- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
What Is The Science Behind A Red Lipstick?

Credits: Pexels
When I was growing up, something that struck my mind was Taylor Swift’s fourth studio album from 2012, Red. The song ‘22’ especially had an impact on me. I looked at Taylor, she looked gorgeous in that red lipstick and so I started putting it on too. Little did I know that it would become ‘my thing.’
It gave me confidence and a sense of empowerment, which is what triggered me to write about it.
Is there any psychology behind red lipstick? Well, psychologist Dr Jennifer Baumgartner believes that red lipstick is a bold and confident colour and is associated with power and desire. In an interview with Dermaliscio, she said, “Red lipstick is the ultimate power colour. When a woman wears red lipstick, she is sending a message that she is confident and in control.”
A study by the University of Manchester also found that women who wore red lipstick felt more confident, attractive and successful.
Cultural Significance
In the ancient world, painted red lips were seen as the symbol of opulence and sophistication. In Egypt, both men and women would highlight their features with naturally available makeup. Queen Cleopatra would crush red ants and beetles to make the scarlet colour, say the historical records.In Chinese culture, the colour red is also associated with luck and prosperity.
Historically too, red lipstick has been associated with women's empowerment. For instance, during the suffragette movement of 20th century, red lipstick became a symbol of self-identity and freedom. It was used as a tool to be heard. Experts suggest that the colour red draws one’s attention to it. If you wear the colour on your lips, it will draw people’s attention to your mouth and what you say.
“In order to gain more notoriety and attention to their cause, some ladies would wear lipstick to their public events. This was seen as the mark of the independent, emancipated woman, which at the time was thought to be quite scandalous. This subversive action would have brought censure from men, and some women who regarded these women as morally lacking.” said cosmetic historian Gabriela Hernandez in an interview toTeen Vogue.
Even during the World War II, red lipstick was used as a cultural weapon and as an image of ‘a modern woman.’ During this time the US government encouraged women to wear red lipstick while their partners, who were men, fought in the war.
How does it empower you?
Clinical psychologist Carla Marie Naly says that red tones suggest passion, power and sexual virility to men. Since it has been used as a cultural tool and image of control, it symbolises women’s agency over themselves in all aspects. “It can affect your self-confidence,” says Manly.While clinical psychologist Holly Schiff says that while it is attention-grabbing, “red lips are also linked with confidence.”
These are the factors why wearing red lipstick makes one feel empowered. The most important part is that it lets women claim the spaces which they have been historically and institutionally denied to. This is also the reason why the international non-profit organisation which raises awareness about sexual violence is named Red My Lips.
From COVID To Flu: Tracking New Disease Variants That Emerged In 2025

Credits: Canva
The year 2025 served as a stark reminder that COVID is no longer the only illness demanding public attention. Over the months, several diseases resurfaced or intensified, some reaching epidemic levels. In many cases, the surge was driven by new variants that altered how these illnesses spread, how severe they became, and how quickly they overwhelmed health systems.
From respiratory infections to vector-borne diseases, 2025 showed how familiar pathogens can return in unfamiliar forms. Mutations made some infections more contagious, while others blurred early symptoms, delaying diagnosis and treatment. Below, we take a look at new variants of diseases that we witnessed in 2025.
New Disease Variants That Emerged In 2025
COVID-19 New Variants
In 2025, fresh COVID-19 variants continued to circulate, most of them linked to Omicron sublineages. These strains spread quickly but, for many people, caused symptoms closer to a bad cold, flu, or seasonal allergies. Common symptoms included stomach issues, body pain, exhaustion, and fever.
Health authorities continued to advise testing through RAT or RT-PCR, short-term isolation, and medical care where needed. As with earlier waves, acting early made a clear difference in recovery and containment.
As per World Health Organization, some of the Covid variants that appeared in 2025 include:
XFG Variant
The XFG variant of COVID-19, also known as Stratus, surfaced in early 2025 as a recombinant strain. Recombinant variants form when two different COVID strains infect the same person and merge during mutation, a process that occurs naturally as viruses evolve. XFG drew attention because of how easily it spread and its ability to infect people despite previous infection or vaccination. Classified as a recombinant Omicron subvariant, XFG was detected widely across regions including North America, Europe, and Asia.
According to WHO-linked data from mid to late 2025:
In the United States, XFG became the leading variant, responsible for around 85 percent of reported cases by the end of September 2025.
In the United Kingdom, XFG and related sublineages accounted for a sizeable share of infections, with reports suggesting nearly 30 percent of cases in July 2025.
