- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Delhi Air Pollution: Damage Risks Are Beyond Your Lungs, It Can Affect Your Kidney Too, According To Doctor
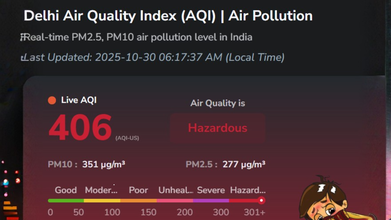
Credits: AQI.in
As of 6.17am on October 30, 2025, the AQI in Delhi is recorded at 406, and falls under the category 'Hazardous'. Major pollutants are PM2.5, PM10, CO, So2, No2, and O3. We have long known air pollution's impact on respiratory health and lungs, however, it is beyond that. With levels as high as 'hazardous', the pollution could also damage our kidneys.
Dr Sanjeev Gulati, nephrologist in Fortis, Delhi, writes that the detrimental effects of air pollution are not only evident in the respiratory and circulatory system, but it can also extend to renal function. He writes, "The kidneys are particularly vulnerable to the toxic effects of environmental pollutants due to their critical role in filtration. Environmental and occupational exposure to pollutants remains a common cause of kidney disease globally, especially in developing countries."
Up to 22% of the global disease burden and 23% of deaths are attributed to environmental pollution. There have been various studies that show the long-term exposure from particulate matter and how it is linked to an increased risk of membranous nephropathy and decline in renal function.
What Is Membranous Nephropathy?
It is a kidney disease caused by the damage to the kidney's filtration system. This could lead to significant protein leakage into the urine. This could happen due to the PM exposure.
In fact, a 2025 study published in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology highlighted the role of air pollution in the rising risk of new kidney diseases. The study was able to track 2.5 million veterans, who were free of kidney diseases in 2003 and 2004, over an average of 8.5 years. The researchers then compared their health outcomes to air pollution levels. The study then found that for every 10 microgram increase in pollution per cubic meter of air, there was a 25 to 37% increase in new kidney disease case, a 36% rise in rapid kidney function decline, and a 31% increase in the risk of kidney failure requiring dialysis.
How Does Pollution Damage Your Kidney?
Dr Sean Hashmi, MD, MS, FASN, a board-certified nephrologist and obesity medicine specialist in the Southern Carolina, US, in a video on his YouTube channel that he uploaded to explain the impact of air pollution on kidney says, "your kidney is force to process a chemical soup day after day after day. And the main villain here is PM2.5."
Dr Hashmi notes that once the PM2.5 is in your bloodstream, your body treats them like foreign invaders. "This triggers powerful inflammation throughout your system. Inflammation is your immune system's response to injury and threat. However, when inflammation becomes chronic [due to long exposure of PM2.5], it can damage healthy tissues."
He says, as a result, these particle-filled blood arrives in your kidney. "Your kidneys have millions of tiny filters glomerulus, they are like cluster of blood vessels that act like coffee filters for your blood. The constant flow of abrasive particles creates low-grade sand blasting on these fragile filters. Over years this leads to permanent scarring and reduced kidney functions."
British Airways Crew Hospitalized After Eating Weed-Laced Gummies

Credit: Canva
Three British Airways cabin members were taken to the hospital after they ate marijuana-laced sweets handed to them by a passenger during a flight from London Heathrow to Los Angeles.
The staffers were unaware that the sweets contained up to 300mg of THC, the main psychoactive compound in weed a produces the psychoactive effect.
The affected members are said to have had 'out-of-body experiences' after unknowingly consuming the weed-laced gummies. The airline has now launched an investigation to find the passenger who gave the crew member the marijuana edibles.
"It is a godsend in this case the sweets in question were not shared out among the crew until they had arrived in the US," one source told The Sun.
"They were consumed in the crew bus after touchdown, and tired staff gratefully gobbled them up. Almost immediately BA staff realized something was wrong.
