- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Kate Middleton Opens Up About Her 'Really Difficult' Time During Chemotherapy And How Nature Helped Her Heal

Credits: Wikimedia Commons
Kate Middleton or Catherine, Princess of Wales reflected on the aftermath of chemotherapy in her first public appearance since she had unexpectedly withdrawn from Royal Ascot just two weeks ago.
She has called the entire experience "really difficult". On her visit to a wellbeing garden at Colchester Hospital in Essex, England on Wednesday, she told the patients, "You put on a sort of brave face, stoicism through treatment, treatment’s done – then it’s like ‘I can crack on, get back to normal.’ But actually the phase afterwards is really difficult, you’re not necessarily under the clinical team any longer, but you’re not able to function normally at home as you perhaps once used to."
The reason she visited the hospital garden in the Southeast of England was to "celebrate the incredible healing power of nature", noted Kensington Palace.
She also met with patients and hospital staff at the Cancer Wellbeing Centre "to understand how gardens in healthcare setting play a crucial role in promoting good health outcomes, preventing poor health and supporting increased recovery time."
Now 43, Kate herself has pointed out to the importance of nature in her health journey over the last year.
Is There Any Scientific Proof That Nature Could Actually Heal you?
Lisa A Cooper, MD, MPH writes in the 'Letter from the Director' at John Hopkins Medicine that nature does have healing power. She notes that green spaces play a role in cardiovascular health, and also facilitates to interact with other people who are there to enjoy nature. The American Psychological Association (APA) also noted that spending time in nature is linked to both cognitive benefits and improvements in mood, mental health and emotional well-being. The University of Cincinnati also points out that being out in nature can further reduce anxiety, lower blood pressure, enhance immune system function, and boost self esteem and mood.
In fact in a video, which was posted by Kate on X to mark Mental Health Awareness Week in May, she said, "over the past year, nature has been my sanctuary."
Kate Middleton Cancer Timeline
In March, Princess Kate publicly shared her cancer diagnosis and confirmed she had begun chemotherapy. As she focused on her recovery, she stepped away from the public eye, making only a few limited appearances over the summer. By September, she announced she had completed chemotherapy and was "doing what I can to stay cancer-free."
Since then, the Princess of Wales has been gradually re-engaging with her royal responsibilities. While she has increased her public appearances this year, palace insiders say she is carefully managing her return to balance her health with her official duties.
Earlier this summer, Kate made high-profile appearances at key royal events, including the Trooping the Colour parade in London and the Order of the Garter service in Windsor. However, she later withdrew from the Royal Ascot at the last minute, signaling that her return to full-time royal duties is still being handled with care.
Just last week, Kate resumed in-person engagements, joining Prince William in hosting philanthropist Melinda French Gates at Windsor Castle. The meeting, reportedly focused on their shared philanthropic interests, marked one of her first official engagements in recent weeks.
On Wednesday, the Princess made a meaningful visit to Colchester Hospital, where she helped plant several “Catherine’s Rose” plants—a specially bred rose named in her honor by the Royal Horticultural Society. The visit coincided with the hospital receiving a donation of 50 such plants.
The rose holds special significance: proceeds from its commercial sale will go to The Royal Marsden Cancer Charity, supporting cancer patients through treatment and beyond. The funds will help the charity develop a dedicated program focused on improving quality of life for those living with cancer and those who have completed treatment.
Also Read: Why Everyone Is Suddenly Talking About Ivermectin As A Cancer Breakthrough?
Princess Kate has deepened her connection with the Royal Marsden since her diagnosis. In January, Kensington Palace announced she had been named joint patron of The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust, the specialist cancer center in Chelsea, west London, where she received treatment.
Her involvement with the charity and efforts to raise awareness reflect her commitment to supporting others navigating a cancer diagnosis. While her return to public life is cautious and measured, each appearance signals both her resilience and her intention to use her platform for meaningful causes.
As she continues to recover and adjust, the Princess of Wales remains one of the most admired and closely followed members of the royal family—balancing personal healing with her public role.
Almond Kit Cough Syrup Banned After Toxin Detection: What Ethylene Glycol Poisoning Can Do To The Body

Credits: Canva
The Tamil Nadu government has prohibited the manufacture, sale, distribution, and use of the cough syrup Almond Kit after laboratory testing confirmed it contained the highly toxic chemical ethylene glycol, according to a press release issued by the state’s drug control authority. Officials said the syrup, which is produced in Bihar, was found to be contaminated with ethylene glycol, a substance known to trigger serious and, in some cases, fatal health problems. But what exactly is ethylene glycol poisoning, and what health conditions can it cause?
