- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
Dermatologists Share 9 'Quick Fix' To Try When Acne Won’t Clear

Image Credit: Canva
Struggling with stubborn acne that just won’t go away? You’re not alone! Acne isn’t just about clogged pores—it’s influenced by hormones, stress, diet, and even the products you use daily. From painful cysts to pesky blackheads, breakouts can feel frustrating. But don’t lose hope! With the right skincare routine, patience, and dermatologist-approved tricks, you can take control of your skin.
Acne can be stubborn, frustrating, and emotionally draining. For many, persistent breakouts don’t just affect their skin but also their self-confidence. If you’ve tried everything and still see blemishes, you might need to tweak your approach. While acne is an inflammatory condition, several other factors contribute to its persistence. Here’s what you can do when nothing seems to work.
1. Stick to a Treatment for at Least Four Weeks
One of the biggest mistakes people make when treating acne is switching products too frequently. It’s tempting to try a new cream or cleanser every few days, but this can irritate your skin and worsen breakouts. Acne treatments require time to work—typically four to six weeks for noticeable improvement and two to three months for significant clearing. Even when your skin improves, continue using the treatment to prevent new breakouts.
2. Target Different Causes of Acne Simultaneously
Acne isn’t caused by just one factor; bacteria, clogged pores, excess oil, and inflammation all play a role. If a single treatment isn’t working, consider adding a second product that targets a different cause of acne. For instance:
- Benzoyl peroxide helps kill acne-causing bacteria.
- Retinoids like adapalene gel unclog pores and reduce oiliness.
- Salicylic acid eases inflammation and clears out pores.
Using a combination of these ingredients—rather than just one—can be more effective in reducing stubborn acne.
3. Follow Instructions Carefully
Even the best acne treatments won’t work if not used correctly. If a dermatologist prescribed a regimen, follow it precisely. Using too little may be ineffective, while using too much can cause irritation. Read product labels carefully and stick to recommended usage.
4. Wash Your Face Twice a Day (But Not More)
While cleanliness is important, over-washing can strip your skin of natural oils and lead to increased oil production, worsening acne. Dermatologists recommend washing your face:
- In the morning
- Before bed
- After sweating
Use a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser to remove dirt, excess oil, and bacteria without irritating your skin.
5. Stop Scrubbing Your Skin
Scrubbing might seem like a good way to deep-clean your pores, but it can actually aggravate acne-prone skin, leading to more breakouts. Opt for a gentle cleansing routine using your fingertips rather than washcloths or harsh scrubs.
6. Choose Non-Comedogenic Skin Care Products
Many skin care and cosmetic products contain oils and ingredients that can clog pores. Look for labels that say:
- Non-comedogenic
- Oil-free
- Won’t clog pores
Even with these labels, some people may still react to certain products, so consider testing new ones on a small patch of skin before full application.
7. Stop Touching, Picking, and Popping Pimples
It’s tempting to pop a pimple, but doing so can push bacteria and debris deeper into the skin, leading to increased inflammation and a higher chance of scarring. Resist the urge to touch your face, as your hands carry bacteria that can worsen acne.
8. Apply Acne Medication to All Acne-Prone Areas
Many people make the mistake of applying acne treatments only to visible pimples. However, acne often forms beneath the surface before appearing. Applying a thin layer of acne treatment to all acne-prone areas (not just individual blemishes) can help prevent future breakouts.
9. Consult a Dermatologist
If over-the-counter treatments aren’t working, it may be time to see a dermatologist. Professional treatments like prescription retinoids, oral antibiotics, or hormonal therapies can address stubborn acne more effectively. Seek medical advice if:
- Your acne is severe, causing painful cysts or nodules.
- You have persistent acne despite months of treatment.
- Acne is leaving scars or affecting your confidence.
We Can Predict Heart Attacks Before They Happen, So Why Are We Not Doing It?

Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of death globally, and while technology has evolved to the point where predicting heart attacks is possible, the medical world still struggles to put this into practice. Experts point to both promise and pitfalls in predictive cardiology, revealing why such life-saving tech is not yet a mainstream reality.
The Tech Is Here, But We Are Not Using It Enough
Dr. Vikrant B. Khese, Cardiologist at Jehangir Hospital, Pune, says the idea that we can predict heart attacks before they happen is both “exciting and frustrating, because while the technology exists, its real-world implementation remains limited.”
He explains that artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have incredible potential in this field. These tools can analyse vast datasets, such as blood pressure, lipid profiles, ECGs, imaging, and even genetic markers, to uncover patterns that might be invisible to the human eye. “These tools can detect subtle risk factors that may be missed in routine clinical practice. However, several challenges continue to hold us back,” he says.
