- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
Signs You May Be A Co-dependent Parent

Credits: Canva
Are you a co-dependent parent? Do you often get this doubt? Let's see what it really means? Codependency is not just a term tied to addiction; it has expanded to describe relationships, and can exist even between a child and the parent. Understanding what codependent parenting is vital because it has the potential to harm a child’s development and identity.
What Is a Codependent Parent?
If you have to go by the definition, a codependent parent has an unhealthy attachment to their child and often tries to control their life excessively. This behavior can stem from the parent’s emotional dependence on the child’s well-being for their self-esteem or stability. While it is true that a parent always cares about the child's well-being, in a co-depended relationship, the parents' emotions depends on the child and often becomes a restriction for the child's growth. So, even though, it may appear to be a sign of a close family bond, it often reflects underlying dysfunction.
Codependency is not always easy to recognize. It’s influenced by various biological, psychological, and social factors. Look out for these signs in you or your partner to see whether you are a codependent parent:
You Love To Control
Codependent parents often feel their identity hinges on their relationship with their child. This can lead to over-involvement. For instance, stepping in to solve every problem in the child’s life, regardless of their age or capability.
It can also result in inappropriate caretaking, which means the parent is doing things for the child that they should manage themselves, like choosing clothes for an older child or overseeing a teenager’s schedule. Furthermore, the parents may be shouldering responsibilities and maybe taking blame for the child’s emotions or mood swings.
Sacrificing Other Relationships
Codependent parents may neglect their romantic relationships or friendships to focus solely on their child. For instance, they might cancel plans to attend to a non-urgent need of their child, leading to isolation and strained personal connections.
Manipulating Emotions
Manipulation isn’t always intentional but can still harm the child. Common behaviors include:
- Passive-aggressive tendencies: Using indirect aggression to influence the child.
- Projection: Transferring unresolved feelings onto the child.
- Guilt-tripping: Inducing guilt to elicit a desired response, such as expecting daily school updates by framing it as an emotional need.
Exhibiting Dogmatic Behavior
A codependent parent often resists criticism or alternative viewpoints. They may interpret disagreements as rebellion, threatening their sense of control and authority.
Playing the Victim
Some parents share negative personal experiences to gain sympathy from their child, unintentionally shifting emotional support responsibilities onto them. This dynamic, known as parentification, places undue pressure on the child to care for the parent’s emotional needs.
Struggling With Boundaries
Codependent parents often fail to enforce boundaries out of fear of rejection. They might:
- Avoid disciplining their child to prevent conflict.
- Resent their partner for setting rules that the child doesn’t like.
Tying Self-Esteem to the Child
Parents with low self-esteem may depend on their child’s achievements or happiness for validation. They might push the child to fulfill dreams they couldn’t achieve themselves.
Reacting With Denial
If the idea of being a codependent parent makes you defensive, it could be a sign. Denial is a defense mechanism that can prevent you from addressing underlying issues and seeking help.
How Codependency Hurts Children
Parent-child codependency can hinder a child’s emotional growth. It may:
- Suppress their ability to form their own identity.
- Teach them controlling behaviors, perpetuating a cycle of codependency.
- Prevent them from developing independence and self-confidence.
How to Break Free From Codependency
Acknowledging the issue is the first step. Here’s how to start healing:
- Practice self-care: Fulfill your own needs without relying on your child.
- Encourage independence: Allow your child to face age-appropriate challenges.
- Listen actively: Pay full attention and validate their thoughts without projecting your own feelings.
Seeking Help
If you suspect codependency, consider professional counseling or therapy. Online support groups and resources like books can also provide guidance. Remember, progress takes time and patience, so be kind to yourself as you navigate healthier parenting dynamics.
By addressing codependency, you can create a healthier relationship with your child, fostering their growth and your well-being.
Paracetamol During Pregnancy Could Cause Neurodevelopment Disorders In Newborns – Study

(Credit-Canva)
Pregnancy is a sensitive and difficult time for expectant mothers. They must be careful about what they eat and how long they are active. It is also advisable for them to avoid certain medications, unless they have been prescribed by a doctor. As you may know, what the mother consumes will eventually affect the child, so while something that the mother can handle can be fatal to the child as it is at a very vulnerable stage. As such, a few studies have suggested that consuming medications like paracetamol can affect the child’s brain.
A new study published in the BioMed Central suggests that taking paracetamol (also known as acetaminophen) during pregnancy might be linked to a higher risk of autism and ADHD in children. This is a significant finding because paracetamol is a very common over-the-counter medicine that many pregnant women take for headaches, pain, or fever.
Researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai looked at 46 past studies involving more than 100,000 people. They found that the better-quality studies were more likely to show a connection between using paracetamol during pregnancy and a child's risk of developing these disorders.
