- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Are Fluoride Levels In US Drinking Water Harmful? New Findings Link Them to Stronger Teen Cognition

Credits: Canva
The long-standing practice of adding fluoride to community drinking water in the United States is now under sharp review as questions rise about whether its advantages continue to outweigh possible risks. A fresh set of findings pushes back against recent warnings about fluoride in water and suggests that it might offer added benefits.
This renewed national discussion began after a government report from the National Toxicology Program stated that high fluoride exposure was tied to lower IQ in children. That report, however, assessed fluoride amounts that were at least twice higher than federal recommendations and had limited information about what happens at lower, commonly used levels, as per CNN.
However, the latest study examined fluoride quantities that match the usual suggested range in drinking water. Researchers found strong evidence showing that children who grew up with water containing these lower levels of fluoride performed better on cognitive assessments than those who had no fluoride exposure.
Fluoride in US Public Water Faces Renewed Questions
Dr. Rob Warren, lead author of the study released in Science Advances, said he was surprised by the National Toxicology Program’s earlier conclusions and felt the need to produce evidence more suitable for public policy. He explained that he pursued the work because it was a major question without a clear answer.
The national debate has also intensified as US Department of Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. has labeled fluoride an industrial waste and pointed to possible IQ loss while calling for a rollback of federal guidance. Utah and Florida have already moved to prohibit fluoridation of public water.
As per CNN, Warren compared the situation to testing a heart medication. If the advised dose is 100 milligrams, but a study measures reactions to nearly a million milligrams, the results do not reflect what happens at the normal dose. He said that this is how much of the fluoride research has been structured and that only extremely high doses have shown harmful effects, which is not helpful for policy decisions.
Warren directs a long-running program that began in the US Department of Education and has followed tens of thousands of Americans from their high school years in the 1980s through several decades.
Fluoride and Cognition: What The Study Found
For the current analysis, the team linked math, reading and vocabulary test scores from nearly 27,000 participants to the level of fluoride in their childhood drinking water. These measurements were based on older records from the US Geological Survey and the Department of Health and Human Services, as per CNN.
Researchers worked under the assumption that participants spent their entire upbringing near their high schools. They sorted people into three groups. One group had steady exposure to recommended fluoride levels either through natural sources or public water treatment. Another group never had fluoride in their water. A third group had mixed exposure because their community changed its water policy at some point.
Students who had fluoride for only part of their childhood scored higher on tests than peers who never had it. Those who grew up with fluoride throughout all their childhood years scored even better. Follow-up testing that continued up to 2021, when many had reached about 60 years of age, also showed no sign that fluoride contributed to cognitive decline.
Warren clarified that cognitive tests are not exact IQ scores, although they relate strongly. Test results reflect both mental ability and the learning opportunities a person receives. He is currently working on a follow-up project that will look more closely at fluoride and IQ with improved childhood location data.
Other studies this year suggested that removing fluoride from public water in the United States could lead to more than 25 million extra cavities among children and teenagers in five years along with nearly 10 billion dollars in dental treatment costs. Although the new study did not measure dental health, experts noted that pain from untreated cavities can interfere with a child’s ability to attend school or stay focused, which may influence academic scores.
Why Experts Still Differ on Fluoride Policy
Fluoride occurs naturally in some groundwater and foods. It protects teeth by strengthening enamel, which can be damaged by acids formed from bacteria, plaque and sugar. Communities in the United States started adding fluoride to water systems in 1945 to improve oral health in a cost-effective way.
The American Dental Association and numerous specialists continue to support community water fluoridation. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has also kept its recommendations unchanged. The agency does not have authority to require fluoridation, but it considers 0.7 milligrams per liter the ideal amount.
Recently, the US Food and Drug Administration restricted the use of prescription fluoride supplements. The agency noted that unapproved fluoride products may alter the gut microbiome and that better options exist to protect teeth.
In a written response published with the new research, Dr. David Savitz from Brown University argued that before ending a decades-long public health practice, there must be clear proof of harm at commonly used fluoride levels. He wrote that there is still no convincing evidence that fluoridation lacks benefit or causes damage at recommended doses.
He quoted a well-known saying, noting that if something is not broken, there is no reason to fix it. He said the new study suggests that fluoridated water remains on the side of being effective and safe.
British Woman Gives Birth After Rare Womb Transplant Surgery

Credit: PA Media
For the first time, a baby boy has been born to a mother with a womb transplanted from a deceased donor at Queen Charlotte’s and Chelsea hospital in London.
Weighing merely 3.09kg (6lb 13oz), Hugo Powell was born to Grace Bell and Steve Powell from Kent, right before Christmas 2025. "It's simply a miracle. I never, ever thought that this would be possible," Bell said. "I'm the happiest I've ever been in my life. When I was 16, I was told that this would never be possible," she said of her son's birth.
