- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
Blueberries To Green Beans: Fruits & Vegetables With Maximum Pesticide Content

Green Beans (Credit: Canva)
There are more than 1000 different types of pesticides used around the world to ensure that food is not damaged or destroyed by pests. Each of them brings its own toxicology to the table. Moreover, there are many of the older, less costly (off-patent) pesticides, such as dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) and lindane, which can remain for years in soil and water.
According to World Health Organization (WHO), pesticides are the leading cause of death by self poisoning, particularly in low and middle income nations. This includes agricultural workers who apply pesticides and anyone else in the immediate area during, and shortly after, pesticides are spread. For the general population, while the amount of pesticides they consume is low, the harm is caused majorly due to the pesticides that remain in their food and water.
ALSO READ: 6 Food Cravings and What They Mean for Your Body
Every year, the Environmental Working Group (EWG) releases the Dirty Dozen — a list of the 12 non-organic fruits and vegetables highest in pesticide residues.
Strawberries: Conventional strawberries consistently top the Dirty Dozen list. In 2023, the EWG found that 30% of all strawberry samples contained ten or more pesticide residues.
Spinach: 76% of spinach samples contained pesticide residues, including permethrin, a neurotoxic insecticide that is highly toxic to animals.
Kale, mustard, and collard greens: 86% of all samples of leafy greens were found to contain two or more pesticide residues, including the neurotoxins imidacloprid, bifenthrin and cypermethrin.
Peaches: Over 99% of the peaches tested by the EWG contained pesticide residues, with 65% containing at least four.
Pears: Over 63% of pears tested by the EWG contained residues from five or more pesticides.
Nectarines: The EWG detected residues in nearly 94% of nectarine samples, with one sample containing over 15 different pesticide residues.
Apples: The EWG detected pesticide residues in 90% of apple samples. What’s more, 80% of the apples tested contained traces of diphenylamine, a pesticide banned in Europe.
Grapes: Conventional grapes are a staple on the Dirty Dozen list, with over 96% testing positive for pesticide residues.
Bell and hot peppers: Sweet bell peppers contain fewer pesticide residues compared to other fruits and vegetables. Yet, the EWG cautions that pesticides used on sweet bell peppers "tend to be more toxic to human health."
Cherries: The EWG detected an average of five pesticide residues on cherry samples, including a pesticide called iprodione, which is banned in Europe.
Blueberries: The EWG found that 90% of blueberries had pesticide residues, with 80% containing two or more.
Green beans: The EWG added green beans to the Dirty Dozen list after finding that 90% of samples contained pesticides, including acephate, a neurotoxin banned by the EPA in 2011.
ALSO READ: Overthinking Before Bed? Try Cognitive Shuffling To Silence Your Thoughts For Better Sleep
How Does Avocado Affect Our Weight? The Answer May Shock You

(Credit-Canva)
Rich in healthy fats, insoluble fiber and many vitamins as well as protein, avocados are known for being one of the highest-fat based plant foods. According to the Nutrition Source they are a great source of fiber and are notably high in healthy fats (more than carbohydrates), making them popular in lower-carbohydrate diets, such as those for managing diabetes.
Their heart-friendly fats don't raise blood cholesterol, which can make traditional cholesterol-lowering diets more satisfying. As one of the highest-fat plant foods, avocados are also a favorite in vegan and vegetarian diets. Many nutritionists suggest people eat avocados for weight loss, however does it actually help? How does a fruit with a high calorie count as well as 67% fat content, be good for weight loss.
We spoke to Anshul Singh, Clinical Nutrition and Dietetics Department Lead, Artemis Hospitals
to understand the nutritional nuances of avocado.
Avocados Help You Feel Full Longer
Mr. Anshul explained that foods with good fats and fiber make you feel full and content. They slow down how quickly food leaves your stomach. Since avocados are rich in both, they keep you satisfied longer. One study showed people eating avocado for breakfast felt less hungry. "They also have healthy fats, like monounsaturated fats, which may help the body break down fat and lose belly fat. People who eat avocados tend to have better diets and weigh less."
