimated 670,000 lives worldwide in 2022. In India, breast cancer is also increasing, with one in 28 women now at risk. This makes it all the more important to understand ways to lower risk through lifestyle and dietary choices.
6 Foods To Prevent Breast Cancer
Nutritionist and weight loss specialist Leema Mahajan took to her Instagram to highlight the power of food in breast cancer prevention. She emphasizes starting early: “Introducing these foods into your diet from a young age can help reduce your chances of developing this disease later in life.” Mahajan identifies six key foods backed by research for their potential protective benefits.
1. Pomegranate
Pomegranates are rich in compounds called ellagitannins, which studies suggest may help slow down the growth of cancer cells and limit estrogen-driven tumour development. Mahajan recommends enjoying one cup of fresh pomegranate each day. “Fresh pomegranate seeds can support your body’s fight against abnormal cell growth. It’s simple, delicious, and effective,” she says.
2. Cruciferous Vegetables
Vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts belong to the cruciferous family, known for their cancer-fighting properties. These vegetables contain sulforaphane, a compound that aids the liver in breaking down harmful estrogen by-products and may help prevent tumour formation. Mahajan advises, “Include cruciferous vegetables in your meals three to four times a week. You can eat them raw in salads or lightly steamed to retain their nutrients.”
3. Berries
Berries such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are packed with antioxidants, particularly anthocyanins, which help combat cell damage and inflammation. Adding a handful of berries to your breakfast or as a snack is a tasty and nutritious way to support your body’s natural defenses.
4. Fatty Fish
Omega-3 fatty acids found in salmon, mackerel, and sardines may have anti-inflammatory properties that reduce cancer risk. Including fatty fish two to three times a week can support overall health and may help maintain hormone balance.
5. Green Tea
Green tea contains polyphenols, which have been shown to slow cancer cell growth in laboratory studies. Drinking two to three cups daily can be a simple, comforting habit with potential protective benefits.
6. Tomatoes
Tomatoes are rich in lycopene, an antioxidant linked to lower cancer risk. Cooking tomatoes, such as in sauces or soups, makes lycopene more easily absorbed by the body.
Small Changes, Big Impact
Incorporating these foods into your daily meals isn’t just about prevention, it’s also about building a sustainable, healthful lifestyle. While diet alone cannot prevent breast cancer, combining these nutritious foods with regular exercise, adequate sleep, and routine medical screenings can strengthen overall health and reduce long-term risk.
Eating with awareness, enjoying colorful fruits and vegetables, and making consistent, balanced choices can empower women to take charge of their health, one meal at a time.
Cancer Risk May Increase Depending On Where You Carry Fat: Study Links Excess Fat In This Part Of Body To Cancer

(Credit-Canva)
New research suggests that the common way doctors measure a healthy weight, called Body Mass Index (BMI), may not be the best tool for figuring out a person's risk for cancer. Instead, the study found that where a person carries their extra fat, especially fat around the stomach, is a much more important clue.
A new study published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, found that belly fat plays a big role, not just in our general health but also in cancer. However, how does fat around your mid-section define this?
Where Your Fat Sits May Be Key
For many years, doctors have used BMI (which is calculated from your height and weight) to see if someone is overweight or obese and then use that status to estimate their risk for various cancers. However, this new study found that relying only on BMI is too basic. The research suggests that the location of extra fat on your body might be just as important, if not more so, in deciding whether your risk of developing several types of cancer goes up or down.
How Belly Fat Increases Risk Of Cancer
The study used advanced methods to look at the relationship between fat in five different areas of the body and the risk for 12 common cancers linked to being overweight. The clearest and most alarming finding was that fat around the abdomen (belly fat) was the most dangerous type of fat:
Increased Risk
Belly fat was directly linked to a higher chance of developing three specific cancers: endometrial cancer (of the uterus), esophageal cancer (in the food pipe), and liver cancer.
Worse Health Marker
Doctors pointed out that carrying fat in the center of your body is already known to cause problems like diabetes and heart disease. They believe this is because central fat causes a lot of inflammation inside the body, and this inflammation is what can actually encourage cancer to grow.
Are There Benefits Of Having Belly Fat?