One of the biggest concerns is the source of the data feeding these algorithms. “The majority of AI models are trained on Western datasets that do not reflect the unique genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors of Indian or Asian populations. This creates a mismatch, resulting in lower accuracy and reliability for non-Western patients.”
Dr. Khese adds that cardiovascular disease is deeply multifactorial. It is not just about clinical metrics. “Stress, socioeconomic status, cultural diet patterns, air pollution, and unstructured physical activity all influence risk but are difficult to quantify in a dataset. AI still struggles with these intangible but crucial variables.”
And even when predictive tools are developed, another hurdle lies in the healthcare system’s ability to use them. “Data-driven predictions can only be as good as the data input. In India, inconsistent electronic medical records, underreporting, and fragmented healthcare systems make it harder to gather high-quality longitudinal data, limiting the AI's learning potential.”
Crucially, there is also a behavioural gap. “Even when prediction tools exist, they are not routinely used by clinicians due to scepticism, lack of training, or workflow disruption. Bridging the gap between innovation and implementation is a major hurdle.”
According to Dr. Khese, technology must complement clinical judgement, not replace it. “AI is a powerful tool but not a standalone solution. Until we combine high-quality, representative data with clinical wisdom and system-level integration, the promise of predicting heart attacks before they happen will remain underutilised. The future lies in synergy; technology must empower doctors, not replace them.”
Prediction Tools Exist—But We’re Waiting for Symptoms
Dr. Vijay D'Silva, Medical Director of White Lotus International Hospital and Clinical Advisor and Mentor of Heartnet India, backs this view and draws attention to major international trials. “Research from the University of Oxford has suggested that a global trial of an AI tool that can predict the 10-year risk of heart attack has shown that in about 45 per cent of patients with chest pain, treatment could be improved,” he shares.
“Early detection of cardiac risk allows timely treatment and monitoring that can help reduce the mortality rate,” he says, explaining that most coronary blockages are asymptomatic. “Some present with chest, arm or jaw pain on exertion (angina pectoris). Few present as a heart attack or sudden death. People seek treatment after a heart attack when the damage is already done.”
According to Dr. D’silva, “With the help of the right tools, it is now possible to predict a heart attack before it occurs.” Among these tools are blood tests, ECGs, and advanced risk calculators such as the AHA PREVENT calculator, ASCVD Risk Calculator Plus, QRISK3, and SCORE2.
He points out how the 2023 AHA PREVENT calculator estimates 10-year cardiovascular risk in individuals aged 30 to 79, and 30-year risk in adults aged 30 to 59. “Early-stage detection of CVD minimises the cost and also reduces the CVD mortality rate,” he says.
This tool divides patients into four risk categories, each with its own treatment strategy:
- Low risk (<5%): Maintain healthy lifestyles and reassess every five years.
- Borderline risk (5–7.4%): Lifestyle changes and monitoring of risk-enhancing factors like BP, sugar, weight and lipids. CAC scoring can further stratify risk. Annual reassessment recommended.
- Intermediate risk (7.5–19.9%): Calls for lifestyle management, preventive medication (statins or aspirin), stress testing and CT coronary angiogram. Yearly reassessment is needed.
- High risk (≥20%): Requires intensive lifestyle changes, pharmacotherapy, imaging and close follow-up.
Despite these advances, Dr D'Silva says, “The gap lies in implementation. Most people still wait for the symptoms to appear before seeing a doctor. Heart attacks, unfortunately, strike without any warning, especially in women and younger patients, where symptoms can be atypical.”
He stresses that predictive cardiology is not yet standard in clinical practice. “People who are at risk seek care when symptoms arise. But in cardiology, symptoms often come too late. Up to 50 per cent of heart attack victims had no prior warning signs.”
Why Risk Calculators Are NotFoolproof
While risk calculators are promising, Dr. D’silva also points out their limitations. “The risk calculator may underestimate the risk in the following situations,” he says, listing specific high-risk groups such as:- Patients with LDL cholesterol ≥190 mg/dL
- Those with familial hypercholesterolemia
- Patients with type 1 diabetes
- People with other risk-enhancing factors like family history of early cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, chronic kidney disease, chronic inflammatory diseases (psoriasis, RA, lupus), or early menopause
The Way Forward
Both experts agree: predictive tools are no longer science fiction, but adoption is patchy. As Dr. Khese puts it, “The future lies in synergy; technology must empower doctors, not replace them.”Dr. D'silva concludes, “The ability to predict heart attacks is advancing continuously, but we need public awareness and equitable access to make predictive cardiology more standard.”