Cough Syrup Banned In Tamil Nadu Due To Ethylene Glycol Contamination
The Tamil Nadu government has imposed a complete ban on the manufacture, sale, distribution, and consumption of the cough syrup Almond Kit after laboratory tests detected the presence of ethylene glycol, a highly dangerous chemical, the state drug control department said in a press statement. Citing news agency IANS, officials confirmed that the syrup is manufactured in Bihar and was found to be contaminated with ethylene glycol, a compound associated with severe and sometimes life-threatening health complications.
What Is Ethylene Glycol Poisoning And What Are The Early Symptoms?
Ethylene glycol is a colourless, odourless liquid with a sweet taste, most commonly used in antifreeze. It may be consumed accidentally or intentionally, including in cases of self-harm. Once inside the body, ethylene glycol breaks down into glycolic acid and oxalic acid, which are responsible for most of its toxic effects.
According to Medline Plus, early symptoms of ethylene glycol poisoning include a feeling of intoxication, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. As the poisoning progresses, symptoms can worsen and may include reduced consciousness, headaches, and seizures.
Ethylene Glycol: What Health Conditions Can It Lead To?
As per the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), exposure to ethylene glycol can result in severe and potentially fatal health conditions, particularly when ingested through contaminated medicines.
One of the most serious effects is acute kidney failure, which can develop rapidly and may cause the kidneys to shut down within a few days if treatment is delayed. Ethylene glycol can also harm the brain and nervous system, leading to confusion, poor coordination, seizures, and even coma.
The toxin can cause severe metabolic acidosis, a condition in which the blood becomes dangerously acidic, interfering with normal heart function and breathing.
In certain cases, ethylene glycol exposure can also lead to lung-related complications, including fluid accumulation in the lungs that makes breathing difficult.
Without prompt medical intervention, ethylene glycol poisoning can be fatal, especially in children and individuals with existing kidney or liver disease. This is why its detection in any oral medication is treated as a serious public health concern.
Almond Kit Cough Syrup: Which Batch Is Affected?
According to IANS, consumers have been advised to check for batch number AL24002 and strictly avoid using the syrup. People who already have the product have been asked to contact authorities for instructions on safe disposal. The Directorate has also stepped up inspections and monitoring across pharmacies and hospitals in Tamil Nadu to ensure the contaminated cough syrup is fully removed from circulation.
What A Finger-Prick Blood Test Could Mean for Alzheimer’s Diagnosis
Credits: Canva
Finger-prick test for Alzheimer's could actually change its diagnosis. An international research trial is exploring if a simple finger-prick blood test could one day help diagnose Alzheimer's disease much earlier and more easily than current methods. The study has involved 1,000 volunteers aged over 60 from the UK, the UK, and Canada, and aims to detect biological markers in the blood linked to the condition.
If the test is successful, it could shift the Alzheimer's diagnosis. The test has the potential to make the diagnosis cheaper, which may not require expensive scans and invasive procedures.
Why Is This Finger-Prick Alzheimer's Test So Important?
Alzheimer's disease does not begin when memory problems become obvious. Research also shows that abnormal proteins linked to the disease, particularly amyloid and tau, can start building up in the brain more than a decade before symptoms appear.
By the time cognitive changes become noticeable, these damage may already occur. This is why such a test is important to ensure that the condition is diagnosed early. New treatments work best in early stages, which makes it more so important.
How Does The Finger-Prick Test Work?
The trial is examining three specific proteins in the blood that have been strongly associated with Alzheimer’s disease. By measuring their levels and concentration, researchers hope to identify whether someone may be at risk, even before symptoms develop.
All volunteers are also undergoing existing gold-standard tests. These include specialized brain scans using radioactive tracers or lumbar punctures to collect cerebrospinal fluid. These methods are accurate but costly, time-consuming, and invasive. As a result, only a small fraction of patients currently receive them.
One of the biggest advantages of the finger-prick test is that it is simple. Unlike traditional blood tests, this test does not require needles, hospital visits or refrigeration. In the future, it could potentially be done at home, with samples mailed to a laboratory for analysis.
Experts say this could dramatically shorten the time it takes to receive an accurate diagnosis. Many families currently wait months or even years, often navigating multiple appointments before getting clear answers.
Participants have also chosen to take a part due to their personal experience with dementia in the families. For them, the possibility of early screening and new treatment is a way to avoid worsening the condition. Participants who have received negative results describe relief, while also recognizing that individual outcomes are just one part of a much larger study. Researchers will only know how effective the test truly is once data from all participants has been analyzed.
What Happens Next?
So far, 883 volunteers have enrolled, with more than 360 completing every test required. The group includes cognitively healthy individuals, people with mild impairment, and those in the early stages of Alzheimer’s. At least a quarter of participants come from under-represented communities. The trial is also expected to run until 2028.