How Does Paracetamol Affects Pregnancy And The Baby?
The researchers believe there could be a biological reason for this connection. They explain that when a pregnant person takes paracetamol, the medicine can cross from their body to the baby. Once there, it might cause stress to the baby's cells, mess with their hormones, and even change how their genes behave. These changes could interfere with the normal development of the baby's brain.
Since the number of autism and ADHD cases seems to be increasing around the world, these findings are very important. They could change how doctors and health officials think about the use of this common drug during pregnancy.
Should Pregnant Women Take Paracetamol For Pregnancy?
It's important to remember that this study does not prove that paracetamol directly causes autism or ADHD. However, the evidence is strong enough to raise concerns about how much it's being used.
Because of these findings, the study's authors suggest that pregnant women should use paracetamol with caution, for a short period of time, and only under a doctor's guidance. They also say that more research is needed to fully confirm these results and understand the risks.
Is This Accurate For All Children?
While it is ok to be cautious, there are other studies that do not draw the same conclusion. A 2024 study published in the JAMA network found no such link. The study suggested that using paracetamol during pregnancy does not increase a child's risk of developing autism, ADHD, or intellectual disability. This finding goes against some previous studies and is important for managing pain and fever during pregnancy. The study, which looked at over 2.4 million children born in Sweden, found that a direct link could not be made when other factors were considered.
What the Sibling Study Showed
When the researchers compared the siblings, they found no evidence that paracetamol use during pregnancy was linked to a higher risk of autism, ADHD, or intellectual disability.
- The risk for autism, ADHD, and intellectual disability was virtually the same in the exposed and unexposed siblings.
- The study found no connection even when mothers took more paracetamol.
This suggests that the slight link found in the initial analysis was likely due to "confounding factors," meaning other family-related reasons—not the medication itself—were responsible for the difference in risk. For example, a mother with a certain condition that requires her to take paracetamol might also have a genetic trait that affects her children.
In short, this new research provides strong evidence that paracetamol use during pregnancy is not a direct cause of these neurodevelopmental disorders.
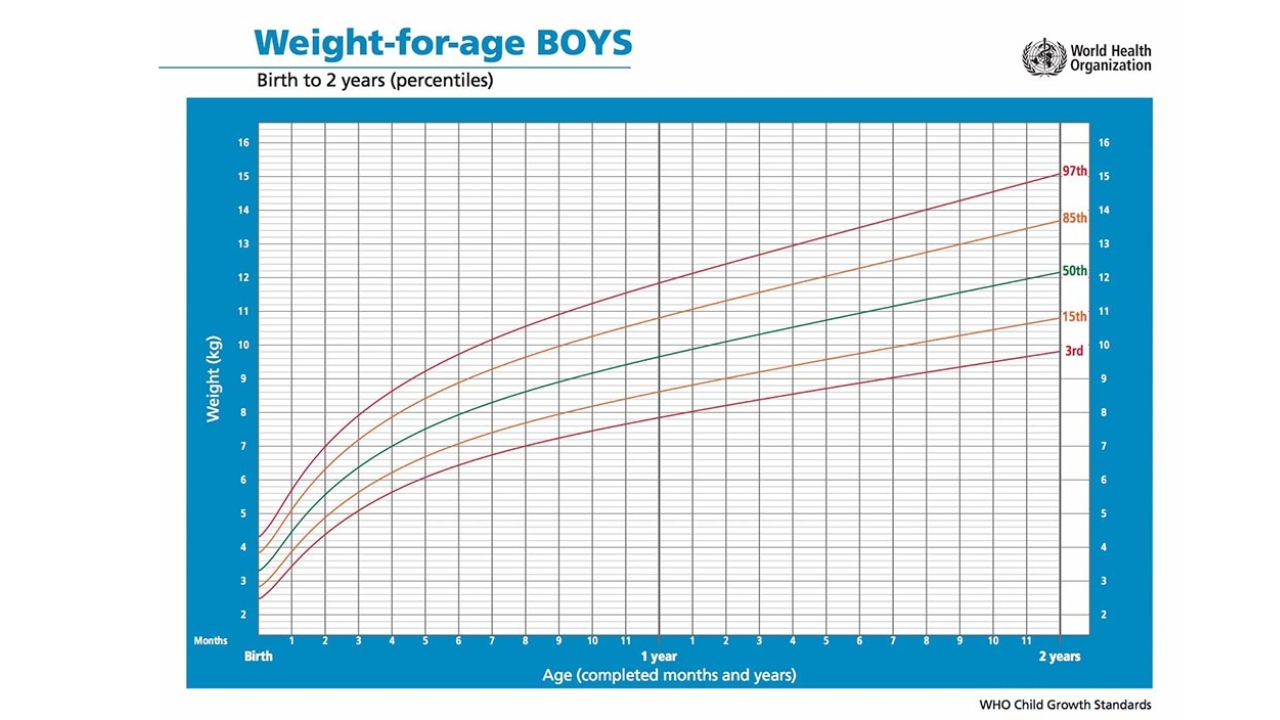
How To Decipher What Percentile Your Baby Is Using A Growth Chart?

