- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Can You Use Viagra For High Blood Pressure?
Credit: Canva
Nearly three decades ago, Viagra (sildenafil) was invented in a Pfizer laboratory as a groundbreaking treatment for erectile dysfunction (ED). Since then, the drug used has been highly marketed for its ability to enhance blood flow to the penis by inhibiting an enzyme called Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5). Interestingly, Viagra was not initially developed for ED.
Researchers originally studied sildenafil as a potential treatment for high blood pressure. However, during clinical trials, participants experienced erections as a side effect, leading to the drug's repurposing as an ED medication.
Viagra Can Be Used For High Blood Pressure
Given its origins, it is not surprising that Viagra can temporarily lower blood pressure. A 2002 study published in Urology examined the effects of sildenafil on blood pressure among men with and without hypertension. The findings revealed that a 100-milligram dose reduced systolic blood pressure by an average of 6 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure by 4.5 mmHg. Older participants experienced slightly greater reductions, though not to a dangerous extent.
Despite these effects, Viagra is not a reliable treatment for hypertension. More importantly, individuals taking certain medications must be cautious, as Viagra can interact with other drugs and cause a significant drop in blood pressure.
What Are The Risks?
One of the more serious risks associated with Viagra is hypotension or dangerously low blood pressure. This can lead to dizziness, lightheadedness, or, in severe cases, a heart attack or stroke. The risk is particularly high for individuals taking nitrates for chest pain, high blood pressure medications, or heart failure drugs such as riociguat (Adempas). Recreational drugs known as "poppers"—which contain amyl or butyl nitrites—can also trigger dangerous interactions.
Additionally, sildenafil is used in another medication, Revatio, which is prescribed for pulmonary hypertension—a condition that affects blood flow between the heart and lungs. Revatio is taken in smaller doses multiple times a day, and individuals using it should avoid Viagra or other PDE5 inhibitors to prevent complications.
You Must Always Consult A Doctor For Erectile Dysfunction
Even if you do not have high blood pressure, discussing ED with a healthcare professional is essential before starting Viagra. ED can sometimes signal underlying health issues such as high cholesterol, obesity, type 2 diabetes, sleep disorders, or substance use problems.
Moreover, ED is increasingly recognized as an early warning sign of cardiovascular disease. A 2021 study published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine found that ED could precede serious cardiovascular events—such as a heart attack or stroke—by about three years. This is because the smaller blood vessels in the penis often show signs of damage before larger vessels near the heart, brain, and lungs.
Before seeking ED treatment, individuals should undergo a comprehensive evaluation of their cardiovascular health, including risk factors like family history, metabolic conditions, and lifestyle habits.
This Health Parameter May Be More Important Than BMI or Body Fat, According To Doctor
Credits: iStock
We have been told for long that BMI or the body mass index is the ultimate measurement for your healthy life. However, while it could predict how healthy you will be in the coming years down the line, it is not the only parameter that you should be focused on. In fact, several studies have shown that BMI in fact is not the right parameter, as it does not take in account for one's body type. Tracking the right parameter could actually help flag potential problems long before symptoms even appear. This can give you enough opportunity to intervene through lifestyle changes.
A Bengaluru-based dermatologist, Dr Priyanka Reddy, who is also a cosmetologist and trichologist, and the founder of DNA Skin Clinic and Wellness Centre, highlighted that one crucial health parameter is actually visceral or centripetal fat.
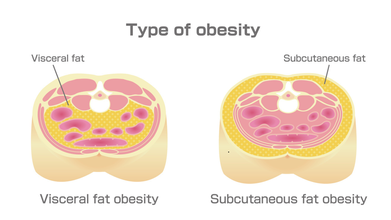
What Is Visceral Fat?
"This is the centripetal or visceral fat - the fat around the abdomen and internal organs. It starts in your late 20s to early 30s and it can predict your future health problems like these and it is closely linked to insulin resistance, poor sleep cycle, stress and other factors like these. This is also called apple-shaped obesity,” she explains.
How To Track Visceral Fat?
Tracking visceral fat does not always require expensive tests. Experts say there are both simple at-home ways and more precise clinical methods to understand whether your levels are in a risky range.
The easiest place to start is waist circumference. For women, a waist size above 80 cm signals higher health risk, while for men the risk increases beyond 90 cm. This measurement is quick, affordable, and surprisingly informative when done correctly and consistently.
Another helpful marker is the waist-to-height ratio. If your waist measurement is more than half your height, meaning a ratio of 0.5 or higher, it is considered unhealthy and linked to higher metabolic risk.
For clinical accuracy, DEXA scans are considered the gold standard. Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry provides a detailed breakdown of fat distribution, including visceral fat stored around organs.