In short, we can predict heart att but until we normalise risk screening, improve data systems, and bridge the clinical gap, too many heart attacks will continue to catch people and systems off guard.
World Alopecia Day: Experts Bust Popular Myths and Reveal Hidden Health Issues Behind Hair Loss
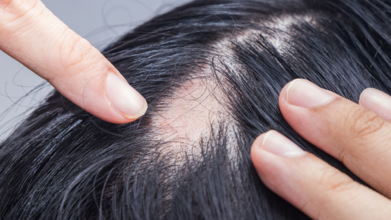
When strands clog your shower drain or your brush looks full every time you run it through your hair, panic is a natural response. Hair loss, or alopecia, is not just a cosmetic concern; it often hints at something deeper. And yet, thanks to internet half-truths and old wives’ tales, myths about alopecia spread faster than a viral meme. On World Alopecia Day, we turn to experts to separate fact from fiction while spotlighting the hidden medical conditions that might be behind the hair fall.
It is Not Just "Shedding Season": Medical Reasons Behind Hair Loss
Alopecia does not always pop up on its own. According to Dr Jijith K Ravindran, Chief Cosmetologist and Dermatologist at Cosmalife Skin Clinic in Bengaluru, alopecia often walks hand in hand with other medical conditions, and sometimes, it is your body’s way of waving a red flag.Autoimmune Disorders (Alopecia Areata):
Dr Ravindran explains, “In this condition, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss on the scalp or other body parts.” It is unpredictable, affects people of all ages, and may be triggered by stress or genetics. If you have noticed coin-sized bald patches cropping up suddenly, your immune system could be the rogue agent.Hormonal Imbalances (Thyroid Disorders and PCOS):
Blame it on your hormones? Sometimes, yes. “Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt the hair growth cycle, causing diffuse hair thinning,” says Dr Ravindran. Women with PCOS are especially vulnerable. “Elevated androgen levels in PCOS weaken hair follicles, leading to noticeable hair fall.” It is not uncommon for women with irregular periods or acne to also see their hair thinning.Nutritional Deficiencies:
Crash diets might help you drop pounds, but they can also drop your hair count. “Low levels of iron, vitamin D, and essential proteins can contribute to excessive hair shedding,” warns Dr Ravindran. If your plate lacks balance, your scalp might pay the price.The good news? “Early diagnosis and treatment of these conditions can help restore hair growth and prevent permanent damage,” he assures.
Wigging Out Over Myths
Even as more people talk openly about hair loss, alopecia still suffers from a major PR problem, mostly due to persistent myths. Dr Roopam Gangurde, a dermatologist with an MD in Skin & VD, breaks down the most common fallacies that often do more harm than good.Myth 1: “Only men experience alopecia.”
“While male pattern baldness is more commonly discussed, women are equally susceptible to alopecia due to hormonal imbalances, thyroid issues, and nutritional deficiencies,” says Dr Gangurde. Yes, ladies lose hair too and not just from brushing too hard.
Myth 2: “Stress alone is responsible for hair loss.”
While stress is definitely not good for your scalp’s health, it is not the lone cause. “Alopecia usually has multiple triggers, including genetics, autoimmune conditions, and underlying medical issues,” explains Dr Gangurde. Translation: stressing about stress causing hair fall might make things worse.
Myth 3: “Alopecia is always permanent and untreatable.”
This one might be the most damaging myth of all. “Many forms of hair loss, especially those caused by hormonal or nutritional factors, are reversible with timely medical intervention,” says Dr Gangurde. PRP therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes can all turn things around if you act early enough.
Do Not Just Shed Tears, Seek Help
If your hair has been thinning or falling out in clumps, resist the urge to DIY it with oils, serums, or social media hacks. “If you experience sudden or persistent hair loss, consult a dermatologist or trichologist promptly,” advises Dr Gangurde. “Early intervention can address the root cause, prevent progression, and in many cases, restore healthy hair growth.” Remember that alopecia is not just a surface-level issue. And with the right diagnosis, it is often more fixable than you think.
What Makes Flu Season 2025 Different? Unique Symptoms Of Flu In 2025 And How Long The Infection Lasts

Credits: Canva
The 2025 flu season has turned out to be unlike any other in recent memory. This year, the flu season is marked by record-setting infections, multiple viral peaks, vaccine mismatches, and an overstretched healthcare system.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), this year’s influenza activity is the most intense since the 2009 swine flu pandemic, with over 80 million estimated illnesses and rising. What’s driving this intensity, and what should the public know about prevention and symptom management?