"By the time the group had reached the crew hotel, three staff members who had numerous sweets began suffering 'out-of-body' experiences. They felt totally out of control and became panicked and scared."
As a result, the entire crew had to be grounded in LA and a new team was out in place to operate the return service. The affected members were flown back on a separate service days later as passengers.
What Is THC?
THC is essentially the compound that causes the euphoric “high” associated with cannabis. It’s commonly consumed through smoking cannabis, edibles, tinctures, and capsules. THC also offers medical benefits but is more likely to cause psychoactive side effects.
Known for helping with nausea, appetite stimulation, chronic pain, and insomnia, this FDA-approved edible is used in synthetic forms (like dronabinol) for treating chemotherapy-induced nausea and appetite loss in conditions like AIDS.
THC can cause temporary effects like dry mouth, red eyes and increased heart rate. Long-term use, especially in adolescents, may be linked to psychiatric issues such as anxiety or low motivation.
While CBD is not intoxicating but has mild psychoactive properties, such as promoting relaxation, THC, however, directly binds to brain receptors, causing euphoria or a “high.
Why Is THC Dangerous?
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is considered dangerous primarily due to its psychoactive effects that impair brain function, cognition, and motor coordination, increasing risks of accidents and addiction.Furthermore, THC disrupts normal brain function, affecting memory, learning, and attention, especially in developing adolescent brains. It can cause acute panic, anxiety, and, in some cases, induce psychosis.
Along with this, it impairs coordination, slows reaction time, and alters judgment, directly contributing to motor-vehicle accidents.
Frequent use of marijuana has been previously linked to a higher risk of developing schizophrenia or other psychoses in people who are predisposed to these conditions.
According to the American Health Association, smoking cannabis also causes respiratory issues such as lung irritation and coughing as well as increases heart rate and blood pressure, which can raise the risk of heart attacks or strokes.
Erythritol Sweetener Could Be Linked To Stroke Risk, Finds Study

Credits: Canva
Erythritol sweetener, commonly found in most of the food we consume, whether it is a protein bar or energy drink could be linked to stroke risk. While it is considered as a safer alternative to sugar as a natural sweetener, a study from the University of Colorado suggests it could damage cells in the blood-brain barrier.
The blood-brain barrier is brain's security system that keeps the harmful substance off the limits, while letting in nutrients. Research also suggests that it would lead to serious consequences for heart health and stroke risk.
Erythritol Sweetener Risk: What Did The Study Find?
In the latest study, researchers exposed cells that form the blood–brain barrier to erythritol levels typically seen after consuming a soft drink sweetened with the compound. What followed was a cascade of cellular damage that could leave the brain more vulnerable to blood clots, one of the leading causes of stroke.
The researchers found that erythritol triggered intense oxidative stress, overwhelming cells with unstable molecules known as free radicals. At the same time, it weakened the body’s natural antioxidant defences. This double hit impaired normal cell function and, in some cases, led to cell death.
Damage to blood–brain barrier cells is particularly concerning because this barrier plays a crucial role in protecting the brain from harmful substances circulating in the bloodstream. When its integrity is compromised, the risk of neurological injury rises sharply.
Erythritol Sweetener Risk: How It Disrupts Blood Flow Control
Even more troubling was erythritol’s effect on how blood vessels regulate blood flow. Healthy blood vessels constantly adjust their width—expanding when organs need more oxygen and nutrients, and narrowing when demand is lower.
This process depends on a delicate balance between two molecules: nitric oxide, which relaxes blood vessels, and endothelin-1, which causes them to constrict. The study found that erythritol disrupted this balance by reducing nitric oxide production while increasing endothelin-1 levels.
The result is blood vessels that stay constricted longer than they should, potentially restricting blood flow to the brain. This kind of dysfunction is a known warning sign for ischaemic stroke, the most common form of stroke caused by blocked blood vessels.