Support Weight Management
Research shows people who eat more fruits and vegetables, including avocados, often have lower body weights. A big study found avocado eaters tended to have healthier diets and a lower risk of certain health issues. This suggests avocados fit well into a healthy eating plan. There's no need to avoid them if you're trying to manage your weight; in fact, regular eaters were less likely to become overweight. "People felt less hungry and more satisfied for hours when they replaced carbs with avocado fats and fiber. This was mostly because hormones like PYY and GLP-1 make you feel full. Adding just half an avocado to lunch made people 23% more satisfied and 40% less hungry over the course of three hours, even though the meal had more calories." says Mr Anshul
Avocados Might Help with Weight Loss
It's not fully clear if avocados directly cause weight loss, but they may help. The healthy fats in avocados might be burned for energy faster and could even increase your body's calorie burning after meals. According to Mr. Anshul, "Nuts and yogurt are good for you, but avocado is more filling and has fewer calories and no added sugar or salt. It feels like a treat without the guilt because it's creamy, healthy, and light. Avocado might be the tastiest way to stay on track when you want to snack smart and reach your goals." They may also reduce your appetite, making you less likely to overeat. However, more research is needed to fully understand these specific effects.
Avocados and Belly Fat
Some early studies suggest avocados could help with weight loss, especially targeting belly fat. One study showed people eating a daily avocado as part of a reduced-calorie diet lost weight and had changes in gut bacteria. Another found daily avocado consumption led to significant belly fat loss. Animal studies hint that even avocado extract, without fat, might help reduce appetite and weight gain.
Are Avocados "Fattening"?
Don't worry about avocados being "fattening." When eaten as part of a balanced diet with whole, healthy foods, they're beneficial. Avocados have many qualities that support weight management. While more evidence is building, there are strong signs they can help. Mr Anshul warns, "Avocados are very nutritious, but if you don't pair them well, they can lose their benefits or upset your stomach. Don't mix them with heavy dairy, sugary fruits like mango or banana, or salty processed snacks. These combinations can make you feel bloated, make the flavors clash, or raise your blood sugar levels." Enjoying avocados in reasonable amounts can certainly be a valuable part of an effective weight loss plan.
He closes the statement with a few avocado friendly food pairings for people who are trying to lose weight. " Instead, eat avocado with whole grains, lean proteins, fresh veggies, citrus vinaigrette, or nuts to keep its creamy, healthy edge. This will make it taste light and easy to digest."
What Happens To Your Liver When You Consume Soybeans?
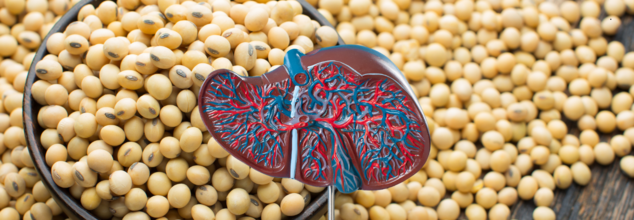
Credits: Canva
Soybeans are widely celebrated for their high protein content, especially among those on plant-based diets. But beyond being a protein powerhouse, soybeans also contain a wealth of nutrients and bioactive compounds that play a vital role in maintaining liver health.
With rising concerns around fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, and liver-related conditions, including soybeans in your diet could be a simple, natural step toward better liver function. Here’s how this humble legume works to support one of the body’s most important organs.
A Natural Source of Liver-Supporting Protein
One cup of boiled soybeans (about 172 grams) offers roughly 31 grams of protein. The main proteins in soybeans—glycinin and conglycinin—account for around 80% of that content. These aren’t just for building muscle; they support lipid metabolism and enzyme activity, two processes that are central to how the liver breaks down fats, regulates hormones, and processes nutrients.
Additionally, these proteins provide essential amino acids that are critical for the repair and regeneration of liver cells. This helps ensure the liver continues to perform its detoxifying functions efficiently.
Reduces Liver Damage
Soybeans are rich in isoflavones, plant-based compounds known for their antioxidant effects. These antioxidants work to reduce oxidative stress, which is a major contributor to liver cell injury and long-term liver damage.
Isoflavones also help regulate apoptosis—the process of programmed cell death—which is essential for removing damaged cells but harmful when it happens excessively. By balancing this process, soy isoflavones help protect healthy liver cells from being destroyed.
Improves Fat Metabolism in the Liver
Another liver-friendly compound found in soybeans is lecithin. Lecithin plays an essential role in the breakdown and transport of fats, helping the liver manage its fat content more effectively. It boosts the formation of lipoproteins, which help move fat out of the liver and through the bloodstream, thereby reducing the risk of fatty liver disease.
Research has also shown that soy lecithin can lower total cholesterol and triglyceride levels, while increasing HDL (“good”) cholesterol, further easing the burden on the liver. In addition, lecithin contributes to the regeneration of cell membranes and helps prevent liver fibrosis, a condition where liver tissue becomes scarred.
