- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
Headaches That Hurt Your Eyes: 5 Signs It’s Not Just Stress

Credits: Canva
Have you ever experienced one of those annoying headaches that's right behind your eyes, and it makes it even more difficult to concentrate or even keep your eyes open? You dismiss it, think of it as stress or getting too much screen time—but what if it's something more? Headaches related to eyes are a real thing, and they tend to go unnoticed until they begin affecting your daily activities. Whether you're always on your computer, missing eye exams, or simply believe it's "normal" to reach for a pain reliever and tough it out, this tale is your reminder to pause and pay attention to what your body—and even more specifically, your eyes—are trying to say.
Headaches are a common experience—unwelcome, usually inconvenient, and usually dismissed as the aftermath of a long day or hectic schedule but when that headache targets the back of your eyes and starts disrupting your daily routine, it's time to listen more intently. That is not tension alone it may be your body communicating something more.
For health professionals, especially ophthalmologists, chronic headaches that focus around or behind the eyes can be more than mere stress. They can be indicative of latent ocular or neurological conditions that require professional intervention. To learn when a headache can be more than just about stress—and when it's time to seek medical attention—we spoke with Dr. Neeraj Sanduja, an eye surgeon and ophthalmologist.
Link Between Your Headaches and Eyes
The eyes are intricate, high-performance organs which are used continuously—whether reading, driving, or working on computer screens. When they're being worked too hard or strained from underlying problems, they tend to express discomfort as headaches. These would usually be known as ocular headaches, and in contrast to those caused by stress, they can be accompanied with characteristic signs like eye pain, pressure, redness, or visual changes.
Dr Neeraj says, "The eyes are complex organs that work tirelessly throughout the day. When they are strained or affected by underlying conditions, the resulting discomfort can manifest as headaches. These headaches are often referred to as ocular headaches and can have specific characteristics that differentiate them from other types."
Curiously, pain felt in or around the eye isn't necessarily from the eye. Most of these are "referred pain"—a condition in which pain is felt in one location but is caused by another. This is why it is so easy to miss the actual cause, particularly when visual symptoms are minimal or none at all.
Signs Your Headache Isn't Just Stress
While stress is sure to produce headaches, the following indicators could mean that your headache stems from an eye condition or some other health problem:
1. Frequent or Daily Headaches Behind the Eyes
If you’re waking up with headaches or experiencing them routinely at the end of your workday, eye strain may be playing a central role. This is especially common in people with undiagnosed vision issues or those who stare at screens for extended hours.
2. Blurred or Fluctuating Vision
Headaches with associated changes in your ability to see clearly may point to issues like astigmatism or imbalance of the eye muscles. Such vision inconsistencies make the eyes work harder, resulting in pain that is referred to the temples or brow.
3. Eye Pain Without Redness or Obvious Irritation
If your eye appears to be fine but you still have pain in deep or rear parts of your eye, it might be connected to neurological or inflammatory disorders like optic neuritis. This necessitates urgent professional attention to eliminate pressure buildup or other severe conditions.
4. Glare, Halos, or Nausea
Conditions like glaucoma may raise intraocular pressure, leading to severe headaches and sensations like halos around lights, vomiting, or extreme eye pain. These are warning signs of the utmost concern that need immediate attention.
5. Difficulty with Focus and Coordination
A less familiar condition known as binocular vision dysfunction happens when the eyes are slightly out of alignment. This causes eye muscles to overwork, causing headaches, dizziness, and problems concentrating. Even slight misalignments can drastically affect your quality of life.
Dr Neeraj shares a list of causes which could indicate more than just a simple headache, indicating towards a serious problem at times.
Common Eye-Related Causes of Headaches
Eye Strain (Asthenopia): Prolonged activities like reading, using digital screens, or driving can strain the eye muscles. This strain often leads to a dull ache around the eyes or temples.
Uncorrected Vision Problems: Conditions such as nearsightedness (myopia), farsightedness (hyperopia), or astigmatism can cause the eyes to work harder to focus. This extra effort may result in headaches, especially after activities that require sustained focus.
Incorrect or Outdated Prescription Glasses: Wearing glasses or contact lenses with an incorrect prescription can strain the eyes, leading to headaches. Regular eye checkups are crucial to ensure your prescription is up to date.
Computer Vision Syndrome (Digital Eye Strain): Spending long hours in front of screens without adequate breaks can cause headaches due to digital eye strain. Symptoms may also include dry eyes, blurred vision, and neck pain.
Glaucoma: This condition increases intraocular pressure and can cause intense headaches, often around the eyes. Headaches due to glaucoma may be accompanied by symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or halos around lights.
Eye Muscle Imbalance: Misalignment of the eyes, even if minor, can lead to strain as the muscles work harder to maintain focus. This condition, known as binocular vision dysfunction, can cause frequent headaches.
Inflammatory Eye Conditions: Conditions like uveitis or optic neuritis (inflammation of the optic nerve) may cause severe headaches along with other symptoms such as vision changes or eye redness.
When to Seek Professional Help?