In India, where XFG circulated by mid-2025, early clusters were largely reported from Maharashtra, followed by Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Gujarat. It later emerged as the dominant strain in states such as Madhya Pradesh.
The nickname “Frankenstein” was informally attached to XFG because it combines genetic material from different Omicron subvariants. Experts from institutions like the Institute Pasteur and the University of Nebraska Medical Center noted that while it spreads rapidly, it has not been linked to more severe disease.
Omicron NB.1.8.1
NB.1.8.1, informally called “Nimbus,” is a distinct Omicron lineage that was first identified in early 2025. The World Health Organization classified it as a “Variant Under Monitoring” after noticing its steady global rise, particularly across parts of Asia and North America. Although it contributed to visible spikes in case numbers, there was no strong evidence that it caused more serious illness. Vaccines continued to offer reliable protection.
By mid-2025, NB.1.8.1 had become one of the faster-spreading Omicron offshoots, driving fresh COVID waves in several countries. Despite its speed, health agencies confirmed that existing vaccines remained effective and that the variant was not linked to increased severity. The WHO officially placed it under monitoring in May 2025.
Flu New Variants
H3N2 “Subclade K” Variant
The flu strain seen during the winter months of 2025 was identified as H3N2 subclade K, a seasonal influenza A virus. Some public commentary labelled it “super flu,” though this term has no medical basis and does not suggest the virus is inherently more dangerous or resistant to treatment. A key concern was that many people had limited prior exposure to this strain, resulting in lower community immunity. Flu vaccines, however, continued to protect against severe outcomes.
Data from NHS England showed a sharp rise in flu-related hospital admissions. During the first week of December, hospitals reported an average of 2,660 flu patients per day, marking a 55 percent increase from the previous week. The number of admissions was high enough to fill more than three entire hospital trusts.
Monkeypox New Variant
Clade LB Variant
Health authorities in England detected a new mpox variant after testing a person who had recently travelled to Asia, as per BBC. Genetic sequencing revealed that the strain was recombinant, combining elements of two circulating mpox types: clade 1, which is associated with more severe illness, and clade 2, which was responsible for the 2022 global outbreak.
The UK Health Security Agency stated that it was still evaluating the implications of this strain. While most mpox cases remain mild, officials advised people who qualify for vaccination to get immunised as a precautionary step.
Chikungunya New Variant
In 2025, Chikungunya did not see the emergence of a single newly named variant. Instead, there was a renewed spread of the East, Central, and South African genotype, particularly the Indian Ocean Lineage. This lineage has developed mutations that improve its ability to spread.
According to the National Institutes of Health, certain CHIKV lineages, including the E1-226A variant, previously helped shift infections into urban settings. More recent severe cases reported in India, including outbreaks in Pune in 2024, showed signs of neurological involvement such as paralysis and darkened nasal tissue. These symptoms are thought to be linked to mutations like E1-226V or A and E2-I211T, along with improved adaptation of the virus to Aedes aegypti mosquitoes, pointing to continued viral evolution aimed at more efficient transmission.
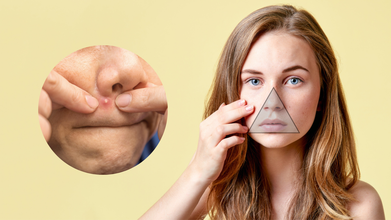
The “Triangle of Death” on Your Face: Why You Should Never Pop a Pimple There
Credits: iStock
Pimples on skin is something we see on a day to day basis. Often, without even thinking much, we pop them. But did you know there is a 'Triangle of Death' on your face, where you should never pop a pimple?
Reacting to a video, Dr Sermed Mezher, a UK-based GP, and a health communicator who goes by @drsermedmezher on his Instagram handle says, "You should never pop pimples but it is even more important not to do it in a specific triangle of the face."
He reacts to a video where a boy shares his experience of popping a pimple on his face, which has left him in pain, and made him enable to use the side of his face with pimple. His face is now swelled.
Also Read: 8 Red Flags That May Suggest Cancer Growth In Your Body
What Is The Triangle of Death On Your Face?
Dr Mezher says that while it is named unscientifically, the area extends from the top of the nose to the upper lip. This is important because it drains the cavernous sinus. "So, we don't want bacteria to get into there," he notes.
Why Is Triangle Of Death A Dangerous Place To Pop Your Pimples?
“We naturally have bacteria on our skin, and every time we pop a pimple, we damage the skin barrier. That creates an opening for bacteria to move deeper into the skin. If those bacteria reach the cavernous sinus through the facial ‘triangle of death,’ it can cause a serious condition called cavernous sinus thrombosis," notes Dr Mezher.