Erythritol Sweetener Risk: How It Interferes With Body's Clot Defense
The most alarming finding in the study was how body's natural protect against blood clot is disturbed. Under normal circumstances, cells release a substance called tissue plasminogen activator, which is described as a natural 'clot buster', which helps dissolve clots before they become dangerous. However, erythritol could interfere with this protective mechanism and allow clots to persist and cause damage.
Several have shown that people with higher blood levels of erythritol face significantly increased risks of cardiovascular events. In one major study, individuals with the highest erythritol levels were nearly twice as likely to suffer a heart attack or stroke.
However, researchers caution that the experiments were conducted on isolated cells rather than full blood vessels. More advanced models that better replicate human physiology will be needed to confirm the findings.
Erythritol occupies a unique space in the sweetener world. Classified as a sugar alcohol rather than an artificial sweetener, it escaped recent World Health Organization guidance discouraging artificial sweeteners for weight control. Its sugar-like taste has also made it a favorite in “keto-friendly” and sugar-free foods.
FDA Refuses To Review Moderna's Flu Vaccine Application
Credits: Canva
FDA refuses to review Moderna's flu vaccine: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has declined to begin reviewing Moderna’s application for its experimental flu vaccine. The company made the announcement on Tuesday. The decision marks another signal of stricter vaccine oversight under the Trump administration and has already rattled investor confidence, with Moderna’s stock falling nearly 7% in after-hours trading.
Read: CDC Vaccine Schedule: Coverage Falls From 17 to 11 Diseases For Children
Moderna said the FDA’s refusal came as a surprise and contradicted feedback the company had received earlier, before it submitted the application and launched phase three trials for the vaccine, known as mRNA-1010. The company has now requested a meeting with the agency to better understand what it described as an unclear “path forward.”
FDA Refuses: Objections Raised Over Trial Design
According to Moderna, the FDA did not flag any safety or efficacy concerns with the vaccine itself. Instead, the agency objected to the design of the clinical trial—despite having previously signed off on it. Moderna added that the setback would not affect its financial guidance for 2026.
The experimental flu shot had shown encouraging results in phase three trials last year, successfully meeting all primary trial endpoints. At the time, Moderna positioned the stand-alone flu vaccine as a critical step toward developing a combined influenza and COVID-19 vaccine, a key long-term goal for the company.
FDA Refuses: Shifting U.S. Vaccine Policy Landscape
The decision comes amid sweeping changes to U.S. immunisation policy over the past year under Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr., who has long expressed skepticism toward vaccines. Moderna on Tuesday pointed to the FDA’s top vaccine regulator, Vinay Prasad, who returned to the agency in August after being removed earlier.
Prasad currently heads the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) and has publicly argued for tighter regulatory standards for vaccines. He has also drawn controversy for comments linking child deaths to COVID-19 vaccines.
FDA Refuses: FDA Letter Cites Comparator Concerns
In a letter dated February 3 and signed by Prasad, the FDA stated that its refusal to review Moderna’s application was solely due to concerns about the trial’s design. Specifically, the agency objected to Moderna’s choice of comparator, arguing that comparing the experimental shot to a standard, approved flu vaccine did not represent the “best available standard of care.”
As a result, the FDA concluded that the study did not qualify as an “adequate and well-controlled” trial under its regulatory definition.
Moderna has strongly disputed this interpretation, arguing that FDA rules do not require companies to use the most advanced or highest-dose vaccine as a comparator in clinical trials.
FDA Refuses: Moderna Pushes Back, Eyes 2026–27 Timeline
In a statement, Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel said the decision undermines innovation and fails to advance shared public health goals. He emphasized that the trial design had been discussed and agreed upon with CBER before the study began.
Moderna now expects the earliest possible approval for its flu shot to come in late 2026 or 2027, pending regulatory reviews across the U.S., Europe, Canada, and Australia.
The FDA declined to comment, stating it does not discuss regulatory communications with individual companies, reported CNBC.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

