- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Is There A Difference Between Zoonotic, Non-Zoonotic And Reverse Zoonotic Diseases
We have all, by now, know that while 2024 was a year disease, but 2025 awaits even more. At the starting of the year only we saw a rise in the cases of bird flu, and saw the virus spread among people too. Then there was trichomoniasis in birds in the UK, and FMD in Germany, and many more. While the source of it all might be animal, not all of these are zoonotic diseases. Not all animal diseases are zoonotic diseases, some are zoonotic, some are non-zoonotic, and some are reverse zoonotic diseases. But, what are the difference?
What Are Zoonotic Diseases?
Zoonotic diseases or zoonoses are infectious diseases that can be spread between animals and humans. It originated with the domestication of animals, animal products or animal derivatives. The word also stems from the Greek word zoion, which means animal, and nosis, which means diseases.
The term was first used in 1885 by Rudolph Virchow in his Handbook of Communicable Diseases. It spreads between vertebrates and humans, which means animals with a backbone, and birds. The way their bodies work is similar enough to ours that pathogens can sometimes adjust to live in both.
While some zoonotic diseases spread only from animals to humans and do not spread from person to person. There are other diseases like Ebola, Mpox, COVID-19, and many more which come from animals, but continue to spread in humans, through humans, and cause outbreaks. Some of them also spread in humans and then mutate to infect only humans, like HIV
Many pathogens are limited to infecting a single type of host—humans, specific animals, plants, or even other microorganisms. However, zoonotic diseases are unique because they can infect both humans and other vertebrates. In some cases, these diseases originally affected only animals, but genetic mutations enabled them to "jump" to humans and cause infections.
Zoonotic illnesses are typically caused by bacteria, parasites, or viruses. However, they can also stem from other sources, such as fungal infections like ringworm or prion diseases like variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD), often referred to as “mad cow disease.” Animals that carry zoonotic diseases:
- Bats
- Birds
- Cats
- Deer
- Dogs
- Livestock
- Non-human primates, monkeys, apes and chimpanzees
- Rodents
What Are Non-Zoonotic Diseases?
Not all animal diseases are zoonotic. Zoonoses are infectious diseases that can transfer between animals and humans such as rabies, anthrax, influenza, Nipah, COVID-19, brucellosis, and tuberculosis. However, not all animal diseases are zoonotic. Many diseases affect livestock without posing a risk to human health. These non-zoonotic diseases are species-specific and cannot infect humans. Examples include Foot & Mouth Disease (FDM), PPR, Lumpy Skin Disease, Classical Swine Fever, and trichomoniasis in birds and animals.
What Are Reverse Zoonotic Diseases?
It is the case where a disease transmits from humans to animals. This also poses threats to animals health as well as public health, due to the potential for animal disease reservoirs to form.
In 2020, several mink farms in the Netherlands experienced a severe respiratory disease outbreaks, upon investigation, it was revealed that minks had been infected with SARS-CoV-2, the same virus responsible for COVID-19. The minks came in contact with infected farmworkers.
There have been cases when domesticated dogs, cats and ferrets have developed flu-like symptoms caused by influenza A virus, passed on by their owners. Human-derived pathogens also pose significant risks to endangered wildlife. For example, in Tanzania, an outbreak of human metapneumovirus resulted in fatalities among a population of wild chimpanzees. The virus was believed to have been transmitted by researchers and visitors to the national park where the chimpanzees lived, highlighting the potential consequences of human-wildlife interactions.
The 4 Parkinson's Signs That Appear Years Before Diagnosis

Credit: Canva
Parkinson's disease is a progressive, neurodegenerative movement disorder caused by the loss of dopamine-producing brain cells, primarily affecting people over 60. Apart from motor loss, the disease also causes cognitive decline, depression, anxiety and swallowing problems.
The first symptom may be a barely noticeable tremor in just one hand or sometimes a foot or the jaw. Over time, swinging your arms may become difficult and your speech may become soft or slurred. The disorder also causes stiffness, slowing of movement and trouble with balance that raises the risk of falls.
However, before clear symptoms begin to appear, Neurologist Rachel Dolhun says certain signs may help identify the onset of the disease decades before it is diagnosed.