He explains that this blood clot can lead to severe headaches, fever, pressure and pain behind the eyes, difficulty moving the eyes, and even eye swelling or bulging. "While it is usually treatable, prevention is far easier than cure, which is why popping pimples should be avoided."
According to Cleveland Clinic, this small segment of your face has a direct line to your brain, which is the cavernous sinus. It is a network of large veins located behind your eye sockets. Through this sinus, blood drains from your brain. This is why, any infection in this area, could a picked pimple or even a nose piercing gone wrong could impact your brain. Dermatologist Alok Vij, MD, tells Cleveland Clinic, "There is the possibility for a facial infection to become an infection that impacts the rest of your body."
Is The Triangle Of Death Really Fatal?
Well, as the name suggest, the triangle of death cannot actually kill you. Dr Vij says, "Thankfully, it is relatively unlikely. But, whenever there is a violation of the skin and interaction with bacteria, there is always a possible for infection, which can lead to greater health concerns."
In rare cases, an infection of the face can lead to septic cavernous sinus thrombosis, or a blood clot in your cavernous sinus. It could also lead to some life-threatening health issues, including:
- Brain abscess (pus that causes swelling of your brain)
- Brain infection
- Damage to your facial nerves, including paralysis of your eye muscles
- Meningitis
- Pneumonia
- Septic emboli (infected blood clots that travel through your bloodstream)
- Stroke
How To Deal With A Pimple In You Triangle Of Death?
- Apply a warm compress, use a clean cloth and apply it on the area for 10 to 15 minutes. Soak the clean cloth in warm water.
- Use a pimple patch or an overnight zit sticker that could soak up some of the drainage, in case your pimple has already opened.
- See a dermatologist.
8 Red Flags That May Suggest Cancer Growth In Your Body
Credits: iStock
In 2022, there were around 19,976,499 cancer cases diagnosed from around the world, notes the World Cancer Research Fund. Out of them, 10,311,610 were men, and 9,664,889 were women. In 2024, several reports say that there were over 19 million new global cases in that year. The cases of cancer are rising, so is there any way one can stay one step ahead of it?
While it is important to get screenings done frequently, especially if one has a family history of cancer, there could be certain red flags, one must look out for to book an appointment with oncology.
Here are the cancer red flag one must keep a look out for:
Persistent Fatigue
Persistent fatigue remains one of the most overlooked symptoms of oncology. This is not like a routine tiredness, this is a kind of exertion that stays despite rest, balanced meals, and time off. Data from 2022-24 shows that over 30% of early stage cancer patients reported unexplained fatigue prior to diagnosis.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Oncologists explain that over 40% of newly diagnosed gastrointestinal and lung cancer patients experienced weight loss. This could happen due to metabolic changes caused by tumors, which can alter energy absorption and consumption, often suppressing appetite and leading to a rapid loss of body fat.
When to see a doctor? If you have lost more than 5% of your body weight in under 6 to 8 weeks, it is important that you seek immediate medical attention.
Chronic Pain
If there is a pain that does not go away, it could be because of cancer. Many patients have complained of persistent pain as one of the fist symptoms of their cancers. This is particularly true for back pain, which is common in pancreatic or ovarian cancer. Bone pain too is common in metastasis, and pelvic pain is common in uterine or colorectal cancer.
Skin Changes
Not all cancers start inside the body, some also show up on the skin. These changes could be new moles, non-healing wounds, or changes in pigmentation. In fact, unusual rashes also signal changes like skin cancer.
Changes In Bowel And Bladder Habits
If you experiences changes in your bowel and bladder habits and find blood in your stool or urine, it is best to see a doctor. Colorectal, bladder and prostate cancers often start subtly. Before it becomes serious, keeping a track of your bowel and bladder habits could prevent the cancer from spreading.
Lump Or Thickening Of Body
While lumps could be benign, they are also one of earliest signs cancer. For instance, the early detection of breast cancer and testicular cancer are from lumps, which are observed while self examination. In fact, the early detection, thanks to self examination, has even increased by 22%.
Persistent Cough
While this may be a season of virus and flu, but if your cough does not go away, it may be a serious sign. If you find blood in your cough, see a doctor, take scans. If you are a smoker, you may be more prone to early stage throat cancer.
Headache That Does Not Go Away
There could be certain neurological issues, including a stubborn headache that does not go away. This may be an indication of a tumor in the brain.
If you have any of these stubborn symptoms, it is best to book a doctor's appointment and go for a screening.
Note: Health and Me is not a substitute for doctor's advice, please consult a registered doctor, if you face any of these symptoms.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