Many people also rely on smart scales, which offer a visceral fat score. A score above 9 may indicate increased risk. However, experts caution that this number should be seen as a trend over time rather than a medical diagnosis.
In general, a healthy waist range is slightly lower than risk cut-offs. For women, a waist below 75 to 80 cm is considered healthy, though risk rises after 40. For men, a waist under 88 to 90 cm is ideal, with risk also increasing after 40.
Why Visceral Fat Increases
Visceral fat builds up due to a combination of lifestyle and hormonal factors. Poor sleep, chronic stress, insulin resistance, low muscle mass, frequent alcohol intake, and diets high in ultra-processed carbohydrates all play a role. Hormonal shifts such as PCOS, menopause, or low testosterone can further worsen fat accumulation around the abdomen.
How to reduce visceral fat
Experts recommend strength training three to four times a week as a non-negotiable habit. This should be combined with Zone 2 cardio and one or two HIIT sessions weekly. Meals should prioritize protein and fibre, while sugary drinks and late-night eating should be minimized. Consistent sleep of seven to eight hours and active stress management through yoga, dance, or breathwork are equally important. Alcohol should be paused if levels are high.
If visceral fat does not reduce despite consistency, it may be time to check for thyroid issues, insulin resistance, high cortisol, or hormonal imbalances.
Long-term maintenance
To keep visceral fat in check, track your waist monthly, lift weights year-round, prioritize sleep, and manage stress before cutting calories. Experts emphasize that visceral fat is a metabolic issue, not just a weight-loss problem. Address the root causes, and fat loss often follows naturally.
Oprah Winfrey Shares Her Fitness Journey While Being On GLP-1 Weight-loss Drugs

Credits: Instagram
“I would have been thinking, ‘How many calories in that croissant? How long is it going to take me to work it off? If I have the croissant, I won’t be able to have dinner.’ I’d still be thinking about that damn croissant!” This morning, however, she is blissfully unbothered: “I felt nothing. The only thing I thought was, ‘I need to clean up these crumbs.’ ” These are the thoughts that would come to Oprah Winfrey's mind whenever she would try to eat something butter, she shared in an interview with PEOPLE. However, now, she can eat a croissant, like a croissant, without being obsessed about it for an entire day. “I’ve just had a croissant. And I ate the full thing,” she said describing her breakfast.
Winfrey started taking GLP-1 weight-loss jabs two and a half years ago, when she thought that she suffers from obesity and she cannot fight it without help. “I thought it was about discipline and willpower. But I stopped blaming myself,” said Winfrey.
Also Read: Explained: Indore Water Contamination Linked to E. coli and Klebsiella Bacteria — What Are They?
From Diet Culture to Self-Blame
These medications transformed the way she looked at life. As she soon turns 72 on January 29, she no longer sees exercise as a punishment. She said she could be happily "side-planking and deadlifting." She now no longer drinks alcohol. “I could outdrink everyone at the table,” she notes with a laugh) and is amazed that she’s satisfied after she eats. “I’m not constantly punishing myself,” she says. “I hardly recognize the woman I’ve become. But she’s a happy woman.” She told PEOPLE.
Winfrey's weight has always been a struggle for her, especially when she read painful headlines like 'Oprah - Fatter Than Ever' or 'Oprah Warned: 'Diet or Die''. In fact, in her first appearance on The Tonight Show in 1985, she was goaded into agreeing to lose 15 lbs. by hot Joan Rivers. While she became the one-name star, she always remained aware about her weight. “I’ve always been confident in whatever I was doing, but I was at the same time disappointed in my overweight body. “Was I embarrassed by it? Yes. Was I disappointed in myself for continuing to fail? Yes, every single time. I felt it was my fault,” she writes in her book, co-authored by obesity expert Dr Ania M Jastreboff: Enough: Your Health, Your Weight and What It's Like to Be Free.
She wrote that she “felt doubly shameful because I have access to so much: chefs and trainers and the healthiest of foods.”
For decades, Oprah Winfrey lived under a microscope, her body turning into both public spectacle and personal battleground. She now openly admits that while she endured relentless humiliation, she also helped normalize weight shaming herself. In 1988, she survived four months on liquid shakes alone, famously dragging a wagon filled with 67 pounds of fat onto her show to prove she could fit into size 10 jeans. Years later, she lost 20 pounds simply because Vogue suggested it before a cover shoot. At the time, it felt like willpower. In hindsight, it felt like survival.
