- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
How Widespread Is Thalassemia In India—And What Can Be Done?

Credits: Canva
Thalassemia and Sickle Cell Anemia are among the most common inherited single-gene disorder in the world. They affect hundreds of thousands of babies each year. It is also estimated that between 300,000 and 400,000 babies born each year have severe hemoglobin disorders globally. These conditions also have a lifelong health implication. However, with awareness, testing and medical advancements, they can be managed and prevented.
What is Beta Thalassemia?
Beta Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder which is caused by a mutation in the beta globin gene. This gene is also essential for the production of normal hemoglobin. This is the protein in red blood cells that are responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. Every person has two copies of the beta globin gene.
If one of these genes is mutated, the person becomes a carrier, also known as having thalassemia minor. Carriers generally do not show any symptoms and have mild anemia, with their hemoglobin levels around 9d/dl and smaller red blood cells.
However, if both genes are mutated, the child could have thalassemia major, a severe form of disease. The symptoms usually appear around six months of age. The children suffer form chronic anemia and require lifelong, regular blood transfusion.
How Is It Diagnosed?
Carrier detection is possible with a complete blood count and a test called High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). Indicators include:
- Low haemoglobin (~9 g/dL)
- Low MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume, ~65)
- HbA2 levels above 3.5%
Once confirmed, genetic testing can identify the specific mutation in the family, helping with future planning and prenatal testing.
What Could Be Done To Manage Thalassemia?
There are three main options that can help one manage thalassemia, which includes:
Regular Blood Transfusions and Iron Chelation Therapy
Transfusion happens every 3 to 4 weeks, which helps in maintaining hemoglobin levels and support normal growth. However, each transfusion adds iron to the body, which can then damage vital organs. Thus, iron chelation, using oral medication like Deferasirox, or injections like Desferal, which are necessary to remove the excess iron.
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Also known as bone marrow transplant, this is currently the only curative treatment. If a child has a healthy HLA-matched sibling donor, stem cells can be transplanted after destroying the patient’s defective immune system. The success rate is 85%, though complications like graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) may occur. Programs like Coal India’s CSR initiative support patients with financial aid up to ₹10 lakh.
Gene Therapy
This advanced treatment involves repairing or replacing the faulty gene in the patient's own stem cells. Although it is still in the early stages and is currently available abroad at a cost of around $2 million.
The Growing Burden in India
India bears a high burden of beta thalassemia and sickle cell disorders. Around 3–4% of the population — approximately 35 to 45 million people — are estimated to be carriers. The prevalence is higher among certain ethnic and tribal groups (up to 17%).
Data from Maharashtra and Gujarat shows varying carrier rates between districts, with the expected rate of affected babies ranging from 0.28 to 0.39 per 1,000 births per year.
Why Prevention Is Important?
For a populous country like India, prevention is key. A National Thalassemia Control Programme can play a vital role by:
- Promoting public awareness and encouraging voluntary carrier testing before marriage or early in pregnancy.
- Offering antenatal testing (via chorionic villus sampling at 12 weeks) for couples who are both carriers.
In parallel, ensuring access to safe blood transfusions and affordable iron chelation for affected children is crucial to improving quality of life.
This Is Endometriosis, A Short Film On Debilitating Health Condition Wins BAFTA Award 2026, Know More

Credits: Instagram/ IMDb
This Is Endometriosis, a 2024 intimate, expressive film by Georgie Wileman and Matt Houghton won a BAFTA Award 2026 for Best British Short Film. This 19.27 minute long film shows how Georgie was robbed of her time due to endometriosis. The film sets in present-day narrative with memories from her past.
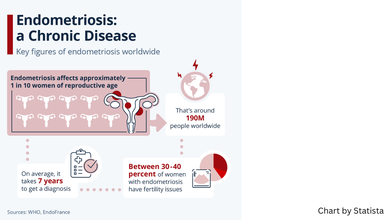
Endometriosis is a condition, that Georgie notes is often dismissed by many doctors as just "painful periods". However, her film portrays how truly disabling this medical condition. It is a condition in which cell similar to the lining of the uterus or the endometrium, grow outside the uterus. It affects 1 in 10 born with a uterus and could cause pain, often "worse than the last stages of child labour", notes thisiseno.com, the official website of the short film. Around 190 million people worldwide are impacted by the condition, however, what the film points out is how "dangerously underfunded, under researched and misinformed" doctors continue to remain despite the condition being so widespread.
