- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
World’s First ‘Trojan Horse’ Blood Cancer Drug Rolled Out By NHS In England

Credits: Canva
The England National Health Service (NHS) is the world's first healthcare system to offer a revolutionary blood cancer treatment called a "Trojan horse" drug. The trailblazing treatment, officially known as belantamab mafodotin, has the potential to add years to the lives of thousands of patients fighting multiple myeloma, a vicious and currently untreatable form of bone marrow cancer.
This innovation, now being rolled out to eligible patients throughout England, highlights the revolutionary promise of precision medicine and targeted treatments to change cancer care.
How Does This Therapy Work?
At the center of this medical innovation is belantamab mafodotin, also known as Blenrep and produced by GlaxoSmithKline. In contrast to traditional chemotherapy that gets into both healthy and cancer cells, this new medication uses a targeted approach: it binds to myeloma cells, enters them quietly, and delivers a fatal dose of chemotherapy directly within, effectively killing the malignancy from the inside out.
This "Trojan horse" metaphor comes from Greek mythology, as Greek warriors entered the city of Troy disguised within a wooden horse. In the same way, this drug corrupts cancer cells by smuggling a toxic payload into them disguised as an antibody—spared most healthy tissues in the process.
NHS England National Clinical Director for Cancer Professor Peter Johnson called the treatment "life-changing" and said, "Myeloma is an aggressive blood cancer, but the advent of belantamab mafodotin brings with it a new hope of highly extended disease control.
Multiple myeloma is a plasma cancer that arises in plasma cells present in the bone marrow. Although there are continued advances in medicine, the disease is still incurable and relapsing in nature. The majority of patients have a pattern of recurrence after remission, requiring multiple treatment lines.
Trials of belantamab mafodotin, particularly in combination with other drugs such as bortezomib and dexamethasone, have shown that the treatment can stop disease from progressing for a period of three years—three years longer than the 13-month postponement achieved with the drug of choice at present, daratumumab.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), having checked the effectiveness and value for money, accelerated approval for the rollout of the treatment. NICE director Helen Knight stated, "This recommendation shows our determination to get patients the best treatment quickly while protecting value for the taxpayer."
Who Will Benefit?
The NHS rollout will first address about 1,500 patients per year in England that have relapsed or are resistant to their existing treatments. These are often those with advanced myeloma who have run out of other standard treatments.
Significantly, this represents a move toward personalized, next-generation treatments being accessible through public healthcare facilities—an accomplishment welcomed by health activists and oncologists alike.
Shelagh McKinlay, Myeloma UK's Director of Research and Advocacy, hailed the announcement: "We have campaigned aggressively for the last year to get this drug approved. It will change the lives of thousands of myeloma patients."
Paul Silvester, who is 60 and from Sheffield, was diagnosed with multiple myeloma in 2023. When ordinary treatment and even a bone marrow transplant did not halt the disease, he was put on an early-access trial for belantamab mafodotin at the Royal Hallamshire Hospital.
The change was almost instant," he explained. "In the first two or three weeks following the first dose, I was in remission. I like to think this treatment has brought the party balloons into the house."
Paul is now in remission and mapping out history-themed travel excursions—something he never thought he'd ever be able to do a few months ago.
How Does Belantamab Mafodotin Work?
Belantamab mafodotin is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), a new class of cancer drugs. The drug's antibody component targets a protein (BCMA) on the outside of myeloma cells. After binding to the cancer cell, the complex is taken into the cell where it drops off a potent chemotherapy drug, essentially killing it from within.
This internal targeting results in much less collateral damage to normal cells—a major problem with standard chemotherapy—and decreases the overall treatment burden.
Side Effects and Safety Issues
Although thought to be less toxic than many standard therapies, belantamab mafodotin is not without adverse effects. Patients can have dry eyes, blurred vision, and occasionally more severe ocular toxicity due to the mechanism of action of the drug leaking into surrounding tissues after cell kill.
Clinical teams are trained to monitor and manage these effects, often adjusting dosage or incorporating supportive therapies to preserve patient safety.
Health Minister Karin Smyth emphasized the significance of this development: “This groundbreaking therapy puts the NHS at the forefront of cancer innovation. By harnessing cutting-edge ‘Trojan horse’ technology, we’re offering new hope to blood cancer patients across the country.”
In fact, the move by the NHS to be the first healthcare system in the world to introduce this treatment establishes a precedent for the incorporation of high-cost, high-impact biologic therapies into national care.