The father added: "When he came over the curtain, it was just sort of overwhelming emotions. I felt like I wanted to cry, but couldn't. From where we started - first meeting - to where we are today, with Hugo, is nothing short of a miracle after everything we've been through. It just felt quite unreal at the time, because this has been a long journey for us both."
The couple also paid tribute to the "kindness and selflessness" of their transplant donor and her family for their "incredible gift", while also thanking medical teams in Oxford and London who supported their journey.
"There are no words to say thank you enough to my donor and her family. Their kindness and selflessness to a complete stranger is the reason I have been able to fulfil my lifelong dream of being a mum.
"I hope they know that my child will always know of their incredible gift, and the miracle that brought him into this world," Bell said.
What Is Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser Disorder?
Bell, an IT programme manager, was born with Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser (MRKH), a disorder that causes the vagina and uterus to be underdeveloped or absent. MRKH syndrome is also called:
- Müllerian agenesis
- Müllerian aplasia
- Congenital absence of the uterus and vagina
- Rokitansky syndrome
While women with MRKH syndrome have normal external genitalia, functioning ovaries, breast and pubic hair development, they are unable to carry a pregnancy and rely on either surrogacy or a womb transplant, as in the case of Bell.
There are two versions of the disorder:
- Type 1: The patient has normally functioning ovaries and fallopian tubes but a blocked or missing upper vagina, cervix and uterus. No other organs are affected.
- Type 2: The patient has a blocked or missing upper vagina, cervix and uterus as well as issues with ovaries, fallopian tubes, spine, kidneys or other organs.
However, these genetic changes have been found in only a small number of affected people and subsequent studies have not identified a clear association between MRKH syndrome and any specific environmental factors. It remains unclears whether they actually cause MRKH syndrome.
Treatment for MRKH depends on the patient's goals and symptoms and some options include:
- Vaginal dilators: Dilators are made of plastic or silicone and vary in length and width. These tubelike devices help expand and stretch the inside of the vagina.
- Vaginoplasty: This is a surgical procedure to create a vagina. There are several ways surgeons perform vaginoplasty, but most involve creating a hole and lining it with tissue from another part of your body.
- Uterus transplant: This is a major surgery that involves placing a donor uterus inside someone without a uterus. Uterine transplants give people with MRKH an opportunity to carry and deliver a child. Uterus transplants are rare.
How Did Bell Conceive Her Child?
Recalling her initial diagnosis, Bell said: "About 16 years ago, I was diagnosed with MRKH. It was a tough journey. I must admit, a very sad journey. I remember the story of the first womb transplant in Sweden, many years ago now, and following that story intently."I still can't believe that I'm here today and I've gone through this. It's just amazing."
At the age of 16, the new mother was told she wouldn't be able to carry her own child. However, in 2024 she received a phone call saying a womb had been donated and a transplant was possible, a moment she recalls left her "in complete shock" and "really excited".
Bell's womb transplant operation lasted 10 hours and took place at The Churchill Hospital in Oxford in June 2024 After her transplant surgery, she began fertility treatments several months after the transplant in 2024 and her son was born a year later.
According to The Guardian, Bell's transplanted womb will be removed when the couple have finished having children, to save her from a lifetime of taking immunosuppressant drugs.
15 States Sue Trump Administration Over Revised Vaccine Schedule
Credits: iStock
15 US states sued President Donald Trump led administration after the Department of Health and Human Services led by Health Secretary Robert F Kennedy Jr. revised vaccine schedule that led to coverage fall from 17 to 11 diseases for children. These 15 states are led Democrats and on Tuesday, they announced suing the Trump administration over unscientific grounds of releasing a new vaccine schedule.
The lawsuit has been filed by a coalition of 14 attorneys general and the governor of Pennsylvania. They have asked the courts to nullify the administration's decision to reduce the number of diseases children are routinely immunized from 17 to 11.
The lawsuit also challenges "the unlawful replacement" of members of the federal Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, who recommend vaccines for Americans. The lawsuit names the Department of Health and Human Services and Health Secretary Robert F Kennedy Jr as defendants. It also names the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and its acting director, Dr Jay Bhattacharya.
Read: CDC Vaccine Schedule: Coverage Falls From 17 to 11 Diseases For Children
15 States Sue Trump Administration Over Revised Vaccine Schedule: What Do The States Want?
In a news briefing on Tuesday, Rob Bonta, attorney general of California said, "H.H.S. Secretary R.F.K. Jr. and his C.D.C. are flouting decades of scientific research, ignoring credible medical experts, and threatening to strain state resources and make America’s children sicker.” Bonta continued, "The fact is, vaccines save lives and save our state’s money."
The lawsuit also notes that the administration's revised vaccination schedule was unscientific and relied instead on comparisons to countries that are different than the United States.
