- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
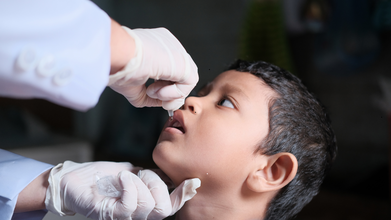
Polio Cases Reported In Pakistan And Nigeria, More Details Inside
Credits: Canva
Thanks to the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI), the cases of polio have decreased by more than 99%, notes the World Health Organization (WHO), however, spread of wild poliovirus sill remain a threat in Afghanistan and Pakistan. In the news, polio is back again, with another country joining the link - Nigeria.
Both Pakistan and Nigeria reported three new cases of polio as per the GPEI.
Polio Cases In Pakistan
Three cases of wild poliovirus type 1 (WPV1) is reported in Sindh. The case also had first experienced paralysis in August. So far, Pakistan has reported a total of 29 polio cases this year, confirmed the National Institute of Health (NIH). Two of the bases have been reported in Singh's Badin and Thatta district, as confirmed by a press release.
In an effort to curb down the numbers, the release said that a sub-national polio vaccination campaign was also conducted across 88 districts of the country, which also included Badin and Thatta.
Polio Cases In Nigeria
Nigeria also reported three circulating variant poliovirus type 2 (cVDPV2) this week from Borno, Kebbi, and Zamfara states. The cases from May and July also reported in paralysis. This year, Nigeria reported a total of 35 cases. Nigeria is also trying to curb down the cases, here local women have stepped in to fight against polio. Aljazeera reports that women set out for a day with a cooler box, "inside are oral polio vaccines packed in ice".
While Nigeria was declared free of wild poliovirus by the WHO in 2020, the cases did not vanish fully.
What Is Polio?
The WHO notes that it is a highly infectious disease caused by a virus that invades the nervous system and can cause total paralysis in matter of hours. The virus is transmitted by person to person spread mainly through the fecal-oral route, or less frequently, by a common vehicle, which could be either from contaminated food or water. The virus also multiplies in the intestine.
NIH notes that the virus responsible for causing Polio belongs to the Picornaviridae family.
Also Read: Why 1 In 6 U.S. Parents Are Rejecting Vaccine Recommendations
Common Symptoms of Polio
The NIH notes that the maximum excretion of the virus is seen in 2 to 3 days prior and 1 week after appearance of symptoms. The spread is especially rapid in areas with poor sanitation, and among the nonimmune population. The rise in cases could be seen in summer months and temperate regions.
As per the WHO, the common Polio symptoms are:
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Vomiting
- Stiffness of the neck a
- Pain in the limbs
The WHO also notes that 1 in 200 infections leads to intervisible paralysis, usually in legs, and among 5 to 10% of those paralysed do not survive.
Who Are Most At The Risk Of Polio?
As per the WHO, Polio mainly affects children under 5 years of age, however, it can happen to anyone of any age who is unvaccinated and may have come in contract with the disease.
Is There Any Cure For Polio?
While there is no cure for Polio, it can very well be prevented. Polio vaccines, which can be administered multiple times, can protect a child for life. There are two vaccines available:
- Oral Polio Vaccine
- Inactivated Polio Vaccines
India AI Summit: Union Health Minister Nadda Launches SAHI And BODH Initiatives To Boost AI In Healthcare

The Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare, JP Nadda, today launched two key national initiatives -- the Strategy for Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare for India (SAHI) and the Benchmarking Open Data Platform for Health AI (BODH) to boost the role of AI in the country's healthcare ecosystem.
The initiatives, launched at the India AI Summit at Bharat Mandapam, in the national capital, are aimed at promoting safe, transparent, and accountable AI in healthcare. It will also help strengthen the digital health ecosystem for equitable healthcare access.
What is SAHI and BODH?
SAHI is a national guidance framework to enable the safe, ethical, evidence-based, and inclusive adoption of AI across India’s healthcare system.
It aims to provide strategic direction on governance, data stewardship, validation, deployment, and monitoring of AI solutions, while supporting States and institutions in responsible adoption aligned with public health priorities.
"SAHI is not merely a technology strategy but a governance framework, policy compass, and national roadmap for the responsible use of AI in healthcare,” said Nadda.
He stated that SAHI will guide India in leveraging AI in a manner that is ethical, transparent, accountable, and people-centric. Nadda also emphasized that SAHI provides a structured framework for collaboration, ensuring that innovation flourishes while public interest remains paramount.
