- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
Maternal Mortality On Rise In US, Reports CDC
Credits: Canva
After two years of decline in maternal mortality, especially in the number of women dying during or shortly after childbirth in the US, the numbers are again on the rise. As per the newly released data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the 2024 figures have renewed concerns about maternal health in the country. US has already been at one of the highest maternal mortality rates among the high-income countries.
The CDC's provisional report stated that 688 women died last year due to pregnancy-related complications. This is a slight increase from the 669 deaths reported in 2023. The maternal mortality rate also rose and reached to 19 deaths per 100,000 live births. This is up from 18.6, the rate recorded a year earlier.
While the numbers do remain below the peak figures which was noted in the COVID-19 pandemic in 2021 and 2022, the reversal of a two-year downward trend has raised alarms.
What Are Maternal Deaths?
As per CDC, maternal deaths occur during pregnancy, childbirth, or within 42 days after delivery. The major point here is that the deaths must occur due to pregnancy-related conditions. These include excessive bleeding, infections, and blood vessel blockages, which continue to be among the leading causes.
The COVID-19 Effect
The numbers of maternal deaths in the US surged during the COVID-19 pandemic. This proved to be dangerous for pregnancy women, since many healthcare systems and hospitals have become overwhelmed. It also led to gaps in care. During the worst phases of pandemic, some physicians also reported burnout. This could have also been the reason why pregnancy related concerns which required immediate attention could have been downplayed.
As the pandemic receded in 2022 and 2023, the number of maternal deaths declined, in part because of improved COVID-19 prevention and treatment protocols. However, experts warn that the progress made during those years is now being undermined by new and persistent challenges.
The Reason Behind These Numbers:
As per the public health experts, there are several factors that have lead to an increase in the number of maternal mortality:
Limited Access to Care: The closure of rural hospitals across the U.S. continues to make it harder for women in remote areas to access prenatal and emergency care.
Legal and Regulatory Changes: The 2022 Supreme Court ruling that overturned Roe v. Wade has had a ripple effect on maternal healthcare. Some doctors, concerned about legal consequences, are reportedly hesitant to provide certain treatments during pregnancy-related emergencies. In states with strict abortion laws, this has translated into delays in care — potentially putting mothers at greater risk.
Worsening Inequities: The U.S. has long-standing racial disparities in maternal health outcomes. Research has consistently shown that Black women die from pregnancy-related complications at much higher rates than white women, due to a combination of systemic racism, limited access to quality care, and implicit bias in medical settings.
The major concern is also that among the many wealthy countries, US has continued to stand out in a way that is not good for it. It has one of the highest maternal mortality rates in the developed world.
Legionnaires' Outbreak: Death Toll Increases To 6 With 111 Hospitalized, How To Spot The First Symptoms
(Credit-Canva)
A sixth person has died from the Legionnaires’ disease outbreak in Central Harlem, according to New York City health officials. The city is currently investigating the outbreak that began in late July, which has now affected over 100 people.
As of Thursday, 111 people have been diagnosed with the disease. The recent death was of a person who passed away outside of New York City earlier this month, but their death was only recently linked to the outbreak. There are currently seven people hospitalized.
The city has identified and cleaned 12 cooling towers on 10 buildings, including a city hospital and a clinic, where the bacteria were found. These cooling towers, which use water to cool buildings, are believed to be the source of the outbreak.
What is Legionnaires' Disease?
Legionnaires' disease is a severe type of pneumonia caused by a bacteria called Legionella. This bacteria thrives in warm water and can spread through a building’s water system. People usually show flu-like symptoms, such as a cough, fever, and muscle aches, within two days to two weeks after they are exposed to the bacteria.
Health officials are advising anyone who lives or works in the Central Harlem area to contact a doctor if they experience these symptoms.
What Are The First Symptoms of Legionnaires’ Disease?
The disease often starts like a mild flu. For the first couple of days, you might have muscle aches, body aches, and headaches. But after this initial phase, the symptoms get much worse.
