- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
Obesity On The Inside: This Is What 250 lb vs. 125 lb Body Scan Reveals About Weight Loss And Health
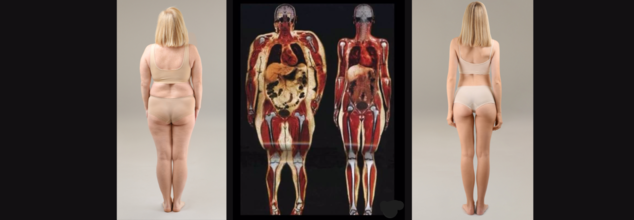
Have you ever wondered what's actually happening inside your body as your weight changes? A body scan of a 250 lb (113 kg) and a 125 lb (57 kg) individual shows more than size—it reveals crucial differences in fat distribution, muscle mass, and health. Obesity isn’t just about numbers on a scale; it’s about how excess weight affects your organs, metabolism, and risk of diseases like diabetes and heart conditions.
Obesity is one of the leading global health challenge, affecting millions worldwide. While weight in itself usually takes center stage in conversations, body composition becomes even more integral to the extent of overall wellness. A head-to-head examination of body scans of a female who weighs 250 lb (113 kg) compared to another at 125 lb (57 kg) produces stark contrasts among fat distribution, muscle mass, and organ functionality. These insights offer a deeper understanding of how excess weight impacts the body internally and why metabolic health should be prioritized over mere weight loss.
World Obesity Day, celebrated every year on March 4th since 2020, works towards tackling the worldwide obesity epidemic by encouraging real-world solutions. While weight alone is often the focal point of discussions, body composition plays an even more crucial role in determining overall health. A side-by-side comparison of body scans of a woman weighing 250 lb (113 kg) versus one at 125 lb (57 kg) reveals significant differences in fat distribution, muscle mass, and organ health. These insights offer a deeper understanding of how excess weight impacts the body internally and why metabolic health should be prioritized over mere weight loss.
The observance emphasizes that obesity isn’t just about aesthetics; it is a complex health issue requiring collective effort to ensure long-term well-being.
How Excess Weight Relates to Internal Changes?
This actual body scans of a 250 lb (113 kg) woman and a 125 lb (57 kg) woman show the way that weight gain changes body composition. Although both could be of the same size and skeletal structure, their muscle-to-fat ratio, organ positioning, and metabolic efficiency are dramatically different. The scan of the heavier person reveals greater visceral fat around major organs, lower muscle mass density, and greater joint and cardiovascular stress. The lighter woman's scan, however, illustrates improved fat distribution, improved organ function, and lower internal levels of inflammation.
Why Is Obesity More Than Weight and BMI?
Obesity is medically described as an excess of body fat that causes harm to health. Although Body Mass Index (BMI) is usually taken as a first-line measure (BMI ≥ 30), it does not consider muscle mass or fat distribution. An individual with increased muscle mass can have a BMI greater than 30 but remain metabolically healthy, while an individual with a lower BMI but increased visceral fat can be at serious health risk. Thus, body composition measurements like body scans can be a better indicator of health risks due to obesity.
Known Health Risks of Obesity
Obesity is a leading risk factor for many chronic diseases. As observed in the comparisons of body scans, excess fat storage especially visceral fat is responsible for serious health complications, including:
Metabolic Diseases – Higher risk of Type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome.
Cardiovascular Problems – High blood pressure, increased risk of stroke, and greater chance of heart disease.
Joint & Mobility Issues – Extra weight puts a strain on joints, resulting in osteoarthritis and pain.
Surgical Complications – Increased risk of complications from anesthesia, impaired wound healing, and longer recovery times.
Malnutrition Paradox – Overweight persons can still be malnourished as a result of eating poorly.
What Is the Role of Visceral Fat?
The single most alarming outcome of the body scans is high visceral fat stores in the woman who weighs 250 lb. Visceral fat, the fat deep inside the abdominal cavity surrounding organs like the liver, pancreas, and intestines, is uniquely dangerous. Metabolically active, unlike the subcutaneous fat (fat under the skin), visceral fat secretes pro-inflammatory chemicals causing insulin resistance, heart disease, and stroke. Elevated visceral fat levels are a separate risk factor for metabolic and cardiovascular disease, which is why beyond mere weight reduction, it becomes necessary to act.
Strategies for Successful Weight Management
To tackle obesity, one needs a holistic strategy beyond mere weight reduction. Healthy and sustainable weight reduction and improvement of health are more about body composition than the mere weight. Major strategies are:
- A balanced diet composed of whole foods, lean meats and good fats in addition to physical exercise encourages sustainable weight reduction.