With its effective implementation in England, belantamab mafodotin could soon be used as a worldwide standard of care for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. As other nations observe outcomes and cost-effectiveness trends, it is possible that health systems globally will look into implementing this Trojan horse technique.
Researchers in oncology are also looking at similar antibody-drug conjugates for other types of cancer, including breast, lung, and ovarian cancers—implying that we are just beginning to see what this technology has to give.
Super Flu Now Reached California, Confirm Health Officials

Credits: Canva
Flu has now reached California, officials at the California Department of Public Health (CDPH) confirmed on Tuesday. The mutated influenza strain, which is dubbed as the 'super flu' is now spreading in California.
The CDPH confirmed a second pediatric death related to flu since the season of this respiratory virus had started. The 'super flu' strain is the mutation of seasonal influenza A H3N2 virus, called the subclade K. While the cases are on the rise, with some record breaking ER visits and hospitalizations, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) noted that the season has not peaked yet, and that there might be more cases in the coming week.
What Are The Symptoms Of Super Flu?
Dr Monica Gandhi, who is an infectious disease expert at UC San Francisco told SFGATE that people infected with the mutated strain will likely get common flu symptoms, such as body aches, fever, cough and headache. "I think this particular strain makes people feel pretty horrible," Gandhi said, and further added, "And the reason that subclade K is important is it may not be covered by the current flu vaccine."
However, experts are still asking people to get vaccinated. In fact, the CDC has also noted that vaccination "has been shown to reduce the risk of flu and its potentially serious complications". However, only 130 million doses of vaccine have been distributed, which covers less than 40% of the US population. "The vaccine remains the most effective means to prevent disease. We still want to encourage people to get the vaccine," said Professor Antonia Ho, Professor and Honorary Consultant in Infectious Diseases at the University of Glasgow. Experts have stressed enough on the immunity that one can receive from the vaccine that that these flu jab remain the best defense against the flu, even though the current strain circulated may have drifted away from the strain included in this year's jab.
Data from the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) also show that vaccines is performing as expect, despite the emergence of subclade K.
K variant causes more intense flu symptoms, they include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Runny nose
This year's flu came after the flu vaccination was made, which means the current vaccination does not align with the mutation, however, experts have pointed out that it still continues to offer protection against the illness.
Update On Flu Activity
Flu activity in the state has shown a downtick from the season high at the end of the December. 15% of flu tests have come back positive by January 3, which is down from 17% rate seen during the week ending with December 27. However, the CDC noted that this downtick does not mean the end of flu season, it could rather mean that less cases were reported due to the holiday season. As the agency has warned more such cases to show up in the coming week.
In fact, hospitalization have been on the rise and hit a season high with 3.8 admissions per 100,000 in the state as of January 3.
India Suffers Second-Highest Economic Burden Globally Due to Diabetes, Study Finds
Credit: Canva
Diabetes isn't just costing Indians their lifelong savings, it's also costing the country INT11.4 trillion.
According to a Nature Medicine study, India faces the second highest economic burden due to this chronic condition. Only the United States ranks higher, with costs touching INT 16.5 trillion, while China comes in third at INT 11 trillion.
While excluding informal care provided by family members, the global costs comes around INT 10 trillion which is about 0.2 per cent of the world’s annual gross domestic product (GDP).
However, if informal care is factored in, costs goes up to INT152 trillion or 1.7 per cent of the world’s yearly GDP, as per the study. (An international dollar, or INT$, is a statistical unit that has the same purchasing power as a US dollar).
The scientists estimated that the economic impact of diabetes was much more than Alzheimer’s disease or cancer in the top three countries.
The Diabetes Crisis In India
Diabetes is a chronic condition affecting several aspects of physical and mental health. It occurs when either the body can’t make enough insulin or can’t use it effectively, which impairs several functions.
Often referred to as the 'Diabetes capital of the world', over 100 million people across India suffer from the chronic condition while another 136 million are living with prediabetes.
According to Pharmeasy 2025 Diabetes Report, one in two people show high blood sugar levels when tested and over 90 percent of reports with high blood sugar also showed abnormality in one or the other parameters for liver, lipid, heart or thyroid issues.
Also known as a 'Silent Killer', diabetes can develop and progress quietly in the body, often without clear or early symptoms. Multiple studies show that over 50 percent of people with diabetes in India are undiagnosed or unaware of their condition.