You might develop a high fever of 100.4°F or higher, along with chills and extreme tiredness. About half of the people who get sick also experience confusion or delirium. Other symptoms include an upset stomach, with nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Since the bacteria attack the lungs, you will likely have a persistent cough that can start out dry but may later produce mucus or even blood. You may also feel short of breath and have chest pain.
How Long Does It Take For Symptoms To Show Up?
The time it takes for you to get sick after being exposed to the Legionella bacteria is called the incubation period. It can be as short as two days or as long as 19 days. Most people, however, start feeling sick around six to seven days after they've been exposed. This is the time the bacteria need to grow inside your body before they cause noticeable symptoms.
What is Pontiac Fever?
Pontiac fever is a milder version of the same infection. Its incubation period is much shorter, usually just one to two days. The symptoms are less severe and include a flu-like sickness with muscle pain, headaches, and a fever. Unlike Legionnaires' disease, Pontiac fever usually goes away on its own without needing a lot of medical care. Because it is so mild, doctors sometimes don't even realize it's Pontiac fever.
How is Legionnaires’ Disease Diagnosed?
Doctors can figure out if you have Legionnaires’ disease using a few different tests. They will often check your blood and urine or look for the bacteria in a sample of your sputum (the mucus you cough up). They may also take a chest X-ray, but this can be tricky because the results look like other types of pneumonia.
The best way to get a clear diagnosis is through lab tests that can directly identify the bacteria. It's also a clue that you have it if your illness doesn't get better with common antibiotics like penicillin. Without treatment, the illness can get much worse and may lead to serious problems like kidney failure, respiratory failure, and even death.
New Stem Cell Transplant Breakthrough Could Replace Chemo In Cancer Treatment
Credits: iStock
Stem cell transplantation has long stood as one of medicine’s most powerful tools, offering hope to patients with genetic disorders, immune deficiencies, and blood cancers. But it comes at a staggering cost: before healthy donor cells can take root, patients typically undergo toxic chemotherapy or radiation to destroy their own diseased bone marrow. The side effects can be devastating — infertility, organ damage, secondary cancers, and sometimes death.
Now, researchers at Stanford Medicine have shown it doesn’t always have to be this way. A Phase 1 clinical trial published in Nature Medicine has demonstrated that an antibody-based treatment can safely prepare patients for a stem cell transplant without using busulfan chemotherapy or radiation. For children with Fanconi anemia, a rare genetic disorder that makes conventional transplants particularly dangerous, this represents nothing short of a medical breakthrough.
Traditionally, transplants hinge on “conditioning” — a process to clear out faulty bone marrow so donor cells can settle in. Until now, that has required high doses of chemotherapy or radiation, treatments that damage DNA and leave lifelong scars.
The Stanford team instead used briquilimab, an antibody that targets CD117, a protein on blood-forming stem cells. By binding to CD117, the antibody wipes out diseased stem cells without blasting the rest of the body with toxins.
“We were able to treat these really fragile patients with a new, innovative regimen that allowed us to reduce the toxicity of the stem cell transplant protocol,” said Dr. Agnieszka Czechowicz, MD, PhD, assistant professor of pediatrics and co-senior author of the study.
For Fanconi anemia patients, who are hypersensitive to DNA damage, eliminating busulfan and radiation could be life-saving.
The Phase 1 trial enrolled three children with Fanconi anemia, each younger than 10 years old. Instead of the usual conditioning, they received a single infusion of briquilimab 12 days before transplant, followed by low-intensity immune suppression but no chemotherapy or radiation.
The donor bone marrow came from their parents — genetically half-matched but specially prepared. Researchers enriched it with CD34+ stem cells while removing alpha/beta T-cells, immune cells known to trigger graft-versus-host disease.
The results stunned the team. Within two weeks, the donor stem cells had taken hold. By 30 days, healthy blood production was underway. Two years later, all three children have nearly 100% donor cells in their bone marrow, far exceeding the trial’s goal of just 1%.
“No one experienced graft rejection, and the outcomes were better than we had dared to expect,” Czechowicz said.