Kris Mayes, attorney general of Arizona, as reported by The New York Times said that the latest vaccine schedule "copies" Denmark's recommendation, where the country already has a nationalized health care and the population is fraction of that of the US. "Copying Denmark’s vaccine schedule without copying Denmark’s health care system doesn’t give families more options — it just leaves kids unprotected from serious diseases."
Also Read: Wegovy And Ozempic Will Cost Less In 2027, Novo Nordisk Slashes Weight Loss Drugs Prices By Half
15 States Sue Trump Administration Over Revised Vaccine Schedule: What Is The Revised Vaccine Schedule?
On January 5, 2026, the federal health officials led by RFK Jr. announced that the new Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), vaccine schedule will include routine shots for 11 diseases for children. This is down from 17 diseases, which were earlier included.
Under the revised schedule, vaccines for a limited number of diseases remain universally recommended for children. These include protection against measles, polio, and whooping cough, which are still considered essential routine immunizations.
Vaccines No Longer Recommended for All Children
The most controversial change is the narrowing of recommendations for several common childhood vaccines. Immunization against the following illnesses is now advised only for high-risk children or after consultation with a health care provider:
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Meningococcal disease
- Rotavirus
- Influenza
- Respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV
Covid-19 vaccination has also shifted to a consultation-based recommendation rather than routine use for all children.
This means shots that were once automatically given at set ages, including at birth, during infancy, and in adolescence, may now depend on individual medical discussions rather than standard guidance.
Wegovy And Ozempic Will Cost Less In 2027, Novo Nordisk Slashes Weight Loss Drugs Prices By Half

Credits: iStock
Wegovy and Ozempic will cost less by January 1 of 2027 as manufacturer Novo Nordisk announced that the prices will be cut in half. The manufacturer said that the popular GLP-1 weight loss drugs will be as much as 50 per cent.
Wegovy and Ozempic Will Cost Less In 2027: How Cheap Can You Get Your Weight Loss Drugs For?
- The list price of Wegovy injections and the new Wegovy pill will be cut in half
- Ozempic injections will be cut by 35 per cent
The manufacturer noted that this cut applies to all doses and the semaglutide tablet Rybelsus will now cost $675 a month. Rybelsus has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to reduce the risk of heart attacks in those with diabetes.
Read: Doctor Explains Why Weight Loss Drugs Like Ozempic Are Truly A Medical Breakthrough
In a statement to PEOPLE, Jamey Millar, Executive Vice President, US Operations of Novo Nordisk Inc. said, "There are more than 100 million people living with obesity and over 35 million with type 2 diabetes and, for some, list price has been a real barrier to access and affordability."
Wegovy and Ozempic Will Cost Less In 2027: What Are The Current Price?
Wegovy injections and pills currently cost $1,349.02 a month, whereas Ozempic and Rybelus cost $1,027.51. These figures have been emailed to PEOPLE by Novo Nordisk.
Read: GLP-1 Drugs Don’t Just Curb Appetite; They Rewire the Brain, Shows Study
People with commercial insurance pay $25 a month, whereas those using cash pay between $149 to $499. Patients on Medicare will pay $274 per month.
Wegovy and Ozempic Will Cost Less In 2027: How Do GLP-1 Weight Loss Drugs Work?
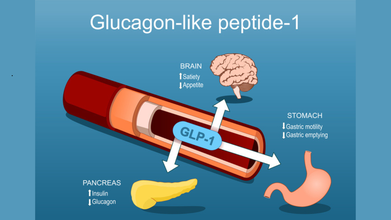
GLP-1 drugs mimic the action of the natural hormone GLP-1 to regulate blood sugar and promote weight loss. They work by increasing insulin release in a glucose-dependent manner, decreasing the liver's production of glucagon, and slowing down the emptying of the stomach, which helps lower blood sugar levels after a meal. They also act on the brain to suppress appetite and increase feelings of fullness, leading to reduced calorie intake.
Read: Zepbound Outperforms Other Weight Loss Drugs, More Details Inside
In people with type 2 diabetes, notes Harvard Health, the body's cells are resistant to the effects of insulin and body does not produce enough insulin, or both. This is when GLP-1 agonists stimulate pancreas to release insulin and suppress the release of another hormone called glucagon.
These drugs also act in the brain to reduce hunger and act on the stomach to delay emptying, so you feel full for a longer time. These effects can lead to weight loss, which can be an important part of managing diabetes.
In September 2025, WHO added GLP-1 drugs to its list of essential medicines, but only for treating diabetes, not for obesity alone. The new guideline extends that conversation, offering a more formal stance on their use in obesity management. The recommendations were developed by a committee of experts in obesity, pharmacology, and public health, following requests from several WHO member states. They also align with approvals already granted by regulators like the US FDA.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