Also Read: Australian Cricketer Damien Martyn in Hospital With Meningitis
When the Body Pushes Back
No diet or discipline seemed to last. No matter how hard she tried, her weight kept returning to 211 pounds, what experts now call a biological “set point.” Even after knee surgery in 2021, daily hikes and eating one meal a day, her body resisted. Ten-mile hikes still resulted in weight gain. The message was clear: this was not a motivation problem.
How Did GLP-1 Medication Transform Oprah Winfrey?
Everything shifted in 2023 when Winfrey hosted a special on obesity and had what she calls an epiphany. She finally understood obesity as a disease, not a personal failure. That realization cracked years of shame. GLP-1 medications, which she had earlier dismissed, suddenly felt like a medical tool rather than a moral shortcut. Starting the injections felt like relief, even a gift.
She briefly stopped the medication in early 2024, believing lifestyle changes alone might be enough. The weight returned. That’s when she accepted the truth: this would be lifelong care, not a phase. Now, she describes GLP-1 as a way to quiet the constant mental chatter around food. The “food noise” faded, replaced by calm, strength, and clarity.
Today, it’s not about a number on the scale. It’s about peace. Better health markers. Deeper relationships. Even unexpected changes, like losing interest in alcohol. Winfrey’s message is simple but radical: if obesity runs in your genes, it’s not your fault. And you deserve compassion, information, and real choices.
Trying To Get Fit In 2026? Here’s A 6-Step Weight-Loss Plan From A Fitness Coach

Credits: Canva
When it comes to losing weight, most people put all their energy into workouts and diet plans, often forgetting one crucial part of the process: mindset. How you think about fitness, food, and consistency plays a major role in whether weight loss feels like a struggle or becomes a sustainable habit. Shifting your approach can make shedding extra kilos feel more manageable and long-lasting.
If staying healthy and losing weight are the goals for the coming year, Raj Ganpath, a fitness coach with over 18 years of experience and the founder of The Quad in Chennai, shares six simple but effective principles to keep in mind. He outlined these points in an Instagram post on 29 December.
6-Step Weight-Loss Plan From A Fitness Coach
1. Eat Less
“You need to eat less,” Raj says plainly. However, he said that this does not mean starving yourself or cutting out all your favourite foods. Instead, it is about being mindful of portion sizes and recognising how often we tend to overeat without realising it. According to him, consistent overeating is one of the most common reasons people struggle to lose weight. Paying attention to how much you eat, even when the food is healthy, can make a noticeable difference over time.
2. Eat Well
Eating less alone is not enough if the quality of food is poor. Raj explains that eating well means choosing nutrient-dense foods that support your body. This includes prioritising protein, vegetables, and whole foods, while reducing items that offer little nutritional value. Sugary snacks, deep-fried foods, and heavily processed or starchy items may be comforting, but they do not help when weight loss is the goal. Making better food choices more often than not builds a strong foundation for fitness.
3. Exercise Regularly
Consistency matters more than intensity. Raj advises exercising at least three days a week, with an ideal range of five to six days if possible. The exact form of exercise is less important than showing up regularly. However, he stresses that strength training should be included at least twice a week. Building muscle supports metabolism and overall strength, making weight loss more effective and sustainable in the long run.
4. Move Often
Exercise sessions alone are not enough if the rest of the day is spent sitting. Raj encourages regular movement throughout the day, separate from structured workouts. Simple activities like walking more frequently can add up. He suggests aiming for at least 6,000 steps daily, with 8,000 or more being a better target. This kind of movement supports fat loss, improves circulation, and keeps the body active beyond the gym.
5. Sleep More
Sleep is often ignored, yet it plays a direct role in weight management. “Most of us don’t sleep enough,” Raj points out. Even going to bed 20 to 30 minutes earlier each night can help. He recommends a minimum of six hours of sleep, with seven hours being ideal. Proper rest supports hormone balance, recovery, and energy levels, all of which influence appetite, motivation, and workout performance.
6. Manage Stress
Stress is unavoidable, and Raj acknowledges that no one can live a completely stress-free life. What matters is how stress is handled. Managing stress allows you to stay consistent with healthy habits instead of turning to food, skipping workouts, or neglecting sleep. Whether it is through exercise, meditation, time outdoors, or personal downtime, finding ways to cope with stress is essential for long-term health and weight loss.
Diet And Exercise Works Together For Weight Loss
Weight loss is most effective when diet and exercise work hand in hand. Diet helps create the calorie deficit needed for fat loss, while exercise protects muscle mass, boosts metabolism, and improves heart and bone health.
Strength training is especially important because muscle burns more calories at rest. While diet controls calorie intake, exercise prevents muscle loss, which can otherwise slow metabolism. Together, they create a balanced and sustainable approach that supports lasting results, healthier habits, and reduced chances of regaining weight.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