The second initiative, BODH, was developed by the Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur in collaboration with the National Health Authority. It is a privacy-preserving benchmarking platform that enables rigorous evaluation of AI models using diverse, real-world health data without sharing underlying datasets.
As a digital public good under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, it is designed to strengthen trust, transparency, and quality assurance in Health AI deployment.
"The collaboration between Government and academia has led to the development of BODH -- the Benchmarking Open Data Platform for Health AI -- which provides a structured mechanism for testing and validating AI solutions before deployment at scale,” said Nadda.
Nadda reiterated that AI solutions must be rigorously evaluated for performance, reliability, and real-world readiness. Together, SAHI and BODH represent India’s commitment to building a trustworthy, inclusive, and globally competitive health AI ecosystem grounded in innovation, responsibility, and public trust.
AI An Indispensable Enabler to Viksit Bharat
Earlier, delivering the keynote address at a session themed “Innovation to Impact: AI as a Public Health Game-Changer”, at the Summit, Anupriya Patel, Union Minister of State for Health and Family Welfare, highlighted AI as an "All-Inclusive Intelligence".
She also emphasized AI's potential in addressing "health inequities across the country".
Patel called technology -- particularly AI "an indispensable enabler" in India's race towards the vision of a Viksit Bharat by 2047.
She highlighted the potential role of AI on India’s vast and diverse population, the rural–urban divide, and the dual burden of communicable and non-communicable diseases, which present unique challenges.
She also noted that AI has been integrated across the entire continuum of healthcare -- from disease surveillance and prevention to diagnosis and treatment.
H3N2 Not Just Common Cold, Experts Say Do Not Self-Medicate

Credit: Canva
While the national capital is seeing a significant rise in H3N2 Influenza A cases, experts explained that it's not just the common cold and people must not try to self-medicate.
Speaking to Health And Me, multiple experts stressed the need to treat the virus properly, as its symptoms can last longer and potentially lead to pneumonia.
What Is The H3N2 Virus?
H3N2 is a subtype of the Influenza A virus that causes seasonal flu. The symptoms are often stronger and more persistent, with many patients reporting prolonged fatigue, cough, breathing difficulty, and slower recovery.
It is highly contagious, spreading via respiratory droplets (coughing/sneezing) and contaminated surfaces. The symptoms usually last 5–7 days, with treatment focusing on rest and symptom management.
Dr. Mohit Saran, Consultant - Internal Medicine and Diabetologist, Manipal Hospital, Gurugram, told this publication: “H3N2 is not just a common cold. While symptoms may not appear instantly, they can lead to high fever, constant cough, body pain, and breathing issues. In some people, this can also increase the risk of pneumonia or the need for hospitalization if not managed early.”
The experts attributed the surge in the disease to factors such as changing weather, fluctuating temperatures and reduced immunity.
Who Is At The Highest Risk For H3N2?
Children, youngsters, senior citizens, pregnant women and people with low immunity or with conditions such as asthma, diabetes, or heart problems are more vulnerable to H3N2. Health care professionals and people who are exposed to crowded places may also be affected by this disease.
Dr. Atul Gogia, Head of Infectious Diseases, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, told Health and Me that the H3N2 virus "predominantly affects elderly people and those who have comorbid illnesses".
"We need to be especially careful because this illness predominantly affects individuals with comorbid conditions, the elderly, and those who are more vulnerable to developing complications that may require hospitalization,” he said.
Why Does H3N2 Last Longer Than The Common Flu?
Symptoms of H3N2 infection can last for two to three weeks, with a lingering dry cough and fatigue being common.
The virus often affects the lower respiratory tract, leading to more intense coughing and breathing discomfort. Young children, older adults, and individuals with chronic health conditions are at higher risk of complications.
"H3N2 is considered more infectious because of its ability to mutate quickly and adapt to the human host. This high mutation rate allows the virus to evade the immune system more effectively and can lead to more severe outbreaks. It spreads easily through respiratory droplets, direct contact, and contaminated surfaces,” explained Dr. Manisha Arora, Director - Internal Medicine at the CK Birla Hospital(R), Delhi told HealthandMe
"Frequent changes in its surface proteins, a process known as antigenic drift, make it harder for the body to recognize and fight the virus, which can result in more hospitalizations and, in severe cases, increased mortality,”
How Can The Disease Be Prevented?
H3N2 can be prevented through regular handwashing, wearing masks in crowded places, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, and avoiding self-medicating. Flu vaccination, timely medical consultation for long-term fever, and adequate rest help reduce the risk and further spread of the condition.