This success is decades in the making. Stanford’s Dr. Irving Weissman first studied CD117 antibodies in mice nearly 20 years ago. Step by step, researchers refined the science until a clinical-grade antibody was ready for human trials.
The first child to benefit was 11-year-old Ryder Baker from Texas. Before his transplant, Ryder was exhausted by his illness. “He was so tired, he didn’t have stamina,” recalled his mother, Andrea Reiley. Today, Ryder is thriving — playing soccer, enjoying pickleball, and even earning the title of “Up and Coming Player” at school.
Reiley says her son takes pride in being a pioneer. “I have conversations with him about how his experience is helping doctors take better care of other kids. I think he takes a lot of pride in that too.”
Why Fanconi Anemia Is So Difficult To Treat?
Fanconi anemia is a genetic disorder of DNA repair. The body’s stem cells can’t fix everyday DNA damage, leading to progressive bone marrow failure. Children often develop fatigue, infections, and bruising before age 12. Without a transplant, they face life-threatening complications.
But because their DNA-repair machinery is so faulty, standard chemo or radiation is especially harmful. “Right now, nearly all of these patients get secondary cancers by the time they’re 40,” Czechowicz noted.
The antibody-based method offers a way out of this deadly paradox, a path to transplant without the genotoxic conditioning that accelerates cancer.
How Stem Cell Anti-Body Approach Expands Donor Options For Patients
Another innovation lies in how donor cells are prepared. For decades, 35–40% of patients never received transplants simply because they lacked a perfectly matched donor. Using half-matched donors like parents — while carefully engineering the graft to reduce complications — expands the donor pool dramatically.
“We are expanding the donors for stem cell transplantation in a major way, so every patient who needs a transplant can get one,” explained Dr. Rajni Agarwal, MD, co-first author and professor of pediatric stem cell transplantation.
This has profound implications not only for Fanconi anemia, but also for other inherited blood disorders like Diamond-Blackfan anemia and even some immune deficiencies.
Stem cell transplants are most commonly used in blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma. While cancer patients may still require some chemotherapy or radiation to clear malignant cells, researchers believe antibody-based conditioning could benefit those too frail for full-dose regimens — including elderly patients.
Another Stanford team is already exploring whether briquilimab could be used in this vulnerable population.
“We may finally have a way to treat these patients with less intensity, so it’s possible for them to get a transplant,” Agarwal said.
What Challenges Still Remain?
Even with this breakthrough, transplants remain grueling. Ryder and the other children spent over a month in the hospital, battling side effects like exhaustion, nausea, and hair loss. And there is the broader issue of drug availability. Briquilimab is still in clinical trials, and scaling up access will take time.
Still, for families who once faced impossible odds, the difference is profound. “When I counsel families, their eyes start to shine as they think, ‘OK, we can avoid the radiation and chemo toxicity’,” Agarwal said.
The Stanford team is now running a Phase 2 trial in more children with Fanconi anemia, and they plan to extend the approach to other disorders. Longer-term, researchers hope antibody-based regimens can be combined with gene editing therapies — replacing faulty genes while avoiding the toxic prep work.
Czechowicz believes this is just the beginning, “We were optimistic, but we’ve been surprised by how well it’s worked. This could redefine how we think about stem cell transplantation.”
First Human West Nile Case Reported In Maryland While Kansas Battles Six Infections
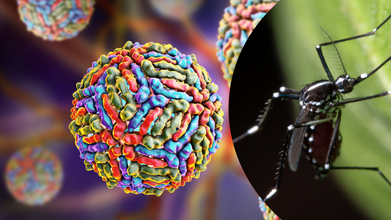
Credits: Canva
Maryland has reported its first human case of West Nile virus (WNV) of 2025, according to the state’s Department of Health. The patient was an adult resident of central Maryland, and officials said Friday that the patient was recovering from the disease. This news highlights the ongoing caution needed as mosquito season picks up across the United States.
West Nile virus is transmitted primarily through bites from infected mosquitoes that have previously fed on birds carrying the virus. While rare, the disease can occasionally spread through other avenues, but mosquito transmission remains the most common pathway.
