- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Rabbit Fever In US, What Is It All About?

Credits: Canva
As per the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), case numbers of infectious disease tularemia, or 'rabbit fever' have surged in the United States over the past decade. The disease is on rise.
The Name and origin
As per a 2014 study in the Balkan Medical Journal, Tularemia was first described as a disease of the rodent group called lemmings in the 16th century in Norway. It was also later described in Japan and Russia in the 1800s. The infectious agent was found from dead ground squirrels in 1911 in Tulare, California. This is where it derives its name from. Due to the region of its discovery, it was known as the Bacterium tularense.
The first human cases were reported by Lamb and Wherry in 1914. Edward Francis was the first one to study the epidemiology of the disease in humans. He said that many people with different "clinical presentations" suffered from the same disease. It was found to be transmitted through contact with the infected meat of rabbits and rodents. "Serological tests were devised for the diagnosis, and a vector role of blood-sucking flies was established," reads the study.
How can humans get infected?
Humans can contact this disease through bites from infected ticks and deer flies, and direct skin contact with infected animals such as rabbits, hares, and rodents. There are other methods of transmission, including mowing over nests of infected animals which can aerosolize the bacteria and infect the person operating the mower. This mode of transmission was first observed in 2000 at a Massachusetts vineyard, where the Tularemia outbreak persisted for 6 months. This resulted in 15 confirmed cases and one death. In fact, one of the several cases reported in Colorado during 2014-25 was also linked with lawn mowing.
As per the CDC, the bacteria is not only classified Tier 1 Select Agent, but it can have the potential to use in bioterrorism. This is when transmitted, without proper treatment, it can be lethal. The CDC report notes: "The case fatality rate of tularemia is typically below 2%, though it can be higher depending on the clinical presentation and bacterial strain."
What are the types of Tularemia?
The F. tularensis (where the F stands for Francis, from Edward Francis, who was the first one to study the epidemiology of the disease in humans), gets into your body and are "eaten" by cells of your immune system. These cells then would usually destroy the bacteria, but instead, the bacteria multiply inside the body. The bacteria destroy the immune cell and infect other cells too.
There are 6 types of Tularemia that can affect your body:
Ulceroglandular Tularemia: This is the most common one that you can get from being bitten by tick or infected animal. This affects your skin and lymph node.
Glandular tularemia: Similar to ulceroglandular tularemia, but it only affects your lymph nodes. You get glandular tularemia from a tick bite or directly from an infected animal.
Oculoglandular tularemia: This happens if you get contaminated water or body fluids in your eyes.
Oropharyngeal tularemia: This happens through contaminated food and can cause a sore throat or digestive symptoms.
Pneumonic tularemia: This can be caused by F tularensis spreading in your lungs from somewhere else in your body, causing you symptoms similar to pneumonia.
Typhodial tularemia: This causes a high fever and affects many parts of your body. You can get typhoidal tularemia the same way as other forms of tularemia.
Symptoms
While symptoms differ on the basis of gravity and the kind of tularemia, here are some common symptoms:
- High Fever
- Open would or ulcer on your skin
- Large, painful, lymph nodes
- Watery eyes
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Muscle aches
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting or diarrhea
British Woman Gives Birth After Rare Womb Transplant Surgery

Credit: PA Media
For the first time, a baby boy has been born to a mother with a womb transplanted from a deceased donor at Queen Charlotte’s and Chelsea hospital in London.
Weighing merely 3.09kg (6lb 13oz), Hugo Powell was born to Grace Bell and Steve Powell from Kent, right before Christmas 2025. "It's simply a miracle. I never, ever thought that this would be possible," Bell said. "I'm the happiest I've ever been in my life. When I was 16, I was told that this would never be possible," she said of her son's birth.
The father added: "When he came over the curtain, it was just sort of overwhelming emotions. I felt like I wanted to cry, but couldn't. From where we started - first meeting - to where we are today, with Hugo, is nothing short of a miracle after everything we've been through. It just felt quite unreal at the time, because this has been a long journey for us both."
The couple also paid tribute to the "kindness and selflessness" of their transplant donor and her family for their "incredible gift", while also thanking medical teams in Oxford and London who supported their journey.
"There are no words to say thank you enough to my donor and her family. Their kindness and selflessness to a complete stranger is the reason I have been able to fulfil my lifelong dream of being a mum.