The experts recommended that all adults above 18 consider annual flu vaccination ideally in August or September, unless they are currently experiencing flu-like symptoms.
Maintaining good hygiene, eating nutrient-rich foods, staying hydrated, and following healthy habits can help boost immunity.
Greater Noida Locals Contract Food Poisoning From Kuttu Flour, Here's Why

Credit: TOI
Over 70 residents in Supertech Ecovillage-3, Royal Court Society and Himalaya Pride Society, Greater Noida have contracted food poisoning after they consumed a specific batch of buckwheat (kuttu) flour during Mahashivratri this weekend.
The widespread outbreak has caused panic and triggered a police investigation. As a result, officials sealed Prashant General Store, a retail shop in Royal Court Society and HD Spices, a primary warehouse in Chipiyana Buzurg village suspected of selling the spoiled batch.
Moreover, four people including the warehouse owner have now been detained by the Bisrakh police. Assistant Commissioner of Food, Noida, Sarvesh Kumar said lab tests are yet to confirm whether the infection was due to bacterial contamination, fungal toxins or adulteration.
This incident adds to a troubling trend of food and water contamination in the area, a topic that has recently reached discussions in Parliament. Improper storage allows toxic molds like aflatoxins to grow, triggering rapid-onset vomiting and dehydration, especially on the empty stomachs of fasters.
This "Buckwheat flour poisoning" occurs because the flour's high natural oil content makes it highly perishable; when stored in humid or warm conditions, these oils oxidize, creating a breeding ground for toxic molds and bacteria.
Why Is Buckwheat (Kuttu) Flour Harmful For Your Health?
Despite its reputation as a "pure" fasting food, buckwheat flour carries a hidden risk: its high natural oil content. Unlike refined grains, these healthy fats are highly unstable; when exposed to heat or moisture, they oxidize and turn rancid.
This transformation from a nutrient-dense staple to a source of food poisoning commonly occurs when households treat it like a non-perishable grocery item rather than the sensitive, short-lived ingredient it actually is.
The real danger of buckwheat flour lies in storage. Because buckwheat flour is used sporadically, it often sits in pantries in unsealed packets, warm cupboards or humid environments for months and becomes a silent breeding ground for dangerous molds and bacteria over time
The degradation is often hard to spot; a faint bitter aroma or slightly clumpy texture can easily be hidden by the strong spices and oils used in traditional fasting recipes.
Along with this, expired or damp buckwheat flour can harbor aflatoxins and other toxic compounds beneath the surface. Once ingested, these irritants attack the stomach lining, triggering a rapid physical "rejection," usually within just a few hours.
What Is Buckwheat-Caused Food Poisoning?
If you suspect someone has consumed contaminated buckwheat flour, these are the primary symptoms to watch for:- Intense Nausea and Vomiting: Usually the first sign, as the body tries to expel the toxins.
- Acute Abdominal Pain: Sharp cramps or bloating in the stomach area.
- Fever and Chills: A sudden rise in body temperature as the immune system reacts.
- Diarrhea (Loose Motions): Frequent and watery stools.
- Extreme Weakness: Feeling dizzy, shaky, or completely drained of energy.
- Dehydration: Dry mouth and reduced urination due to fluid loss.
How To Safely Store Your Flour
- Buy Small, Buy Fresh: Purchase only the amount needed for the current fasting period. Avoid bulk buying buckwheat flour to store for the next season.
- Check the Date: Always look for the manufacturing date. If it’s more than two months old, it may already be turning rancid.
- Airtight & Cool: Transfer the flour to an airtight glass or metal container immediately. Store it in a cool, dry place, or better yet, refrigerate it to slow the oxidation of its natural oils.
- The "Sensory" Test: Before cooking, smell the flour. If it has a bitter, soapy, or musty aroma, throw it away. Fresh buckwheat flour should have a mild, nutty scent.
- Keep it Dry: Ensure your hands and measuring cups are completely dry before touching the flour, as moisture triggers fungal growth.
- Don't Mix Batches: Never mix new flour with old leftovers from a previous fast.
Who Is At The Highest Risk?
While anyone can get food poisoning, women, children and the elderly are at the highest risk. The practice of fasting can actually make the illness more dangerous. On an empty stomach, even a small amount of mold or bacteria can trigger an explosive physical response.
Furthermore, fasting usually involves lower water intake; once vomiting or diarrhea begins, the body loses its remaining fluid reserves instantly, leading to rapid, severe dehydration.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