Dr Neeraj recommends, "If you experience headaches frequently and suspect they might be related to your eyes, it’s important to consult an ophthalmologist." If you’ve tried lifestyle adjustments, hydration, and stress management, and your headaches still persist, it’s time to look beyond the usual suspects. Consider seeking medical attention if:
- The headache is persistent or worsening.
- The headache is accompanied by blurry vision, eye pain, or redness.
- There are additional symptoms such as nausea, sensitivity to light, or difficulty focusing.
- You haven’t had a comprehensive eye examination in over a year.
Even if your symptoms appear to be under control, getting checked out early can avoid complications and reveal underlying conditions that could otherwise go undetected.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Eye-Related Headache
When you go to see an ophthalmologist for headaches, the test normally involves a complete determination of your visual acuity, intraocular pressure, and assessment of the optic nerves. Often, the issue might not be in the eye itself but how the eyes work together or how external usage such as screen time is affecting their health.
Depending on the diagnosis, your treatment could include:
- Corrected vision eyeglasses or contact lenses, updated.
- Lifestyle changes such as the 20-20-20 rule: look 20 feet away every 20 minutes for 20 seconds.
- Surgery or even medication for more severe conditions like glaucoma.
- Vision exercises or therapy for binocular vision dysfunction.
Prevention and Long-Term Eye Care
To avoid eye-related headaches, begin with routine eye exams—even if you don't wear glasses. When working extensively on computers or other digital devices, keep your work area well-lit, employ blue light filters, and take regular visual breaks. Drinking water and stress management will also contribute to overall eye and brain health.
It's also worth mentioning that kids and adolescents increasingly are also coming in with similar symptoms, particularly with our screen-dominated life. So, parents are to stay vigilant about behavioral signs such as irritability, squinting, or complaints of eye strain in younger generations.
All headaches are not equal. If yours center around or behind the eyes, or if they come with visual problems as a bonus, don't attribute them to stress without a probe. Your eyes may be sending a message your body can't ignore.
Dr Neeraj Sanduja is a MBBS, MS, Ophthalmologist, and Eye Surgeon at Viaan Eye and Retina Centre in India
Your Body Pain Has a Pattern: Expert Reveals What It Really Means
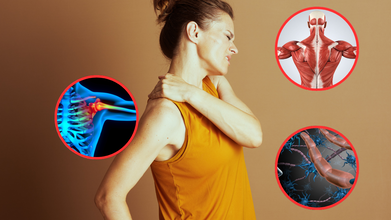
(Credit- Canva)
Sometimes body pain can be quite difficult to figure out. ‘Is it my shoulder muscle, or is it shoulder joint that’s causing me pain?’ We have all had these questions and struggled while answering them at the doctor’s office. This is a common experience that we all go through, and it can make things like finding what medication will help elevate the pain difficult.
So how do doctors figure this out? Explaining this in a video, Dr Pooja Chopra MD, shares a post on Instagram. Posted on 8th September, in the video caption Dr Chopra explained, “As a PM&R and Pain specialist, my first job is to be a detective. Tracing pain back to its precise source is the most critical step, because each source requires a completely different treatment plan.” She further goes on to give a simplified guide to help people understand their pain better. Understanding where the pain comes from can help people feel more at ease as well as figure out how serious the problem could be.
How To Tell Whether Your Muscle Is Causing Pain, Your Joint Or Nerve?
Muscle Pain
Muscle pain, also called myofascial pain, feels like a dull, deep ache. When you press on the sore spot, you'll feel tenderness and might even find what feel like tight knots or bands. This kind of pain gets worse when you use the muscle that's hurt, but it often feels better with simple things like resting, putting a heating pad on it, or doing some gentle stretches. You can usually point with one finger to exactly where it hurts.
Joint Pain
Joint pain, or articular pain, is a deep, internal ache that feels very stiff. It's not on the surface; it feels like it's coming from inside the joint itself. You might feel a sharp pain when you make a specific movement, like reaching high above your head. This type of pain is often at its worst when you first wake up in the morning, but it tends to get better as you start moving around and warm up the joint. Because the pain is deep, it can be hard to say exactly where it is.
Nerve Pain
Nerve pain, also known as neuropathic pain, is the most distinct kind of pain. It feels like sharp, shooting, burning, or "electric" shocks. People often describe it as a tingling sensation, like "pins and needles," or even numbness. A key sign of nerve pain is that it travels along a clear path, for example, from your neck all the way down your arm. This pain can come on unexpectedly, even when you're completely still and not moving the body part.
It's important to remember that these types of pain can be linked. For example, a problem with a joint could make the muscles around it tense up in a protective spasm, which could then pinch a nearby nerve. This is why a proper diagnosis from a specialist is so important. They use advanced tools like diagnostic ultrasound, which lets them see exactly what's happening inside your body, so they can treat the root cause of the pain precisely.
Chronic Insomnia Could Increase The Risk Of Dementia By 40%: Study

A new study has pointed out that people who have chronic insomnia could be at higher risk of dementia. One of the best things a person can do to recover from a tiring day, whether it is from a stressful day or after a tiring workout. However, it is not easy for everyone, there are many people who suffer with sleep problems like chronic insomnia.