“It’s important to stress that not everyone who has these symptoms goes on to develop Parkinson’s,” said neurologist Rachel Dolhun. “But we know that in some people, these can be some of the earliest signs," she told The Washington Post.
Here is what you should look out for:
1. Loss Of Smell
Loss of smell, or hyposmia, is a common and early non-motor symptom of Parkinson's disease, affecting up to 90 percent of patients. This symptom can significantly impact quality of life by reducing the enjoyment of food and diminishing appetite.
While strongly linked to Parkinson's, smell loss can also stem from other causes, including sinus problems, COVID-19, or aging.
2. Acting Out Dreams
Acting out dreams, known as REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD), involves physically enacting vivid, often unpleasant dreams through shouting, punching, or kicking during sleep.
This typically happens because the brainstem fails to temporarily paralyze muscles during REM sleep. It is a strong early warning sign of Parkinson's disease, often appearing years or decades before motor symptoms. About 50 percent of people with Parkinson's experience RBD.
READ MORE: Parkinson’s Patients May Soon Walk Better With This New Personalized Brain Therapy
3. Constipation
Constipation is a very common and significant non-motor symptom of Parkinson's disease that is caused by nerve changes slowing gut muscles and potentially exacerbated by low activity and dehydration.
Constipation can also be caused by Parkinson's medications such as anticholinergics, amantadine and other common drugs such as opioids, iron/calcium antacids.
4. Dizziness As You Stand
The autonomic nervous system fails to properly constrict blood vessels or increase heart rate upon standing, often due to a lack of norepinephrine. This causes the autonomic nervous system to fail in regulating blood pressure. Over time, this leads to Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension.
Beyond dizziness, symptoms include blurred vision, weakness, fatigue, cognitive "fog," and "coat hanger pain" (pain in the neck/shoulders). Often times, patients experience dizziness in the morning or immediately after meals.
Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease is mostly a clinical process, meaning it relies heavily on a healthcare provider examining your symptoms, asking questions and reviewing your medical history. Various imaging and diagnostic tests used to detect disease includes CT scan, PET scan, MRI scan and genetic testing.
What Is Cold Urticaria? Doctors Warn Of Painful Allergy Caused By Cold Exposure
Credits: Canva
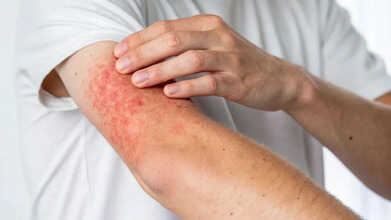
Beyond icy roads and fogged-up car windscreens, the coldest season can also bring on a painful condition that leaves the skin covered in red, itchy patches. Doctors have issued a warning about this lesser-known illness, which tends to worsen in low temperatures.
The condition, known as cold urticaria, affects around one in 2,000 people. It causes swelling and itching of the skin when it comes into contact with cold air, cold water, or even air conditioning. Red welts or hives can appear within minutes, and the discomfort may last for as long as two hours.
What Is Cold Urticaria?
Cold urticaria is an uncommon condition in which the body reacts abnormally to cold temperatures. It typically causes rashes or hives after exposure to cold air, water, food, or drinks. In some cases, symptoms can be more serious. According to the Cleveland Clinic, the condition may sometimes be linked to an underlying blood cancer or an infectious illness.
Griet Voet, head of a dermatology clinic in Ghent, Belgium, as per Express UK, said the condition is often confused with common winter skin problems such as eczema. “This is not just dry skin caused by cold weather, it is a genuine allergic reaction to cold,” she explained. In more severe cases, large areas of the body may be affected, particularly after swimming in cold water or spending extended periods outdoors. This can lead to intense itching, facial flushing, and even headaches, stomach pain, or fainting. Sudden temperature shifts, such as moving from a warm indoor space into cold outdoor air, can also trigger symptoms. Drinking ice-cold beverages may cause swelling of the lips, mouth, or throat.
Cold Urticaria: What Are The Symptoms Of This Disease?
Symptoms of cold urticaria differ from person to person and can range from mild to severe. They may be limited to a small patch of skin or spread across the entire body.
The most common sign is a skin rash that appears after contact with something cold. The rash usually develops once the exposure ends, as the skin begins to warm up.