Credits: Canva
An infant growth chart is a tool that helps parents, doctors, and other health professionals track a baby’s growth over time. By recording key measurements, it gives a clear picture of how your baby is developing compared to healthy growth standards.
The chart records three main measurements:
- Length (height)
- Weight
- Head circumference
These details are plotted so you can see how they change as your baby grows. The vertical axis shows the measurement, while the horizontal axis shows your baby’s age.
Growth charts are more than just numbers. They help assess your baby’s overall health and nutrition. Charts differ for boys and girls, as well as for infants and older children. For babies aged 0 to 2 years, the World Health Organization (WHO) growth standards are used. From 2 years onwards, most states and territories use growth charts based on the US Centers for Disease Control (CDC).
You will usually find a growth chart in your child’s personal health record, which may come in different colours depending on where you live. Parents can also register their child for a My Health Record, a digital platform where healthcare providers can upload growth information and other health updates.
What Are Percentiles?
Percentiles are a common way of showing growth patterns on a chart. They compare your baby’s measurements with those of other babies of the same age.
For example:
- A baby on the 50th percentile for weight is right in the middle. Half of babies the same age weigh less, and half weigh more.
- A baby on the 5th percentile for weight is lighter than 95% of babies that age.
- A baby on the 90th percentile for weight is heavier than 90% of babies that age.
ALSO READ: 99th Percentile Baby: What It Means, Risks, And What Parents Should Know
Every baby grows at their own pace. Some are naturally smaller, others naturally bigger. What matters most is that your baby follows a steady growth pattern over time.
How Growth Charts Are Used
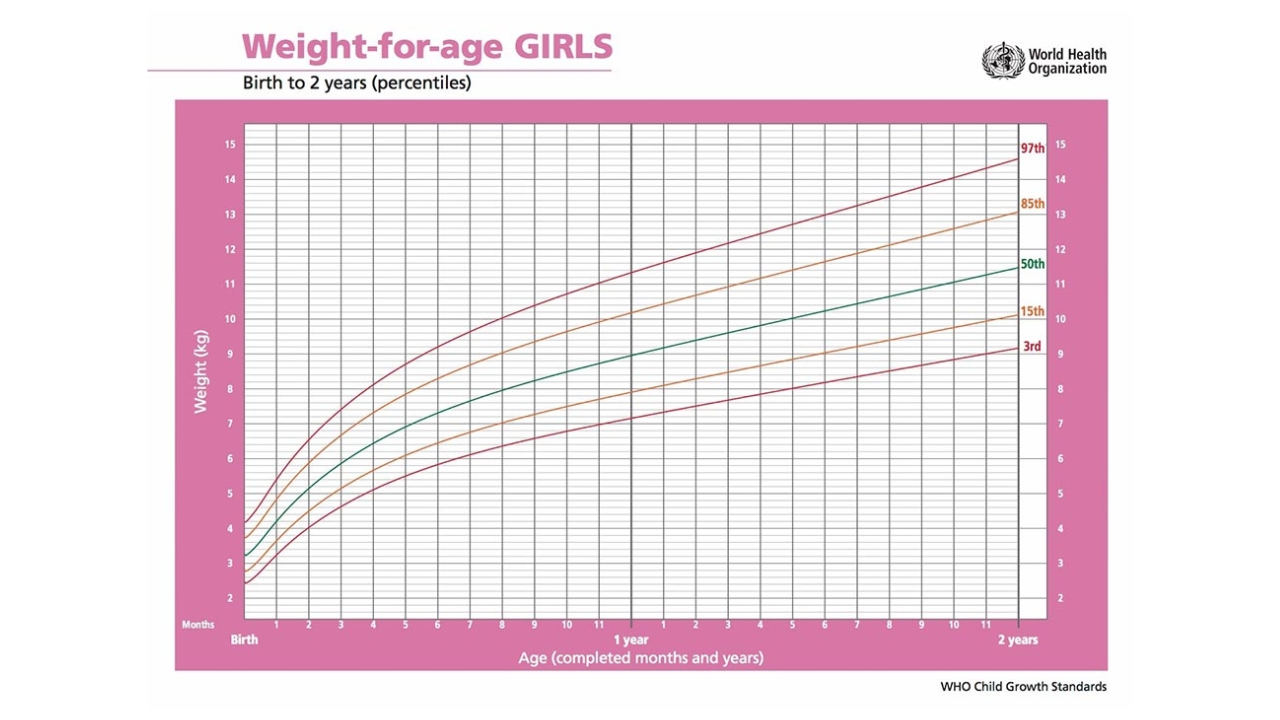
Growth charts help identify whether your baby is following a healthy growth curve. While it is not necessary for a child to match the curve exactly, their growth should generally follow a consistent path.
