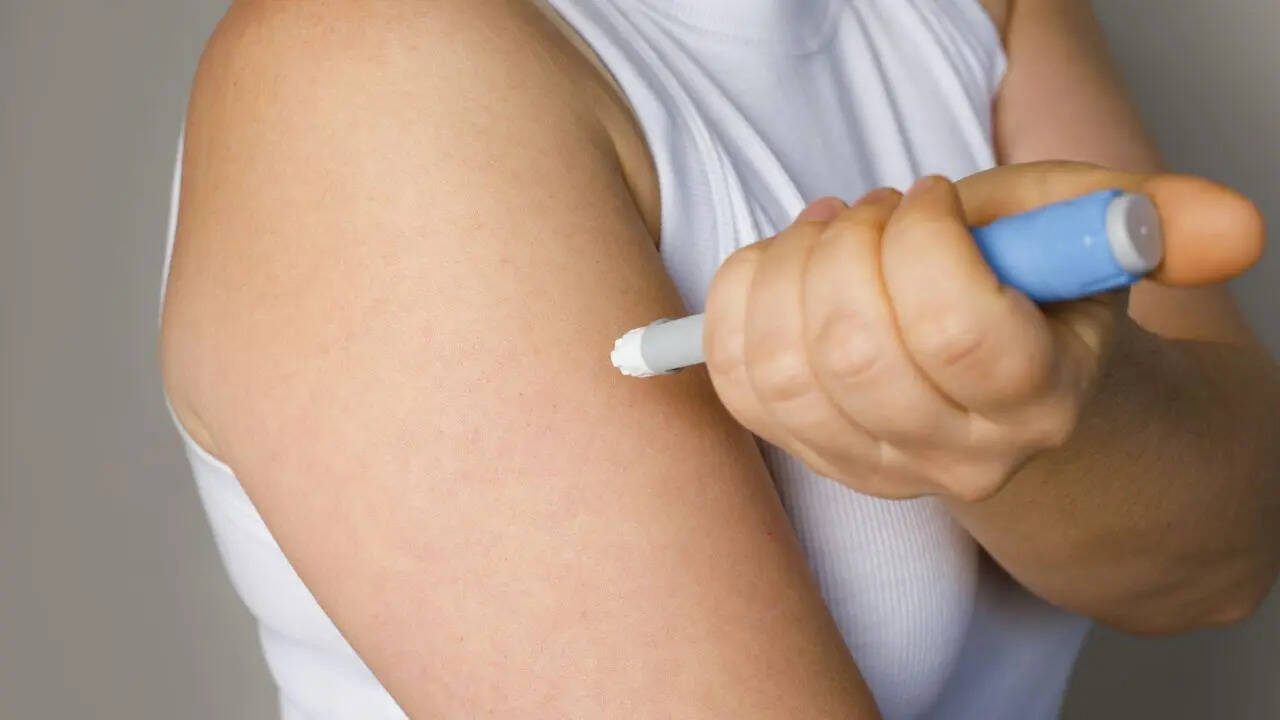
Doctors Issue New Alert For Popular Weight-Loss Jabs Semaglutide And Tirzepatide
Credits: Canva
Summary Major research finds people using weight loss injections like Wegovy and Mounjaro regain weight much faster after stopping treatment, raising concerns about long-term use, nutritional risks, and the need for ongoing lifestyle support.
End of Article