The rash may include:
- Hives, bumps, or raised welts
- Itching
- Redness
- Swelling
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Headache
- Joint pain
- Fainting
- Heart palpitations
- A severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis
- Shortness of breath or wheezing
How Is Cold Urticaria Diagnosed?
A medical professional can often diagnose cold urticaria using a simple test. An ice cube is placed on the skin, usually on the arm, for a few minutes and then removed. If a hive or rash appears several minutes later, the result is considered positive.
In cases of familial cold urticaria, diagnosis may involve exposure to cold air for a longer duration.
Doctors may also suggest blood tests to check for any underlying illness or infection that could be contributing to the condition.
Nipah Virus Symptoms Explained As Doctors Warn Up To 75% Fatality Risk
Credits: AI Generated
Health authorities have urged the public to stay alert to Nipah virus symptoms after doctors warned that up to 75 per cent of infected patients may not survive. The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) has classified Nipah as a “high priority pathogen” because of its severe fatality rate and the absence of any proven treatment.
In India, the federal health ministry has confirmed two cases in the eastern state of West Bengal. This has triggered large-scale containment measures, with local officials placing nearly 200 people who had contact with the infected individuals under quarantine.
Also Read: Vitamin D Supplements Under Scrutiny As It Fails Safety Test
In response, several Asian nations have stepped up airport checks and health surveillance for travellers arriving from India. Professor Paul Hunter, an infectious disease specialist at the University of East Anglia, said identifying Nipah cases at borders is challenging, as symptoms can take a long time to appear.
What Is Nipah Virus?
According to UKHSA, Nipah virus is a zoonotic infection, meaning it can pass from animals to humans. It can also spread through contaminated food or via direct human-to-human contact. The virus was first discovered in 1999 during an outbreak affecting pig farmers in Malaysia and Singapore.
Fruit bats, especially those belonging to the Pteropus species, are the virus’s natural carriers. Research shows that Nipah can also infect other animals, such as pigs, dogs, cats, goats, horses and sheep.
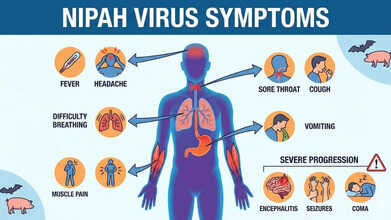
Nipah Virus Symptoms
UKHSA lists the following as common symptoms of Nipah virus infection:- Sudden onset of fever or general flu-like illness
- Development of pneumonia and other breathing-related problems
- Swelling or inflammation of the brain (encephalitis) or meningitis
Symptoms usually appear between four and 21 days after exposure, although longer incubation periods have occasionally been reported. More severe complications, including encephalitis or meningitis, can develop between three and 21 days after the initial illness begins.
Also Read: Nipah Virus Outbreak In India: All That You Need To Know About This Infection
Nipah Virus Symptoms Explained As Doctors Warn 75% Fatality Rate
UKHSA has cautioned that between 40 and 75 per cent of people infected with Nipah virus may die. Those who survive can experience long-term neurological effects, such as ongoing seizures or changes in behaviour and personality. In rare instances, the virus has been known to reactivate months or even years after the first infection.
Nipah Virus: Can You Prevent It From Spreading?
For people travelling to regions where Nipah is known to occur, prevention largely involves reducing exposure risks:
- avoid contact with bats, their habitats, and sick animals
- do not drink raw or partially fermented date palm sap; if consuming date palm juice, make sure it has been boiled
- wash all fruits well with clean water and peel them before eating; avoid fruits found on the ground or those that appear partly eaten by animals
- use protective clothing and gloves when handling sick animals or during slaughter and culling
- maintain good hand hygiene, especially after caring for or visiting ill individuals
- avoid close, unprotected contact with anyone infected with Nipah virus, including exposure to their blood or bodily fluids
Nipah Virus Symptoms Can Be Transmitted Easily?
Many Nipah infections have been linked to eating fruit or fruit-based products contaminated by the saliva, urine or droppings of infected fruit bats. Human-to-human transmission can also occur through close contact with an infected person or their bodily fluids, according to Mirror.
Such transmission has been documented in India and Bangladesh, with cases often involving family members or caregivers tending to infected patients. At present, there is no specific, proven treatment for Nipah virus infection, and no licensed vaccine is available to prevent it.
So far, no Nipah virus cases have been reported in the United States or the United Kingdom.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