Your baby is first weighed and measured at birth. It is normal for newborns to lose some weight in the first few days, which is why they are often weighed again at two weeks to check if they have returned to their birth weight. After that, regular growth checks are recommended, usually monthly in the first year.
Routine health checks continue throughout childhood, with growth charts used until a child turns 18. The timing of these checks may vary depending on your state or territory.
Measuring Your Baby
Special infant scales are used for babies up to 20 kilograms. Newborns are weighed lying down, without clothes or a nappy, to ensure accuracy. After the age of 2, children are weighed standing up in light clothing.
Head circumference is measured with a tape measure to track brain and skull growth.
For babies born prematurely, a corrected age is used until they are 2 years old. This adjustment accounts for the number of weeks they were born early. For example, a 4-month-old baby born one month early would have a corrected age of 3 months for growth chart purposes.
When to Seek Advice
A growth chart is a helpful tool, but it is not the only indicator of a baby’s health. Other signs of healthy development include:
- At least five very wet nappies each day
- Pale urine
- Soft, well-sized bowel movements
- Regaining birth weight by 14 days old
- Contentment between feeds
Most babies double their birth weight by around 4 months. If weight gain is slower than expected, it could be due to feeding difficulties, illness, or other health issues.
If your baby’s growth percentile drops significantly or weight gain remains low, speak to your doctor or child health nurse. They can assess the overall growth trend and investigate if needed.
Finally, avoid comparing your baby’s growth to others. Healthy growth looks different for every child, and the goal is steady development through infancy and beyond.
ADHD Could Be Setting Your Child Up For Failure - Study Reveals Factors That Lower The Quality Of Life In Children With ADHD

(Credit-Canva)
Although many people now know about mental health issues like ADHD, depression and anxiety, a lot of their information comes from social media or movies, which can misrepresent and/or show small aspects of the illness. In reality, living with ADHD is much more difficult than we imagine.
A major study from Deakin University has looked closely at how ADHD affects a child's long-term health and quality of life. While we've known a lot about how ADHD impacts school and daily tasks, this research is one of the first to track the same group of children over 13 years to see the full picture.
The study followed 4,000 Australian children aged 4 to 17 and found that a child's quality of life is influenced by more than just their ADHD symptoms.
What Are Some Negative Factors for Children With ADHD?
Some things that negatively impacted a child who had ADHD, making this more difficult for them, were:
- Being a girl
- Having other medical conditions, like autism
- Taking ADHD medication
- Having a parent with mental health issues
The researchers explained that a child’s health was more likely to be poor if they had a caregiver with a physical or mental illness or if the child themselves had another medical condition like autism. The study also noted that children on common ADHD medications had poorer health outcomes, but the researchers say this specific finding needs more research.
The research showed that Children with ADHD tended to have better health and a higher quality of life if they had two or more siblings, a strong family support system, and were physically active.
Parenting Kids With ADHD – How Well Do Parents Cope?
When it comes to treating a child with ADHD, parents' personal experiences heavily influence the choices they make. A 2022 study published in the Child Care, Health and Development journal aimed to understand what it's like for parents raising a child with ADHD and how those experiences shape their views on different treatment options. The study found two main themes from the parents' stories:
ADHD's Impact on the Family
Parents talked about how ADHD forced them to completely change their family life. They had to constantly try new things to help their child at school and felt pressure from society to make their child "fit in."
Finding the Right Treatment
Parents emphasized the challenge of finding a treatment that truly worked for their child. They wanted to find the "right fit" with doctors and treatments. They also mentioned that factors like cost and location made it hard for everyone to get the help they needed, pointing to a need for more equal access to care.
The study concluded that no matter where they lived or what their background was, parents shared very similar struggles and goals. They all want access to a comprehensive treatment plan that involves the whole family and uses different approaches, not just one type of therapy or medication. The study suggests that we need to figure out what changes in healthcare and policy are needed to make this kind of family-centered treatment more widely available.
Why We Need Better Treatment Options For Kids With ADHD
The findings from the Deakin university research highlight that a child's health is affected by a range of factors, not just ADHD itself. A more holistic approach is needed, one that also addresses a child’s emotional and social challenges, as well as the mental health of their caregivers.
This new information is a good reminder that any changes to a child's treatment plan should always be made in consultation with a medical professional
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