When left undiagnosed and untreated, diabetes can cause severe complications across the body including heart disease, kidney damage or vision loss. These complications disproportionately affect vulnerable parts of the population, especially those in rural areas without access to proper testing and treatment.
Despite the growing economic burden, India faces systemic challenges in addressing diabetes, including inadequate healthcare infrastructure, low public awareness and fragmented policy responses.
What Did The Study Find?
Researchers, including those from the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis and the Vienna University of Economics and Business in Austria, calculated the economic impact of diabetes across 204 countries from 2020 to 2050.They evaluated costs based on medical expenses, productivity losses and caregiving.
While the burden in the US is largely due to high treatment costs and loss of physical capital, the high costs are mainly driven by the sheer number of people affected in India and China, the researchers said.
Author Klaus Prettner, professor of macroeconomics and digitalization at the Vienna University of Economics and Business noted of the results: "Caregivers often drop out of the labor market, at least partially, which creates additional economic costs."
"This is a stark illustration of how medical treatment regimes for chronic diseases such as diabetes are accessible to high income countries only," co-author Michael Kuhn, acting economic frontiers research group leader at the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis, added.
Based on the results, the scientists said promoting healthier lifestyle, regular physical activity and a balanced diet is the most effective way to prevent diabetes and reduce its economic impact in each country in the long run.
‘It Ends With Us’ Author Colleen Hoover Reveals Cancer Diagnosis As She Undergoes Radiation

Credit: Instagram/ColleenHoover
Colleen Hoover, the best-selling author of 'Regretting You' and 'Verity', has revealed that she has undergone treatment for cancer.
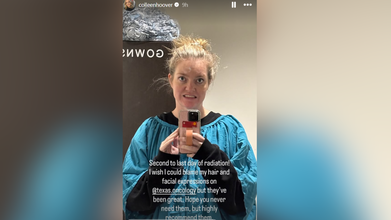
On January 12, Hoover announced via her Instagram Stories that she has one more day of radiation left at Texas Oncology.
"Second to last day of radiation," she captioned the post on her Instagram Stories. "I wish I could blame my hair and facial expressions on @Texas.Oncology, but they've been great. Hope you never need them, but highly recommend them."
In December 2025, the 46-year-old writer wrote on her Facebook page that she had been diagnosed with cancer and had undergone surgery. The film producer also noted that she would only need radiation, but not chemotherapy as a treatment plan.
Hoover said she had been in Canada filming Reminds of Him when she noticed she “had recurring health issues that I continued to put off until the movie was finished" and a check-up revealed that she had developed cancer.
What Kind Of Cancer Does She Have?
While she is yet to reveal which kind of cancer she is receiving treatment for, Hoover has confirmed it was not caused by family genes, HPV or excessive hormones.
In a Facebook post from January 9, she noted that the reason for her illness is 'more than likely' to be environmental/lifestyle, which can be credited to a lack of exercise, poor diet and stress.
"I’m happy and grateful to be alive but I hate vegetables. I hate when I have to get off the couch. I hate sweating. I hate when science is right. If you see me at the gym, don’t even tell me good job. If you see me at a restaurant eating grilled chicken and drinking water, I’m probably real mad about it," she wrote in a heartfelt moment.
Why Has Hoover Been Missing From Public Eye?
Hoover's health updates and cancer treatment come amid a series of cancelled public events. In October 2025, she announced she would not attend the premiere of Regretting You, her latest movie adaptation.
In a sentimental Instagram post, she told her fans: "I’m super bummed, but am having an unavoidable surgery and can’t travel for a while,” Hoover wrote in her Instagram post at the time. I’ll live vicariously through you guys. So sad to miss this movie release and premiere, but so grateful to all the actors and the team who put this together.”
Woman Down is Hoover’s next book release set for January 13. However, the author has had to tell fans that a book-signing tour has not been set up yet and she will not be meeting with the public for now.
“I wanted to make this post and be transparent about why that is. I’m not saying I won’t be up to doing at least one signing, but I just won’t know until I know," she said.
Meanwhile, throughout 2025, production on her hit novel, Verity, has begun in 2025, with Anne Hathaway and Josh Hartnett, being photographed during scenes last February. Additionally, her third movie adaptation, Reminders of Him, is also set to hit theaters on March 13, 2026.
It remains unknown if she will be attending the premiere for Reminders of Him.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

