- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
Is Snoring A Symptom Of Hypothyroidism?

Image Credit: Canva
Snoring is a sleep disturbance that people often dismiss as merely annoying, but sometimes it becomes a warning sign of other underlying health conditions. One such disorder is hypothyroidism, which is a disease characterized by insufficient production of thyroid hormone. There has been emerging research indicating the potential relationship between snoring and hypothyroidism, which can impact quality of sleep and general well-being. Let's see what science says about it and why it matters.
This arises from partial obstruction of airflows during sleep, which provokes the tissues in your throat to vibrate when asleep. Common triggers usually include nasal congestion, allergic reactions, or even simply the anatomy of your mouth and throat. Although less common snoring is perfectly harmless, chronic or excessively loud snoring could call for a more serious warning, such as OSA.
OSA is defined by the recurrent interruption of airflow during sleep because of airway obstruction. In many cases, this leads to snoring of significant amplitude. Hypothyroidism may also come into play here, given the observations that low levels of circulating thyroid hormones increase a person's susceptibility to sleep apnea.
Hypothyroidism is defined as the failure of the thyroid gland to produce appropriate hormones, which are essential to regulate metabolism, energy level, and other body activities. Common symptoms include lack of energy, weight gain, depression, dryness of the skin, brittle hair, and snoring, especially when it relates to respiratory complications.
In severe hypothyroidism, respiratory muscles may be weakened, contributing to sleep breathing difficulties. This weakening can lead to an increased chance of airway obstruction, a factor contributing to snoring and sleep apnea.
Link Between Hypothyroidism and Snoring
Several studies have investigated the association of hypothyroidism and sleep apnea.
It was reported that, as per data obtained from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data in 2019, the risk of sleep apnea was increased 1.88-fold in a person with hypothyroidism compared to someone whose thyroid function is normal.
Interestingly, this association remained even after controlling for body weight, demographics, and lifestyle factors like smoking and alcohol use. This would indicate that hypothyroidism itself—beyond its association with weight gain—may contribute to conditions that cause snoring.
Why Hypothyroidism Can Affect Sleep
Low thyroid hormone levels can affect sleep in several ways:
1. Respiratory Muscle Weakening: Hypothyroidism may weaken the muscles of respiration, making the patient breathe shallow and easily predisposed to an airway obstruction.
2. Higher Risk for Obesity: The common presenting symptom of hypothyroidism is weight gain; it may deposit fat in the neck area, leading to a narrowed airway and contributing to snoring.
3. Associated Sleep Disorders: Subclinical hypothyroidism, which is another mild form of the same condition, has been established to be associated with insomnia as well as other sleep disruptions.
Hyperthyroidism and Snoring
While excess thyroid hormones-producing hyperthyroidism is not directly related to snoring, it is the cause of many other forms of sleep disorders, including insomnia. A 2023 paper published from China reports that individuals with sleep apnea have a higher tendency for the growth of thyroid nodules. This, of course, has implications regarding the possible relationships between sleep apnea and thyroid diseases.
If you or your loved one snores constantly and develops symptoms of hypothyroidism like fatigue, weight gain, or depression, it's time to go see a doctor. The following are persistent snoring symptoms that should be investigated further:
- It is very loud and interrupts your partner's sleep.
- It causes choking or gasping spells during the night
- You experience morning headaches or sore throats
- Continued fatigue even after adequate sleep - Inability to focus or heightened irritability
Diagnosis and Treatment
A healthcare provider can diagnose hypothyroidism with a simple blood test that measures thyroid hormone levels. If diagnosed, hormone replacement therapy, like levothyroxine, is often prescribed to restore normal thyroid function.
Treatment of snoring often involves treatment of the underlying cause, whether hypothyroidism or sleep apnea. Treatments may include:
CPAP: a machine that aids in opening up the airways even at night time.
Lifestyle Measures: lifestyle modifications such as weight control, smoking cessation, and avoidance of excessive alcohol are recommended to manage snoring.
Replacement of thyroid hormones: successful management of hypothyroidism alleviates the secondary symptoms which may include snoring also.
When to Seek Medical Help
Hypothyroidism can be a gradual progression, and its symptoms at first may seem minor, but chronic fatigue, constant snoring, and other symptoms should not be ignored. Consult an ENT specialist or endocrinologist if:
- Your snoring is loud and frequent.
- You experience daytime sleepiness or mood changes.
- You have difficulty breathing during sleep.
An ENT specialist may do sleep studies or imaging tests to assess airway obstruction and may recommend targeted treatment. While snoring occasionally is harmless, persistent or loud snoring could be an indicator of hypothyroidism or other health problems. Understanding the possible relationship between snoring and thyroid health can help in treating symptoms early and improving sleep quality and overall well-being.
With proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals with hypothyroidism can manage their symptoms effectively and enjoy a restful night’s sleep.
The Association Between Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Sleep Quality: A Population-Based Study. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2019
Association between obstructive sleep apnea and thyroid function: A 10-year retrospective study. Sleep Medicine. 2023
World Alopecia Day: Experts Bust Popular Myths and Reveal Hidden Health Issues Behind Hair Loss
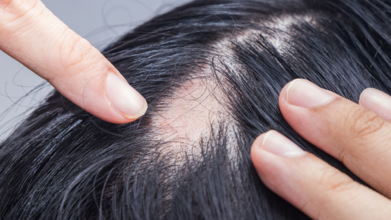
When strands clog your shower drain or your brush looks full every time you run it through your hair, panic is a natural response. Hair loss, or alopecia, is not just a cosmetic concern; it often hints at something deeper. And yet, thanks to internet half-truths and old wives’ tales, myths about alopecia spread faster than a viral meme. On World Alopecia Day, we turn to experts to separate fact from fiction while spotlighting the hidden medical conditions that might be behind the hair fall.
It is Not Just "Shedding Season": Medical Reasons Behind Hair Loss
Alopecia does not always pop up on its own. According to Dr Jijith K Ravindran, Chief Cosmetologist and Dermatologist at Cosmalife Skin Clinic in Bengaluru, alopecia often walks hand in hand with other medical conditions, and sometimes, it is your body’s way of waving a red flag.Autoimmune Disorders (Alopecia Areata):
Dr Ravindran explains, “In this condition, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss on the scalp or other body parts.” It is unpredictable, affects people of all ages, and may be triggered by stress or genetics. If you have noticed coin-sized bald patches cropping up suddenly, your immune system could be the rogue agent.Hormonal Imbalances (Thyroid Disorders and PCOS):
Blame it on your hormones? Sometimes, yes. “Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt the hair growth cycle, causing diffuse hair thinning,” says Dr Ravindran. Women with PCOS are especially vulnerable. “Elevated androgen levels in PCOS weaken hair follicles, leading to noticeable hair fall.” It is not uncommon for women with irregular periods or acne to also see their hair thinning.Nutritional Deficiencies:
Crash diets might help you drop pounds, but they can also drop your hair count. “Low levels of iron, vitamin D, and essential proteins can contribute to excessive hair shedding,” warns Dr Ravindran. If your plate lacks balance, your scalp might pay the price.The good news? “Early diagnosis and treatment of these conditions can help restore hair growth and prevent permanent damage,” he assures.
Wigging Out Over Myths
Even as more people talk openly about hair loss, alopecia still suffers from a major PR problem, mostly due to persistent myths. Dr Roopam Gangurde, a dermatologist with an MD in Skin & VD, breaks down the most common fallacies that often do more harm than good.Myth 1: “Only men experience alopecia.”
“While male pattern baldness is more commonly discussed, women are equally susceptible to alopecia due to hormonal imbalances, thyroid issues, and nutritional deficiencies,” says Dr Gangurde. Yes, ladies lose hair too and not just from brushing too hard.
Myth 2: “Stress alone is responsible for hair loss.”
While stress is definitely not good for your scalp’s health, it is not the lone cause. “Alopecia usually has multiple triggers, including genetics, autoimmune conditions, and underlying medical issues,” explains Dr Gangurde. Translation: stressing about stress causing hair fall might make things worse.
Myth 3: “Alopecia is always permanent and untreatable.”
This one might be the most damaging myth of all. “Many forms of hair loss, especially those caused by hormonal or nutritional factors, are reversible with timely medical intervention,” says Dr Gangurde. PRP therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes can all turn things around if you act early enough.
Do Not Just Shed Tears, Seek Help
If your hair has been thinning or falling out in clumps, resist the urge to DIY it with oils, serums, or social media hacks. “If you experience sudden or persistent hair loss, consult a dermatologist or trichologist promptly,” advises Dr Gangurde. “Early intervention can address the root cause, prevent progression, and in many cases, restore healthy hair growth.” Remember that alopecia is not just a surface-level issue. And with the right diagnosis, it is often more fixable than you think.
What Makes Flu Season 2025 Different? Unique Symptoms Of Flu In 2025 And How Long The Infection Lasts

Credits: Canva
The 2025 flu season has turned out to be unlike any other in recent memory. This year, the flu season is marked by record-setting infections, multiple viral peaks, vaccine mismatches, and an overstretched healthcare system.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), this year’s influenza activity is the most intense since the 2009 swine flu pandemic, with over 80 million estimated illnesses and rising. What’s driving this intensity, and what should the public know about prevention and symptom management?