"I hope they know that my child will always know of their incredible gift, and the miracle that brought him into this world," Bell said.
What Is Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser Disorder?
Bell, an IT programme manager, was born with Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser (MRKH), a disorder that causes the vagina and uterus to be underdeveloped or absent. MRKH syndrome is also called:
- Müllerian agenesis
- Müllerian aplasia
- Congenital absence of the uterus and vagina
- Rokitansky syndrome
While women with MRKH syndrome have normal external genitalia, functioning ovaries, breast and pubic hair development, they are unable to carry a pregnancy and rely on either surrogacy or a womb transplant, as in the case of Bell.
There are two versions of the disorder:
- Type 1: The patient has normally functioning ovaries and fallopian tubes but a blocked or missing upper vagina, cervix and uterus. No other organs are affected.
- Type 2: The patient has a blocked or missing upper vagina, cervix and uterus as well as issues with ovaries, fallopian tubes, spine, kidneys or other organs.
However, these genetic changes have been found in only a small number of affected people and subsequent studies have not identified a clear association between MRKH syndrome and any specific environmental factors. It remains unclears whether they actually cause MRKH syndrome.
Treatment for MRKH depends on the patient's goals and symptoms and some options include:
- Vaginal dilators: Dilators are made of plastic or silicone and vary in length and width. These tubelike devices help expand and stretch the inside of the vagina.
- Vaginoplasty: This is a surgical procedure to create a vagina. There are several ways surgeons perform vaginoplasty, but most involve creating a hole and lining it with tissue from another part of your body.
- Uterus transplant: This is a major surgery that involves placing a donor uterus inside someone without a uterus. Uterine transplants give people with MRKH an opportunity to carry and deliver a child. Uterus transplants are rare.
How Did Bell Conceive Her Child?
Recalling her initial diagnosis, Bell said: "About 16 years ago, I was diagnosed with MRKH. It was a tough journey. I must admit, a very sad journey. I remember the story of the first womb transplant in Sweden, many years ago now, and following that story intently."I still can't believe that I'm here today and I've gone through this. It's just amazing."
At the age of 16, the new mother was told she wouldn't be able to carry her own child. However, in 2024 she received a phone call saying a womb had been donated and a transplant was possible, a moment she recalls left her "in complete shock" and "really excited".
Bell's womb transplant operation lasted 10 hours and took place at The Churchill Hospital in Oxford in June 2024 After her transplant surgery, she began fertility treatments several months after the transplant in 2024 and her son was born a year later.
According to The Guardian, Bell's transplanted womb will be removed when the couple have finished having children, to save her from a lifetime of taking immunosuppressant drugs.
Indore Food Contamination: 6 People Hospitalized In Bhagirathpura

Credits: Canva
Not too long ago, Indore made headlines in water contamination case where a 67-year-old woman, identified as Parvati Bai Kondla also showed signs of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Bacteria like E coli. and Klebsiella were found in the water sample of Bhagirathpura, the epicentre of water contamination.
Indore's Bhagirathpura is again on the news, this time for food contamination.
Indore Food Contamination: What Happened?
Six people have been admitted to a hospital after they consumed contaminated food in Bhagirathpura. At a birthday party in Bhagirathpura on a late Saturday night, 60 people ate the food and some of them developed health problems. Chief Medical and Health Officer (CMHO) Dr Madhav Hasani stated on Monday.
Bhagirathpura was the epicentre of water contamination that claimed 22 lives earlier. The minister said that affected individuals were treated and as a precaution, six of them were admitted to the Government Maharaja Yashwantrao Hospital.
Indore Municipal Corporation Commissioner Dilip Kumar said, “We have found that in case of the construction of the toilet, no safety tank was constructed beneath it. We are also probing the other lapses.”
As per the official statement, all patients are doing well after the treatment.
Indore Food Contamination: What Happened In Indore Before?
Earlier in January, Mayor Pushyamitra Bhargav reported that due to lapses in civic infrastructure. Investigation revealed that a toilet constructed directly above a main drinking pipeline near a police outpost, without a mandatory safety tank resulted in the sewage mixing with drinking water.
Read: Sewage Mixing With Drinking Water Kills 7 in Madhya Pradesh’s Indore, Over 100 Remain Hospitalized
Speaking to The Indian Express, Indore Municipal Corporation Commissioner Dilip Kumar said, “We have found that in case of the construction of the toilet, no safety tank was constructed beneath it. We are also probing the other lapses.”