An estimate of 16.2% of people around the globe suffer with insomnia according to 2025 Sleep Medicine Reviews, which is a condition that makes it hard to fall or stay asleep. A big number of these people have what's called chronic insomnia, meaning they've had this problem for at least three months, with poor sleep happening three or more nights a week.
Previous studies have already connected insomnia to serious health problems like heart disease and diabetes. But now, a new study in the medical journal Neurology has found an even more concerning link: people with chronic insomnia might be at a much higher risk for developing dementia and other memory problems. The study suggests that their brains could be aging faster as a result.
How Does Insomnia Cause Dementia?
For this study, researchers followed 2,750 older adults for an average of five and a half years. At the beginning, everyone was mentally healthy. The researchers found that the people who had chronic insomnia had a 40% higher chance of developing dementia or mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
Researchers explain that this is a huge finding because it means chronic insomnia could be a bigger risk factor for memory loss than having both high blood pressure and diabetes. They also discovered that those who slept less had more of the tell-tale signs of Alzheimer's disease in their brains, like amyloid plaques, and other signs of damage to their brain's blood vessels. This shows that poor sleep isn't just about feeling tired—it's linked to real, physical changes in the brain.
Why You Should Prioritize Sleep?
Experts believe that a big part of the problem is that insomnia is often overlooked. Many older adults just assume that bad sleep is a normal part of getting older. However, doctors stress that chronic insomnia is a real medical issue that goes beyond typical age-related changes. They urge doctors to start talking to their patients about their sleep habits during every check-up.
The good news is that chronic insomnia is a treatable condition. The main treatment is a type of talk therapy called Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I). The hope is that by recognizing and treating insomnia, doctors can help protect a person's brain health for years to come.
How Does Insomnia Affect Our Memory
Previous studies have shown that our cognitive abilities are affected by how much we sleep. A 2020 study published in the Journal of Neuroinflammation, explained that there is a strong connection between a person's sleep and their risk of developing Alzheimer's. We know that sleep is crucial for learning and creating memories. Studies have found that a lack of sleep and conditions like insomnia are not just a symptom of Alzheimer's—they may also play a role in its development.
This means that sleep disorders can have a significant impact on whether someone gets Alzheimer's and how fast the disease progresses. Because of this, it's important for doctors to pay more attention to sleep issues when diagnosing and treating patients. By properly screening for and managing sleep disorders, we might be able to help prevent or slow down the progression of Alzheimer's disease.
Daylights Savings Time May Be Causing You Higher Risk Of Heart Attacks And Obesity, Study Backs Fixed Standard Time

A new study from Stanford University suggests that daylight saving time isn't just an inconvenience; it could actually be bad for our health. The research shows that our twice-a-year routine of changing the clocks disrupts our bodies' natural rhythms, which can lead to serious health issues. This is a big deal because it provides the first real scientific evidence that this time-switching practice has a biological cost.
What is Daylight Saving Time?
According to the Sleep Foundation, daylight saving time (DST) has been an official practice in most of the United States since 1966. Only a few places, like Hawaii and parts of Arizona, don't follow it. The routine is simple: on the second Sunday in March, we set our clocks forward by one hour, losing an hour of sleep. Then, on the first Sunday in November, we set them back, gaining that hour of sleep. This is why many people remember it as "Spring Forward, Fall Back."
How Daylights Saving Time Affects Our Health
According to the study, if the U.S. got rid of daylight saving time and stayed on standard time all year, it could prevent thousands of strokes and significantly reduce obesity. The researchers, using mathematical models and data, estimated that this single change could prevent 300,000 strokes and lead to 2.6 million fewer people with obesity every year. This adds to what we already know about the negative effects of the time change, such as a spike in heart attacks and car crashes in the days after we lose an hour of sleep in the spring.
How Does Daylight Saving Time Affect Sleep?
Our body's internal clock is heavily influenced by light. When the clocks change, the amount of natural light we get in the morning and evening shifts. This can throw off our sleep-wake cycle, making it harder to feel alert in the morning and sleepy at night.
The “spring forward” change is particularly hard on us. One study found that on the Monday after the time change, the average person gets 40 minutes less sleep. This lack of sleep can build up over time, affecting our mood and increasing the risk of accidents.
While the "fall back" change in November can give us an extra hour of sleep, some people still struggle to adjust to the new schedule. For most people, the effects fade after a few days, but some studies suggest that others never fully adjust, leading to ongoing health problems.
Why Time Changes Mess With Our Bodies
The core problem lies in our body's internal clock, or circadian rhythm. Think of it as the conductor of an orchestra, directing all your body's processes. When it's working well, everything is in sync. But when it's thrown off, like by getting light at the wrong time of day, your body's systems can become disorganized.
This can weaken your immune system, mess with your sleep, and increase your risk for diseases like stroke and obesity. The study found that switching between standard and daylight saving time is the worst thing we can do for our body clock, much worse than staying on either time year-round. It's a bit like having the conductor suddenly change the tempo for no reason—the whole orchestra, or in this case, your body, gets thrown off.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