Let’s break down what makes this flu season so severe and what it means for your health.
A Season Like No Other: What Makes 2025 Different?
In most years, flu activity in the U.S. typically follows a predictable pattern, starting in October, peaking between December and February, and fading by April. But the 2024–2025 season has defied that rhythm.
Cases surged past the national baseline in December and then, unexpectedly, peaked again in February, a second wave that blindsided doctors and public health experts.
As of March 2025, the CDC had reported an estimated 37 million influenza infections, 480,000 hospitalizations, and 21,000 deaths. Hospitalizations, in fact, reached their highest levels in 15 years.
One key driver? A mismatch between circulating flu strains and this year’s vaccine. The dominant strains: H1N1 and H3N2, accounted for more than 99% of cases.
H3N2, in particular, is known for mutating quickly and evading immune responses, and only about half of circulating H3N2 samples matched well with vaccine antibodies, according to CDC surveillance data.
Post-Pandemic Immune Gap
Another reason this year’s flu is hitting so hard: our immune systems are still catching up.
During the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, widespread masking, social distancing, and school closures suppressed not just SARS-CoV-2 but also seasonal flu and other common respiratory viruses. While that helped in the short term, it reduced community-level immunity over time, especially among children, who typically build natural resistance through repeated exposures.
“Young children who were toddlers or preschoolers during the pandemic missed early exposures to flu viruses,” explained experts at the nonprofit group Families Fighting Flu. “Now they’re in school, more socially active, and more vulnerable.”
The CDC reported a troubling spike in pediatric flu deaths this season with 216 fatalities, making it the deadliest flu season for children outside of a pandemic year. Neurological complications such as seizures and hallucinations also rose among young patients.
A Shift in Viral Dominance
Another unusual trend: COVID-19 has taken a back seat this winter
Unlike previous years when COVID-19 variants dominated respiratory illness charts, flu has surged ahead as the top driver of doctor visits and hospitalizations. This could be due to a shift in viral dominance, changing weather patterns, or differences in immunity buildup. According to the CDC, nearly 8% of all outpatient visits are currently for flu-like symptoms, much higher than what’s typical for this time of year.
Vaccine Fatigue and Gaps in Coverage
Vaccination remains the strongest tool we have to fight influenza, but uptake has been stagnant, or worse, declining, in key groups.
As of April 2025:
- Only 49.2% of children and 46.7% of adults had received the flu vaccine
- Among pregnant women, that number dropped to 38%
- Medicare beneficiaries aged 65+ had just 48.3% coverage
- And overall, nearly 9.2 million fewer doses were administered compared to the pre-pandemic 2019–2020 season
Barriers like vaccine hesitancy, misinformation, racial and ethnic disparities in healthcare access, and fewer flu shot clinics in rural areas continue to widen the gap.
What Are the Symptoms in 2025?
The 2025 flu has shown typical but often more intense symptoms than in previous years. Here’s what to look out for:
- Sudden onset fever
- Severe body aches and chills
- Sore throat and persistent cough
- Nasal congestion
- Diarrhea and vomiting (more frequent in children)
- Extreme fatigue
- Headache
- In some children, neurological symptoms like confusion or seizures
These symptoms may overlap with COVID-19 or RSV, but tend to come on faster and hit harder in flu cases this season.
How Long Do Symptoms Last?
For most healthy people, flu symptoms begin 1 to 4 days after exposure and typically last about 5 to 7 days. However, fatigue and cough may linger for up to two weeks.
You’re considered most contagious in the first 3 to 4 days after symptoms start but can continue to spread the virus up to a week later. The CDC recommends staying home until you’ve been fever-free for at least 24 hours without medication.
Vaccinated individuals may experience milder or shorter symptoms, but those with underlying conditions, young children, and older adults may have longer recoveries and higher risk of complications.
Can the Flu Cause Serious Health Problems?
Yes, especially in people with weakened immune systems, chronic illnesses, or no prior flu immunity.
Possible complications include:
- Pneumonia
- Ear and sinus infections
- Exacerbation of asthma or heart disease
- Life-threatening conditions requiring ICU care
This is why experts stress that prevention remains the best medicine.
How to Protect Yourself and Your Family
Here’s how to lower your risk during the remainder of the 2025 season:
- Get vaccinated, even now. It may still protect against circulating strains
- Wash your hands often with soap and water
- Avoid touching your face in public settings
- Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
- Stay home if you’re unwell to prevent spreading the virus
'It’s Not Too Late': Even After A Lung Cancer Diagnosis, This One Habit Change Can Save Your Life

Credits: Canva
A lung cancer diagnosis shatters worlds. It thrusts patients into a whirlwind of fear, confusion, and uncertainty. What now? How will I cope? Is this the end? These questions are inevitable and urgent. Yet, amid the anxiety, many patients harbor a dangerous belief: that if cancer has taken hold, quitting smoking is pointless.