What Is E. Coli Bacteria?
Escherichia coli, commonly known as E. coli, refers to a group of bacteria that naturally live in the intestines of humans and animals. Most of these strains are harmless and even play a role in digestion. However, certain types can trigger illness when they enter parts of the body where they do not belong or release harmful toxins.
These disease-causing strains attach themselves to body cells and produce toxins, leading to infection and inflammation.
What Is Guillain-Barré syndrome?
Guillain-Barré syndrome is a rare autoimmune condition in which your immune system attacks your peripheral nerves, leading to symptoms like numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness that progress to paralysis. However, with treatment, most people fully recover from the condition.
Doctors say GBS occurs at any age, but it most commonly affects people between 30 and 50 years of age.
Guillain-Barré syndrome is rare. About 100,000 people worldwide develop GBS every year. To put that into perspective, the world population is about 7.8 billion. That means healthcare providers diagnose GBS in about 1 in 78,000 people each year.
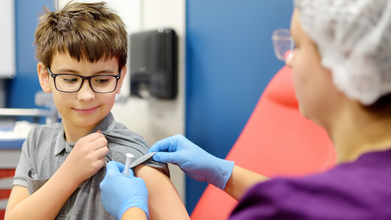
15 States Sue Trump Administration Over Revised Vaccine Schedule
Credits: iStock
15 US states sued President Donald Trump led administration after the Department of Health and Human Services led by Health Secretary Robert F Kennedy Jr. revised vaccine schedule that led to coverage fall from 17 to 11 diseases for children. These 15 states are led Democrats and on Tuesday, they announced suing the Trump administration over unscientific grounds of releasing a new vaccine schedule.
The lawsuit has been filed by a coalition of 14 attorneys general and the governor of Pennsylvania. They have asked the courts to nullify the administration's decision to reduce the number of diseases children are routinely immunized from 17 to 11.
The lawsuit also challenges "the unlawful replacement" of members of the federal Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, who recommend vaccines for Americans. The lawsuit names the Department of Health and Human Services and Health Secretary Robert F Kennedy Jr as defendants. It also names the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and its acting director, Dr Jay Bhattacharya.
Read: CDC Vaccine Schedule: Coverage Falls From 17 to 11 Diseases For Children
15 States Sue Trump Administration Over Revised Vaccine Schedule: What Do The States Want?
In a news briefing on Tuesday, Rob Bonta, attorney general of California said, "H.H.S. Secretary R.F.K. Jr. and his C.D.C. are flouting decades of scientific research, ignoring credible medical experts, and threatening to strain state resources and make America’s children sicker.” Bonta continued, "The fact is, vaccines save lives and save our state’s money."
The lawsuit also notes that the administration's revised vaccination schedule was unscientific and relied instead on comparisons to countries that are different than the United States.
Kris Mayes, attorney general of Arizona, as reported by The New York Times said that the latest vaccine schedule "copies" Denmark's recommendation, where the country already has a nationalized health care and the population is fraction of that of the US. "Copying Denmark’s vaccine schedule without copying Denmark’s health care system doesn’t give families more options — it just leaves kids unprotected from serious diseases."
Also Read: Wegovy And Ozempic Will Cost Less In 2027, Novo Nordisk Slashes Weight Loss Drugs Prices By Half
15 States Sue Trump Administration Over Revised Vaccine Schedule: What Is The Revised Vaccine Schedule?
On January 5, 2026, the federal health officials led by RFK Jr. announced that the new Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), vaccine schedule will include routine shots for 11 diseases for children. This is down from 17 diseases, which were earlier included.
Under the revised schedule, vaccines for a limited number of diseases remain universally recommended for children. These include protection against measles, polio, and whooping cough, which are still considered essential routine immunizations.
Vaccines No Longer Recommended for All Children
The most controversial change is the narrowing of recommendations for several common childhood vaccines. Immunization against the following illnesses is now advised only for high-risk children or after consultation with a health care provider:
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Meningococcal disease
- Rotavirus
- Influenza
- Respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV
Covid-19 vaccination has also shifted to a consultation-based recommendation rather than routine use for all children.
This means shots that were once automatically given at set ages, including at birth, during infancy, and in adolescence, may now depend on individual medical discussions rather than standard guidance.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