- Resistance training helps in preserving muscle retention along with fat reduction which improves metabolic well-being.
- Prescription weight-loss medication can help manage obesity alongside lifestyle changes.
- For people with severe obesity, surgeries such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy may provide significant long-term advantages.
- Prioritize your metabolic health through healthy eating, portion control and mindful eating for long-term success.
Persistent Stomach Issues Could Be A Sign Of Autism: Study Finds Gut Link To Neurodevelopmental Disorder

(Credit-Canva)
While you may have heard of the gut-brain connection, did you know it could also signal neurodevelopmental disorders? A study has found children with autism are far more likely to have ongoing stomach and digestive issues than other children.
A new study from the UC Davis MIND Institute found a strong link between these gastrointestinal (GI) problems and other daily challenges, including difficulties with sleep, communication, and behavior.
How Are Stomach Issues Linked To Autism?
The study followed 475 children between the ages of 2 and 12, with 322 of them having autism. The researchers talked to the families multiple times over the years to track the kids' health. They found that children with autism were not only more likely to report stomach problems like constipation and diarrhea, but they also tended to have several of these symptoms at once.
Even more importantly, these issues often lasted for years, unlike in other children where they usually went away quickly. What's surprising is that many of these problems didn't have an obvious medical cause. This suggests that doctors and parents need to pay closer attention to these symptoms, even when the reason isn't clear.
What is Gut-Brain Connection?
Your brain and your gut are constantly communicating, a connection you've probably felt before. This is why you get "butterflies in your stomach" when you're nervous or why a bad feeling about something is called a "gut feeling." This link is a two-way street: your brain can affect your gut, and your gut can influence your brain.
In fact, the gut and the brain are like best friends. They talk about everything, from how you're feeling emotionally to how your body is working physically. More information travels between these two than any other body part. Your gut even has a huge number of nerve cells, second only to your brain. The conversation between your gut and brain influences many of your body's functions, including:
- Hunger and cravings.
- Digestion and metabolism
- Your feelings
- Pain and thinking
- Immunity
Could Gut-Brain Axis Reveal Autism?
The researchers looked at nine common stomach and digestive symptoms and found that they were strongly connected to other difficulties. Children with more frequent gut problems also had more trouble with sleep, were more anxious and irritable, and struggled more with communication, sensory issues, and repetitive behaviors.
This study reinforces the idea that the brain and the body are deeply connected. When a child feels stomach pain, it's not just a physical problem. It can also influence their mood, how they sleep, and how they interact with the world around them. The researchers stress that treating a child’s gut health is an important step toward improving their overall quality of life.
The researchers pointed out that many of these gut issues are treatable, even if there isn’t a clear medical diagnosis. They hope that doctors, teachers, and families will become more aware of this connection and work together to get children the care they need. They believe that addressing gut health as part of a complete care plan for autism can help children feel better and grow. One of the authors, Christine Wu Nordahl, explained that it's not about finding just one cause for a child's challenges, but about looking at the whole child and helping them in every way possible.
Hearing Loss Linked To Dementia, Doing This One Thing Can Help You Lower The Risk: Lancet Study Reveals

(Credit-Canva)
A simple, 15-minute annual check-up could be one of the most effective ways to protect yourself from dementia. Research now shows that untreated hearing loss is the single biggest risk factor for dementia that you can actually change, even more so than smoking or not exercising. According to Alzheimer’s Research UK, if everyone took care of their hearing, we could prevent seven out of every 100 cases of dementia that occur today.
However, this is not a one-off observation, but other studies have also shown that hearing loss is linked with dementia. A study published in the Lancer showed that treating hearing loss is one of the best ways to decrease risk of dementia.
Interestingly, several studies have shown a significant link between hearing loss and dementia. A recent meta-analysis, which combined data from over 666,000 people, found that individuals with hearing loss had a 37% higher risk of dementia compared to those with normal hearing.
The risk of dementia also increases with the severity of hearing loss. For every 10-decibel drop in hearing ability, the risk of dementia can increase by as much as 24%. This means that even a small decline in your hearing can raise your risk.
How Is Hearing And Dementia Connected?
In the UK, a staggering one in three people have some level of hearing loss, but many wait a full decade before they seek help. At the same time, nearly one million people are living with dementia, a condition that is the leading cause of death in the country. The Lancet Commission on Dementia found that hearing loss in midlife is the number one modifiable risk factor.