It's not just a myth, it’s dangerous. Newer studies show quitting smoking even after a cancer diagnosis can significantly improve survival, make treatments more effective, and alleviate symptoms. In other words: even after cancer strikes, letting go of cigarettes can save your life.
In many small towns across India, where awareness about cancer and tobacco risks is limited, patients often continue to smoke despite their diagnosis. “Some feel it is too late to stop. Others are too addicted or too hopeless to try,” says Dr. Ruchi Singh, HOD & Senior Consultant of Radiation Oncology at Asian Hospital. This is the kind of thinking that kills from the inside out.
The reality is the opposite. Dr. Singh emphasizes, “We try to explain … it is never too late. If they stop smoking, even after the cancer has started, the treatment becomes more effective. It is one of the most important things they can do for themselves.”
Every cigarette after diagnosis undermines treatment, weakens the body, and shortens survival. But should someone quit even late into their cancer journey their lungs begin to heal, treatments work better, and recurrence becomes less likely.
How Does Quitting Smoking Extends or Saves Lives?
Global research aligns with Dr. Singh’s clinical advise, a study by IARC and Russian oncologists followed 517 lung cancer patients who smoked at diagnosis. Those who quit within three months lived 22 months longer on average and had 33% lower mortality risk and 30% lower disease progression, regardless of stage or smoking intensity.
The Prospective cohort of the Annals of Internal Medicine confirmed quitting after diagnosis yields meaningful survival benefits.
MUSC Hollings Cancer Center. A Harvard study of nearly 5,600 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients found former smokers lived longer than current smokers, suggesting even pre-diagnosis quitting increases survival. Additional studies show quitting at or around diagnosis reduces mortality significantly and improves outcomes across all stages of NSCLC.
Smoking cessation isn’t just beneficial—it is one of the most powerful lifesaving interventions for lung cancer patients.
People tend to discount vaccines or preventive care because success makes the threat invisible. Lung cancer prevention has been a public health battle for decades. Policymakers and physicians worked to reduce smoking rates, and incidence fell. But once a cancer diagnosis arrives, all remission plans depend on a foundation of good habits—like quitting tobacco.
Tobacco smoke introduces toxins, weakens immune function, and diminishes treatment outcomes. Continuing to smoke after diagnosis:
- Lowers treatment efficacy
- Increases post-surgery complications
- Heightens the risk of recurrence or second primary cancers
- Shortens survival significantly
- Quitting reverses much of that risk—even post-diagnosis.
How to Quit Smoking After Lung Cancer Diagnosis?
Treatment regimens already overwhelm patients. Quitting smoking under stress and physical duress is tough—but not impossible. With the right support, patients dramatically increase their success odds. Here’s a compassionate roadmap:
- Set your quit date now, delay weakens motivation and clarity.
- Seek medical support, consult your oncologist or a specialist in Siliguri. Therapy, nicotine replacements, or counseling can double your quitting success.
- Lean on loved ones, share your commitment and ask for accountability.
- Identify your triggers- stress, discomfort, or routine can push you back. Replace smoking with walking, meditation, or tea.
- Shift lifestyle habits and replace “smoke with morning coffee” rituals with alternative rituals—like stretching or herbal tea.
- Build habits that support health- hydration, nutritious food, gentle movement and joy—these restore lung health and resilience.
Indeed, about 36% of tobacco-linked lung cancer patients manage to quit after diagnosis. Those are lives reclaimed.
Lung cancer still has a stigma. Many see it as self-inflicted. That stigma often delays help—including quitting support. But as Dr. Singh reminds us: “People think cancer means a death sentence. But many cases are treatable, especially if caught early. If someone quits smoking, we see real improvement such as better breathing, better recovery after surgery, and fewer chances of the cancer coming back.”
For patients, oncology teams, and families, smoking cessation after diagnosis isn’t optional—it’s urgent evidence-backed medicine.
A lung cancer diagnosis changes everything, but it does not define what comes next. Quitting smoking—even when the disease has already appeared—creates space for healing, response, and survival. It says, “I’m still here. I’m still fighting."
If you or someone you love is facing lung cancer- quit, today. It doesn’t erase the past—but it can extend the future. Numbers don’t lie: treatment plus quitting smoking can give us 22 more months, more energy, more peace, and a higher chance of beating this disease. Quitting is more than choice. It’s courage. And it is always worth it.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