Combats Inflammation
Soybeans also contain saponins, plant compounds with powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. These compounds help protect liver cells from toxic substances such as carbon tetrachloride and acetaldehyde—a harmful byproduct of alcohol metabolism that can lead to liver scarring and cirrhosis.
By neutralizing these toxins, saponins act as a shield for liver cells, preserving their structure and function.
Boosts Overall Liver Function
- Soybeans are a natural source of vitamins E, K, and B6, all of which are vital for liver health.
- Vitamin E protects the liver from oxidative damage.
- Vitamin K supports bile production and blood clotting.
- Vitamin B6 is essential for protein metabolism and enzyme function.
- These nutrients contribute to the liver’s ability to process waste, metabolize nutrients, and regulate energy.
Lifestyle Matters, Too
While soybeans can offer excellent support for liver health, they work best as part of a balanced lifestyle. Limiting alcohol intake, avoiding smoking, eating plenty of vegetables and lean proteins, staying physically active, and going for regular health checkups all enhance liver function.
Some natural herbal extracts like milk thistle (silybum marianum) and wasabia extract have also been studied for their ability to support detoxification and improve liver resilience.
4 Foods That People With Fatty Liver Must Avoid Eating

Credits: Canva
Fatty liver disease is increasingly common worldwide, and while it may start off without noticeable symptoms, ignoring it can lead to serious complications. The liver plays a vital role in processing nutrients, detoxifying the body, and managing fat. When fat accumulates in liver cells faster than it can be metabolized, it can disrupt these crucial functions—potentially leading to hepatitis, cirrhosis, or even liver cancer if left untreated.
Fortunately, fatty liver in its early stages is often benign and reversible. Through a combination of medical care and simple but consistent lifestyle changes, many people can manage or even reverse the condition. One of the most important lifestyle changes? Your diet.
Experts emphasize that reducing the intake of certain foods can significantly slow or even stop the progression of fatty liver disease. Here are four food groups that should be limited or avoided if you’re managing this condition.
Sugary Foods
Consuming too much sugar—especially added sugars—can be particularly harmful for people with fatty liver. Excess sugar contributes to weight gain, obesity, and type 2 diabetes, all of which are major risk factors for liver fat buildup.
When your body consumes more calories than it can use for energy, it stores the surplus as fat, particularly in the form of triglycerides. If these triglycerides aren’t broken down efficiently, they begin to collect in the liver. Furthermore, a sugar-rich diet can cause insulin resistance. When this happens, your body produces more insulin, which can further encourage fat storage in the liver.
People with fatty liver or high blood sugar should limit desserts like cakes, ice cream, candies, and sugary beverages. Even fruits high in natural sugar—such as lychees, grapes, bananas, and apples—should be consumed in moderation.
Fried and High-Cholesterol Foods
Fried foods and items rich in cholesterol may seem indulgent, but they can be a direct hit to your liver. These include animal fats, red and processed meats, organ meats, egg yolks, butter, cheese, sausages, and bacon.
Diets high in these foods raise LDL (bad) cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood, which adds extra stress on the liver. They also increase overall fat deposits in the body, exacerbating fatty liver disease.
Instead, opt for heart- and liver-friendly alternatives like using plant-based oils (olive or canola), increasing your intake of leafy green vegetables, and incorporating fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, and mackerel into your meals. These fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to help reduce liver fat.
High-Sodium and Processed Foods
Too much salt can quietly worsen fatty liver disease. Pickled vegetables, canned goods, fast foods, and processed snacks are often loaded with sodium. Consuming these regularly can increase water retention, blood pressure, and fat accumulation in the liver.
Excessive salt intake has also been linked to higher leptin levels (a hormone involved in fat storage), inflammation, and insulin resistance—all of which contribute to liver damage over time.
To protect your liver, aim to keep daily salt intake under 6 grams. Try flavoring your meals with herbs, spices, and lemon juice instead of relying on salt, soy sauce, or other sodium-heavy seasonings.
Refined Carbohydrates
Foods like white rice, white bread, crackers, instant noodles, and rice cakes may not taste sweet, but they break down quickly into sugars in the body. This leads to insulin spikes and, eventually, increased fat storage in the liver.
Choosing whole grains instead—such as brown rice, whole wheat bread, oats, and quinoa—can provide your body with fiber, improve digestion, and help regulate blood sugar levels. These changes can go a long way in easing the liver’s workload and reducing fat accumulation.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