Research suggests that using hearing aids can help reduce the risk of dementia. A review of multiple studies found that people with hearing loss who used hearing aids had a 19% lower risk of mental decline and a 17% lower risk of dementia compared to those who did not.
Another study showed an even more powerful effect, with people at a higher risk of mental decline having a 48% lower chance of their condition worsening into dementia if they wore hearing aids.
These findings suggest that treating hearing loss with hearing aids not only improves a person's quality of life but also plays a key role in preventing or delaying dementia.
The reason for this connection is simple: your brain works much harder when it has to strain to understand conversations, especially in loud places. This extra effort can be exhausting and cause people to pull away from social situations, leading to loneliness and poor well-being. By making it easier to hear, hearing aids help your brain relax and allow you to stay engaged with the world, which is crucial for brain health.
Why Does Treating Hearing Loss Help Dementia?
Interestingly, this positive effect wasn't as clear in a group of healthy volunteers who were at a lower risk for dementia. This might be because their mental decline was already slow, so the study's three-year period wasn't long enough to show a major difference.
Scientists think that hearing aids help people at high risk for dementia by doing more than just improving hearing. They might also boost a person's social connections, reduce feelings of sadness, provide more mental stimulation, and make it easier to talk to doctors about medical care. However, more research is needed to fully understand the long term effects.
A Regular Eye Check-up Led To This 29-Year-Old's High-Grade Aggressive Brain Cancer Diagnosis

(Credit-Canva)
A simple eye exam completely changed the life of 29-year-old Rhiannon. A career-loving Occupational Therapist who enjoys traveling, Rhiannon had no idea she was seriously ill. The Brain Tumor Charity shared her story to raise awareness on Eye Health Day.
While she had noticed small issues like a ringing in her ears and feeling tired, she didn't have the typical, more serious symptoms of a brain tumor, such as seizures or severe headaches.
During her eye check-up, Rhiannon's eye doctor noticed an unusual sign: a buildup of pressure around her optic nerve, a condition called papilledema. The doctor suspected this could be caused by a brain tumor and immediately sent her for more tests.
An MRI scan confirmed a mass in her brain. At first, doctors thought it was a less serious tumor, but a biopsy revealed the heartbreaking truth. Rhiannon was diagnosed with glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), also known as a grade 4 astrocytoma. This is an extremely fast-growing and aggressive form of brain cancer that is not curable. To make matters worse, the tumor's location made it impossible to remove with surgery.
What Is Glioblastoma Multiforme?
According to the American Association of Neurological Surgeons, Glioblastoma (GBM) is a type of brain tumor that grows quickly and aggressively. It invades nearby brain tissue but usually doesn't spread to other parts of the body.
GBMs can either start on their own or develop from a less serious type of brain tumor. In adults, they most often appear in the main parts of the brain, particularly in the front and sides.
This is a very dangerous cancer that, if left untreated, can be fatal in six months or less. It's crucial to get care from experts like a neuro-oncologist and neurosurgeon right away, as immediate treatment can greatly improve a person's chances of survival. The symptoms of a brain tumor can differ depending on where it is located in the brain. Some common signs to watch for include:
- Persistent headaches
- Vision problems, such as blurry or double vision
- Feeling sick, which can include vomiting and a loss of appetite
- Changes in mood or personality
- Difficulty thinking or learning
- New seizures
- Speech problems that get worse over time
How Does Glioblastoma Multiforme Affect People?
Rhiannon is still coping with the shock of her diagnosis. The hardest part for her has been losing her independence. She can no longer work or drive, things she once took for granted. Now, she relies on others for support, which has shown her how truly generous and amazing her loved ones are.
Despite these challenges, Rhiannon is facing her illness with courage. She is taking each day as it comes, finding strength in the moments that matter. She refuses to give in to sadness and holds onto hope that new research will one day lead to a cure.
Rhiannon is sharing her story to highlight how important eye exams can be in finding a brain tumor. She urges everyone not to skip their regular eye appointments, even if they don't have any noticeable problems.
She specifically recommends an OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) scan, which gives a detailed look at the retina. This test can detect various eye conditions early, some of which may not show symptoms until they are more advanced. In Rhiannon's case, this simple test led to her life-saving diagnosis.
Lorcan Butler, an eye specialist, agrees, emphasizing that many health conditions, including brain tumors, can be spotted during a routine eye exam. If you have any concerns about your vision, he advises you to see an eye doctor right away.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