While fat around the stomach was dangerous, the researchers made a surprising discovery about lower body fat. They found that fat carried in the buttocks and thighs actually seemed to help protect against cancer. This fat was linked to a reduced risk of both breast cancer and a type of brain tumor called meningioma. This unexpected result has led some experts to think that the fat cells in the lower body might produce helpful hormones that fight against cancer.
Why BMI Isn't Enough
This research strongly confirms that doctors shouldn't just rely on the single BMI number. As one cancer doctor noted, BMI is a "quick and dirty" measurement that only gives a very basic picture of your health; the location of excess fat matters much more. Scientists believe fat increases cancer risk in a few ways, including:
- Producing extra hormones like estrogen and insulin, which are known to fuel the growth of many cancer types.
- Creating a state of chronic inflammation in the body, which helps tumors get started and grow.
The study concludes that future health plans, both for treating obesity and preventing cancer, should focus on measuring and managing where fat is distributed rather than just focusing on overall weight. While losing weight is still beneficial, the body part where the fat is concentrated is a powerful indicator of risk.
First Kidney Transplant With Universal Blood Type Performed: Here's How Scientists Achieved This
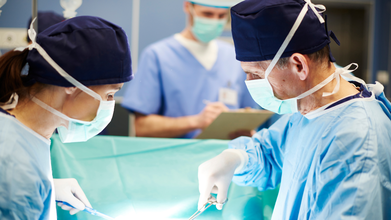
(Credit-Canva)
There are many aspects of an organ donation, not just the need for an organ, but also how compatible it is in terms of blood type. The reason why this is important is because of components known as antigens. The recipient's own body can destroy the new organ if the donated organ has different antigens. However, scientists may have found a way to surpass this issue.
A major scientific breakthrough has occurred: scientists successfully changed the blood type of a donated kidney using a special enzyme and then transplanted it into a patient. This is the first procedure of its kind. Right now, a patient can only receive an organ if the donor has a compatible blood type. If the types don't match, the patient's immune system will immediately produce antibodies or immune soldiers to attack and destroy the foreign organ.
How Did The Mismatched Blood Type Transplant Work?
The research team from Canada and China found a special enzyme that can remove the Type A antigens from an organ. Antigens are the markers on blood cells (and organs) that determine blood type. By removing the Type A markers, the enzyme essentially converts Type A blood into Type O blood.
Type O is considered the "universal" donor type because anyone can receive it. In this first test, the converted Type O kidney was transplanted into a 68-year-old patient. Although the kidney eventually showed signs of rejection after two days, it was able to function and produce urine for six days, proving the concept works.
How Does A Universal Kidney Work?
If doctors can successfully change the blood type of a donor organ, the current limits on transplants would largely disappear, creating enormous benefits for patients.
Significantly Increased Access to Organs
Without the need to match blood types, doctors wouldn't have to wait for an organ that is both a good match and the correct blood type. Instead, they could focus only on other factors important for the transplant's long-term success. By removing the blood type obstacle, this technology would allow for faster matching and quicker surgeries, which will dramatically reduce the painfully long waiting lists that patients currently face.
Shorter, More Efficient Wait Lists
Without the restriction of matching blood types, doctors wouldn't have to wait for an organ that is both a good match and the correct blood type. Instead, they could focus on other crucial factors, like matching proteins and tissues that are important for the long-term success of the transplant. By eliminating the blood type hurdle, this technology would allow for faster matching and quicker surgeries, drastically reducing the painfully long wait lists that patients currently face for life-saving organs.
Eliminating Risky Pre-Treatment for Recipients
This new approach of treating the donor organ instead of the patient is a major advancement. Right now, to perform a blood-type-mismatched transplant, the patient has to get intense treatments beforehand to severely weaken their immune system. These treatments are risky because they significantly increase the patient's vulnerability to severe infections.
Furthermore, for deceased donor organs—which must be used very quickly—there simply isn't enough time to safely administer these pre-treatments. By converting the organ outside the body, doctors can avoid this high-risk step for the recipient, making the transplant safer and much more feasible for emergency cases.
What Happens Next
This successful first attempt proves the enzyme-conversion technique works, but it's just the beginning. The scientists now need to conduct more studies on both brain-dead and living patients. Their main goal is to figure out the best way to adjust the treatment so that the converted organ can function successfully for a long period, ultimately allowing this revolutionary technique to be used in hospitals everywhere.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