The majority of individuals who contract WNV have no symptoms, but in certain instances, particularly in patients with underlying disease, the virus can result in serious disease. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) states that common symptoms develop 2–6 days following an infectious mosquito bite and might include high fever, headache, stiff neck, confusion, tremor, convulsions, loss of vision, weakness of muscles, numbness, or paralysis.
Health authorities note that there is no antiviral treatment available for West Nile virus. The vast majority of patients recover completely, although neuroinvasive infections—where the virus invades the central nervous system—are intensive to treat and tend to have more extended recovery times.
Kansas public health officials are tracking six WNV cases this year thus far. Five of these cases have been designated as neuroinvasive, illustrating the severity of the virus. There were three cases reported in north-central Kansas, and three in south-central Kansas. Non-neuroinvasive cases usually exhibit milder, flu-like illnesses, while neuroinvasive cases can include inflammation of the brain or the surrounding tissues, confusion, paralysis, and loss of vision, said Jill Bronaugh, a KDHE spokesperson.
Though numbers fall short of last year's figures—64 cases and four fatalities—officials caution that mosquito activity will peak in late summer, raising the potential for more cases. To monitor developments, KDHE hosts a weekly-updated West Nile virus dashboard for the surveillance season, which runs July to September.
Is This A Seasonal Surge Or A Cause Of Concern?
The CDC reports that WNV activity in the United States normally begins in mid-August and lasts until early September. Around 2,000 individuals are diagnosed with the virus every year, although cases of mild or asymptomatic infections tend to be under-reported. The health authorities advise residents to use preventive strategies, such as using insect repellents, long sleeves, and pants while outdoors, and removing standing water near homes, which is a mosquito breeding site.
"Prevention is the key," states Dr. Emily Johnson, an infectious disease expert. "Because there's no treatment for West Nile, avoiding exposure to mosquitoes through bites is still the best way to stay safe and your family."
Can Mosquito Saliva Improve West Nile Virus Treatment?
In addition to prevention on a case-by-case basis, scientists are looking at new approaches to fighting mosquito-borne illnesses, such as WNV. Anita Saraf, director of the University of Kansas's Mass Spectrometry & Analytical Proteomics Laboratory, is researching mosquito saliva to determine how viruses are transferred and to discover possible therapy targets.
Saliva collection from mosquitoes is technically difficult because they only produce minuscule amounts. USDA Agricultural Research Service collaborators stimulate the mosquitoes to produce saliva, which is analyzed using sophisticated mass spectrometry procedures by researchers. Saraf's research is being done on the proteome—the entire complement of proteins—in mosquito saliva and how it gives clues about how viruses such as West Nile, dengue, yellow fever, and Japanese encephalitis go about controlling the mosquito host and then impact humans.
Her work utilizes shotgun proteomics in tandem with nanoscale liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (nLC-MS), methods sensitive enough to examine nano-gram levels of protein. "Without the sensitivity, we would require much larger protein samples," Saraf says. "Our strategy permits us to explore these viruses at the molecular level, which might guide future vaccine or therapeutic design."
Preventive Measures For People To Follow
Health officials continue to emphasize simple prevention measures as the best defense against WNV. These are:
- Using EPA-approved insect repellents
- Wearing long-sleeved shirts and pants outside
- Adding screens on windows and doors to prevent mosquitoes from entering
- Eliminating standing water within homes, such as flowerpots, gutters, and bird baths
By doing these, residents will be able to drastically lower their chances of infection, particularly when it comes to the active mosquito season.
While Kansas and Maryland are tracking WNV cases at present, the threat is spread throughout the U.S. and the world. The CDC reports that West Nile virus is a continued public health issue every summer, especially in areas with high mosquito populations. Rare neuroinvasive cases show the virus's ability to cause significant damage to the nervous system, highlighting awareness and prevention.
The research undertaken currently at the University of Kansas demonstrates the innovative work towards understanding mosquito-borne viruses at a molecular level.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