Delhi Pollution Crosses 400 Mark, GRAP-IV Re-imposed; Here's What We Know
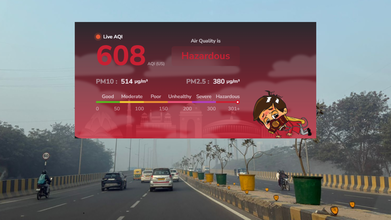
Credits: AQI.in
After a brief period of clear sky, and better air quality index levels (AQI), Delhi is again engulfed with thick layer of smog. Delhiites on Monday morning woke up with the AQI of 418, under the 'severe' category. As per the data released by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), the AQI in the ITO area was recorded 434, Rafi Marg at 417, and areas around Swaminarayan Akshardham temple at 455. All under 'severe' category.
Also Read: NHS England Expands Access To Life Saving Prostate Cancer Drug
- Anand Vihar stood at 462
- Ashok Vihar stood at 473
- Bawana stood at 448
- Burari stood at 460
- Chandni Chowk stood at 454
- Dwarka Sector 8 stood at 427
- Mundka stood at 467
- Narela stood at 437
- Punjabi Bagh stood at 434
- RK Puram stood at 439
- Rohini stood at 437
- Wazirpur stood at 472
GRAP IV Reimposed In Delhi
The Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) imposed Stage IV of the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) on Saturday evening after AQI crossed the 400 mark for the first time in 2026. GRAP-IV is the strictest of all measures, and bans construction activities, along with restrictions on vehicle movement.
What Is Allowed And What Is Not
Under GRAP-IV, all petrol, diesel and CNG stations in Delhi will supply fuel to only vehicles with valid Pollution Under Control Certificate (PUCC).
Vehicles identified through ANPR cameras or other methods and found refuelled without PUCC will be facing penalties.
Verification of the physical certificates or electronic certificates would be done through systems like VAHAN.
Note: These rules do not apply on emergency vehicles on sovereign duty like ambulances, fire tenders and police vehicles. Vehicles carrying essential goods or providing essential services will be exempted too, notified by authorities.
Any vehicle registered outside Delhi and not compliant with BS-VI norms will not be allowed to operate in the city. CNG and electric vehicles, public transport, and vehicles carrying essential goods are exempted.
Trucks or any other carriers that transport construction materials like sand, stones, bricks, cement, ready-mix concrete, debris and similar items, will not be allowed to enter Delhi.
Are Schools Closed Under GRAP-IV?
Under GRAP-IV, physical classes are suspended, and based on previous precedents, educational institutions were directed to shift to online or hybrid learning mode. GRAP-IV restrictions have been reimposed across Delhi and NCR residents, including Gurugram, Faridabad, Ghaziabad, and Gautam Budh Nagar.
Also Read: Delhi Isn't Just Breathing Toxic Air, But Also A Superbug That Resists Antibiotics
Delhi's Air Pollution Continues To Worsen
Delhi is not just breathing toxic air, but also a superbug through its air, which was found in a latest research conducted by the researchers are Jawaharlal Nehru University, published in Nature - Scientific Reports. Apart from the heavy particulate matter or the PM2.5, which are small enough to penetrate through one's bloodstream and cause blockage, Delhi's air also contains airborne bacteria, including staphylococci. The bacteria levels exceed the safety limit by 16-fold as provided by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Will Delhi Use Smog-Eating Surfaces To Deal With Pollution?
The government is pursuing "smog eating" surfaces to deal with the pollution problem in Delhi. While it may sound like a strange thing in India, not to the world. In fact, in the Netherlands these were used to reduce local nitrogen oxide or the NO concentrations in the air, rather than greenhouse gas concentrations.
Smog usually contains a mixture of hydrocarbons, ozone, oxides of nitrogen and sulphur, and particulates. The pollution is caused by both photochemical reactions that involve sunlight, unburned hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides, along with high concentrations of particulate matter, especially from vehicle exhaust, construction dust and biomass burning.
Read: Explained: What Are Smog-Eating Surface And How Is Delhi Using It To Beat Air Pollution
Environment Minister Manjinder Singh Sirsa announced "smog eating" surface as part of its pollution control plan, for which the government has also signed an MoU with IIT Madras.
The smog eating surfaces will be public surfaces coated with photocatalytic materials like titanium dioxide or TiO2 that is used to degrade pollutants.
Smog contains mainly nitric oxide, nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide, ozone, and particulate matter. When all of these interact with photocatalytic materials, gaseous pollutants convert into less harmful compounds, such as nitrogen oxides become nitrates or decompose into ions. This process is also known as pollutant mineralization.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