Read: A Woman Lost Her Ovary To Endometriosis Surgery After Receiving An Ultimatum From Gynecologist
A Film That Documents Personal Struggle
Georgie, while accepting the award wore a symbolic blood-red gown. She said, "It was surreal and beautiful. Knowing how much this win would mean to the [endometriosis] community made it an emotional moment."
She points out that it is more than just a "painful period" and that "It is a full body disease. It important for people to understand the severity of the pain – it’s widely considered to be worse than childbirth." What is shocking is that it takes an average of eight to 10 years to be diagnosed.
She shares being "bed-bound for three months" when she was only 13. She said it first got "really bad" and she was not believed for long time. "It took me a long time to even believe myself. I was just so angry at my body for not working."
While she had been in and out of wheelchair, she was not formally diagnosed with endometriosis until she was 26, and then at 29, she was diagnosed with its 'sister disease' adenomyosis. She has undergone seven surgeries for her endometriosis and a hysterectomy for adenomyosis.
Read: Keltie Knight Was Gaslit By Doctors For Years Before Getting A Hysterectomy
In 2020, after years of feeling dismissed by doctors and watching her condition be misunderstood in the media, she decided she had had enough. That frustration pushed her to tell the story herself.
“It began as a photography project,” Wileman says. “And it meant a lot to people because, for the first time, they felt their experiences were being shown truthfully.”
But she soon realized that still images could only go so far. “There’s only so much a photograph can capture,” she adds.
Why Does It Take So Long For An Endometriosis Diagnosis?
A study published in Obstetrics and Gynecology journal looks at the factors of what leads to such a delay in endometriosis diagnosis. Researchers identified that factors include normalization of menstrual pain, the diversity of symptoms, and a lack of training and prompt referrals among healthcare professionals lead to this delay.
At an individual level, the researchers found that many women struggled to tell the difference between “normal” period pain and something more serious. A common belief was that painful periods were simply part of being a woman and had to be endured. As a result, many relied on self-care measures and delayed seeking medical help, which likely pushed back the timeline for an endometriosis diagnosis.
On an interpersonal level, stigma played a powerful role. Menstrual problems were often seen as too private or embarrassing to talk about. At the same time, society’s tendency to normalize period pain meant that symptoms were minimized, both by those experiencing them and by people around them. This silence and normalization further contributed to delayed diagnoses.
Barriers also existed within the healthcare system itself. Some participants said their general practitioners dismissed their concerns or appeared unfamiliar with endometriosis. Healthcare professionals involved in the study acknowledged gaps in their own training and pointed out the lack of clear clinical guidelines for diagnosing the condition.
Doctors also noted that endometriosis symptoms can overlap with other disorders, making it harder to identify. Diagnosis is particularly challenging because there is no simple, noninvasive test that can confirm the condition with certainty. Delays in referrals were common. One contributing factor was the widespread belief that laparoscopic surgery is the only definitive way to diagnose endometriosis. Some healthcare providers also questioned how useful a formal diagnosis would be, which further slowed the process.
Dr Sophie Davenport, a doctor in England who conducted the research as part of her Master of Public Health dissertation, emphasized that the problem is layered and requires solutions at multiple levels.
“The key highlights of the data are that delays to diagnosis exist throughout the journey,” she explained. “We need to address these at different levels — from society understanding what ‘normal’ menstruation looks like and being open about menstrual problems, to clinicians being well educated, up to date on how endometriosis presents and diagnosed, and truly listening when patients say their periods aren’t normal.”
German Study Shows Squirrels May Be Harboring Mpox Virus
Credit: Canva
Squirrels could be natural hosts of the mpox virus (MPXV) -- that causes monkeypox disease -- according to a recent study by German researchers.
The team from the Helmholtz Institute for One Health (HIOH) identified the fire-footed rope squirrel (Funisciurus pyrropus) as a likely natural reservoir of the MPXV.
The study published in the journal Nature revealed that sooty mangabeys – a primate found in West Africa -- can contract mpox by eating infected squirrels. The disease may present mild lesions, but it can also cause more severe skin lesions or even be fatal.
"Identifying the animal sources of the virus and the exposure routes that lead to inter-species transmission are key steps towards understanding spillover mechanisms and developing effective prevention measures to mitigate the risk of transmission to humans," said Livia V. Patrono, one of the senior authors at HIOH.
Squirrels Suspected MPXV Hosts
While squirrels have long been suspected as potential reservoirs for MPXV, their role was confirmed after an investigation of an mpox outbreak among wild sooty mangabeys (Cercocebus atys) in Côte d'Ivoire.
During the outbreak, reported in early 2023, nearly one-third of the primates showed clinical signs of disease, and four infants died.