Let’s break down what makes this flu season so severe and what it means for your health.
A Season Like No Other: What Makes 2025 Different?
In most years, flu activity in the U.S. typically follows a predictable pattern, starting in October, peaking between December and February, and fading by April. But the 2024–2025 season has defied that rhythm.
Cases surged past the national baseline in December and then, unexpectedly, peaked again in February, a second wave that blindsided doctors and public health experts.
As of March 2025, the CDC had reported an estimated 37 million influenza infections, 480,000 hospitalizations, and 21,000 deaths. Hospitalizations, in fact, reached their highest levels in 15 years.
One key driver? A mismatch between circulating flu strains and this year’s vaccine. The dominant strains: H1N1 and H3N2, accounted for more than 99% of cases.
H3N2, in particular, is known for mutating quickly and evading immune responses, and only about half of circulating H3N2 samples matched well with vaccine antibodies, according to CDC surveillance data.
Post-Pandemic Immune Gap
Another reason this year’s flu is hitting so hard: our immune systems are still catching up.
During the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, widespread masking, social distancing, and school closures suppressed not just SARS-CoV-2 but also seasonal flu and other common respiratory viruses. While that helped in the short term, it reduced community-level immunity over time, especially among children, who typically build natural resistance through repeated exposures.
“Young children who were toddlers or preschoolers during the pandemic missed early exposures to flu viruses,” explained experts at the nonprofit group Families Fighting Flu. “Now they’re in school, more socially active, and more vulnerable.”
The CDC reported a troubling spike in pediatric flu deaths this season with 216 fatalities, making it the deadliest flu season for children outside of a pandemic year. Neurological complications such as seizures and hallucinations also rose among young patients.
A Shift in Viral Dominance
Another unusual trend: COVID-19 has taken a back seat this winter
Unlike previous years when COVID-19 variants dominated respiratory illness charts, flu has surged ahead as the top driver of doctor visits and hospitalizations. This could be due to a shift in viral dominance, changing weather patterns, or differences in immunity buildup. According to the CDC, nearly 8% of all outpatient visits are currently for flu-like symptoms, much higher than what’s typical for this time of year.
Vaccine Fatigue and Gaps in Coverage
Vaccination remains the strongest tool we have to fight influenza, but uptake has been stagnant, or worse, declining, in key groups.
As of April 2025:
- Only 49.2% of children and 46.7% of adults had received the flu vaccine
- Among pregnant women, that number dropped to 38%
- Medicare beneficiaries aged 65+ had just 48.3% coverage
- And overall, nearly 9.2 million fewer doses were administered compared to the pre-pandemic 2019–2020 season
Barriers like vaccine hesitancy, misinformation, racial and ethnic disparities in healthcare access, and fewer flu shot clinics in rural areas continue to widen the gap.
What Are the Symptoms in 2025?
The 2025 flu has shown typical but often more intense symptoms than in previous years. Here’s what to look out for:
- Sudden onset fever
- Severe body aches and chills
- Sore throat and persistent cough
- Nasal congestion
- Diarrhea and vomiting (more frequent in children)
- Extreme fatigue
- Headache
- In some children, neurological symptoms like confusion or seizures
These symptoms may overlap with COVID-19 or RSV, but tend to come on faster and hit harder in flu cases this season.
How Long Do Symptoms Last?
For most healthy people, flu symptoms begin 1 to 4 days after exposure and typically last about 5 to 7 days. However, fatigue and cough may linger for up to two weeks.
You’re considered most contagious in the first 3 to 4 days after symptoms start but can continue to spread the virus up to a week later. The CDC recommends staying home until you’ve been fever-free for at least 24 hours without medication.
Vaccinated individuals may experience milder or shorter symptoms, but those with underlying conditions, young children, and older adults may have longer recoveries and higher risk of complications.
Can the Flu Cause Serious Health Problems?
Yes, especially in people with weakened immune systems, chronic illnesses, or no prior flu immunity.
Possible complications include:
- Pneumonia
- Ear and sinus infections
- Exacerbation of asthma or heart disease
- Life-threatening conditions requiring ICU care
This is why experts stress that prevention remains the best medicine.
How to Protect Yourself and Your Family
Here’s how to lower your risk during the remainder of the 2025 season:
- Get vaccinated, even now. It may still protect against circulating strains
- Wash your hands often with soap and water
- Avoid touching your face in public settings
- Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
- Stay home if you’re unwell to prevent spreading the virus
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