The team conducted viral genome sequencing and found that the infected monkeys carried a virus that was nearly identical to an MPXV strain identified in a fire-footed rope squirrel found dead 12 weeks earlier nearby.
Further, the team analyzed fecal samples from the mangabeys. A sample collected eight weeks before the outbreak's onset contained DNA from both the virus and the rope squirrel. This provided strong evidence of interspecies transmission at that moment.
Sooty mangabeys have been previously observed catching and eating fire-footed rope squirrels, which provide a direct route for the transmission of viruses.
Mpox Continues To Spread Globally
Although mpox is no longer a public health emergency, outbreaks of clade I and clade II strains of the mpox virus are continuing in many countries around the world, especially in Africa.
Last week, Madagascar announced the country's first death from mpox, a 3-year-old girl from the island nation’s eastern city of Toamasina.
The WHO has also confirmed that two cases of the recombinant strain – combining genomic elements of clades Ib and IIb of the monkeypox virus (MPXV) – have been identified to date: one in the United Kingdom and one in India.
Mpox is an infectious disease caused by the monkeypox virus (MPXV), part of the Orthopoxvirus genus, which also includes the virus that causes smallpox.
It spreads through close physical contact, including sexual contact, and in some cases through contaminated materials or respiratory droplets.
Symptoms typically include fever, swollen lymph nodes, rash, and/or lesions.
The global health body has also urged all countries to “remain alert to the possibility of MPXV genetic recombination.” It has also urged for continued epidemiological surveillance, sequencing, vaccination of at-risk groups, and infection prevention and control measures.
This AI Tool Predicts Women’s Breast Cancer Risk Up to Four Years
Credit: Canva
An international group of scientists has created an artificial intelligence tool that can estimate a woman’s likelihood of developing breast cancer within the next four years.
The AI tool, known as the BRAIx risk score, analyzes mammogram images to generate an individualized risk assessment and flag women who may face a higher chance of developing the disease.
It may not only show the current risk but also predict the future risk, enabling early detection and treatments for a better outcome.
According to the findings published in The Lancet Digital Health journal, nearly one in 10 women ranked in the top 2 percent of risk by the AI tool were diagnosed with breast cancer within four years. This was despite previously receiving a clear screening result.
“These risk scores enable future development of personalized screening pathways to transform population breast cancer screening and save lives,” said corresponding author Helen M. L. Frazer of the University of Melbourne.
Frazer noted that identifying women who appear cancer-free but carry very high risk -- comparable to those with inherited BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations -- will unravel both hereditary and non-hereditary causes of breast cancer.
From one-size-fits-all screening to personalization
Breast cancer screening programs have significantly lowered mortality rates -- by roughly 40-50 percent among women aged 50 to 74. However, most screening systems still apply the same approach to all women, regardless of individual risk.
Traditional screening tools use genetics, breast density, and questionnaires to estimate breast cancer risk. On the other hand, new AI-based screening tools, such as BRAIx personalizes screening by gathering information already present in breast scan images to better identify who is at higher risk.
“Our results show that conventional mammographic density is a far weaker predictor of breast cancer risk than the BRAIx risk score, even for interval cancers,” the researchers said in the paper. Interval cancers are aggressive tumors diagnosed after a negative mammogram.
The BRAIx Tool
The BRAIx risk score was developed using mammograms from nearly 400,000 women. To prove its efficacy, the AI tool was tested on data from almost 96,000 women from Australia and then confirmed in an independent Swedish population of over 4,500 women.
The findings showed that:
- The BRAIx risk score estimated breast cancer risk more accurately than the traditional risk factors, such as breast density, country of birth, and even family history.
- For the top 2 percent of women with the highest BRAIx risk score, the probability of a cancer diagnosis within 4 years was 9.7 percent -- a risk level exceeding that typically seen in women with inherited BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations.
The BRAIx risk score can:
- Make breast screening more personalised,
- Improve early cancer detection,
- Reduce false alarms,
- Save lives without increasing costs
Global Breast Cancer Burden
Breast cancer continues to be the most common cancer among women worldwide.
A recent study published in The Lancet Oncology journal predicted that the number of new cases of the deadly disease will reach more than 3.5 million globally in 2050 -- rising by a third from 2.3 million in 2023.
Annual deaths from the disease will also rise by 44 percent -- from around 764,000 to 1.4 million.
However, not smoking, getting sufficient physical activity, lowering red meat consumption, and having a healthy weight can help prevent over a quarter of healthy years lost to illness and premature death from breast cancer.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

