- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Can Apricot Seeds Relieve Cancer Symptoms?

Apricot Seeds (Credit: Canva)
While apricot is known to lower blood pressure and prevent stroke, their seeds are now creating headlines for their controversial link to cancer relief. These seeds, found inside the apricot pit, contain a compound called amygdalin, which has long been associated with anticancer properties. However, despite its early use as a cancer remedy, scientific evidence supporting its benefits remains limited, and concerns about its safety have led health authorities to issue warnings. So can it really treat cancer or the risks involve outweight its benefits?
The interest in apricot seeds stems from the presence of amygdalin, a chemical compound that when meabolized, can release cyanide. This compound was initially believed to have anticancer effects due to its ability to attack cancer cells. Interestingly, in the early 20th century, amygdalin was marketed under the name laetrile (sometimes referred to as vitamin B17) and was promoted as a cure for cancer. While some studies have shown that amygdalin may damage cancer cells in lab settings, this has not translated into reliable, consistent results in human trials. According to a 2023 review, there is not enough empirical evidence that can prive this compound to actually work on humans. Furthermore, research suggests that while amygdalin might target cancer cells in a controlled laboratory environment, its effects on humans are unpredictable. The 2023 review highlights the need for more rigorous clinical trials to understand its potential therapeutic role, if any, alongside standard treatments like chemotherapy.
Risks Of Amygdalin And Cyanide Poisoning
One of the main concerns about apricot seeds and amygdalin is the risk of cyanide poisoning. When metabolized, Amygdalin breaks down into hydrogen cyanide, a potent toxin that can be deadly in large amounts. Thus, consuming apricot seeds, particularly in high doses, can lead to cyanide poisoning.
Symptoms include headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and more severe effects like liver damage, nerve damage, confusion, coma, and even death. This is a significant reason why the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued warnings about the use of apricot seeds as a cancer treatment. In 2024, the FDA reiterated its concerns, urging consumers to dispose of apricot seed products and seek medical attention if they experience any side effects after consumption. The agency also emphasized that the FDA does not approve amygdalin or apricot seeds as cancer treatments.
Nutritional Benefits and Antioxidant Potential
Despite the risks, apricot seeds do contain some beneficial nutrients. They are rich in protein, fibre, carbohydrates, and flavonoids, which have antioxidant properties. These nutrients may help combat oxidative stress in the body, potentially supporting general wellness. However, the potential benefits of apricot seeds for cancer relief are overshadowed by the dangerous risks associated with consuming large amounts.
A Word of Caution
While apricot seeds may contain some beneficial nutrients, their use as a cancer remedy is not supported by scientific evidence. Health experts caution against using apricot seeds or amygdalin as a standalone treatment for cancer. If you are considering alternative therapies or supplements to complement your cancer treatment, it is crucial to speak with a healthcare professional. A doctor or licensed nutritionist can guide you on safe and evidence-backed options that can support your health without jeopardizing your well-being.
Although the anticancer claims of apricot seeds are based on some early studies, they remain unproven in clinical trials, and the risks associated with cyanide poisoning are significant. The FDA has made it clear that apricot seeds are not a safe or approved treatment for cancer. If you or a loved one are considering apricot seeds as a cancer remedy, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider to explore safe and scientifically validated options.
Ramadan Fasting: Avoid Excess Salt And Caffeine To Boost Kidney, Prostate Health, Say Experts

Credit: Canva
Dehydration is a serious concern for people fasting during the month-long Ramadan period, and can severely impact kidney and prostate health. Experts suggested that avoiding excess salt and caffeine can help.
While Ramadan fasting is generally safe for people with early-stage chronic kidney disease (CKD), maintaining adequate hydration between iftar and sehri -- the two important meals each day for faithful observing the fasting -- is of significant importance.
Dehydration can lead to acute kidney injury and electrolyte imbalances for individuals with advanced CKD. As prolonged fasting hours -- more than 12 hours a day -- urine becomes concentrated, increasing the risk for kidney stones and Urinary Tract infections (UTIs).
For men with prostate problems, fasting during Ramadan can pose challenges, such as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) or an enlarged prostate, primarily due to dehydration.
“As a practicing urologist and kidney transplant surgeon in India, I often notice a rise in kidney stone pain and urinary infections during Ramzan. When patients fast for long hours -- especially in our warm climate -- urine becomes highly concentrated. That increases the risk of stones and UTIs. Men with prostate enlargement sometimes report worsening urinary flow because they consciously reduce fluid intake,” Dr. Pankaj Panwar, Additional Director, Urology, Fortis Escorts Okhla, New Delhi, told HealthandMe.
The doctor advised people “to hydrate strategically between Iftar and Sehri, avoid excess salt and caffeine”.
How Excess Salt And Caffeine Impact Ramadan Fasting
Consuming high-sodium foods such as processed meats, pickles, salty snacks, and fast food during iftar or sehri can increase thirst and dehydration.
High salt intake forces the body to pull water from cells to dilute the sodium, leading to severe thirst. It can also lead to bloating.
Similarly, caffeine in coffee, tea, chocolate, and energy drinks can be diuretic and cause the body to lose fluids and salts through increased urination. Particularly, drinking coffee or tea at sehri -- the pre-dawn meal -- can lead to faster dehydration during the day.
Caffeine consumption, especially late in the evening, can also interfere with sleep, making it harder to wake up for sehri.
“Ramzan is a sacred month of fasting, but prolonged abstinence from water, especially in hot climates, can increase dehydration risk. Concentrated urine puts stress on the kidneys and may worsen kidney stones or trigger urinary tract infections,” Dr. Mangesh Patil, Urologist at Saifee Hospital, Mumbai, told HealthandMe.
Dehydration during Ramadan fasting can lead to symptoms like headaches, extreme thirst, fatigue, and dizziness. But in case of severe dizziness, fever, confusion, or blurred vision, the experts warned of immediate medical help.
“Do not ignore warning signs like flank pain, fever, or difficulty passing urine. A little planning can prevent an emergency hospital visit,” Panwar said.
Patil said warning signs include severe flank pain, burning urination, fever, vomiting, blood in urine, or reduced urine output. Men with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia may notice worsening urinary symptoms.
Tips To Prevent Complications
- Drink 2-3 liters of water between iftar and sehri
- Include water-rich fruits
- Avoid excess salt and caffeine
- Individuals with kidney disease, stones, UTIs, or prostate issues should consult their doctor before fasting.
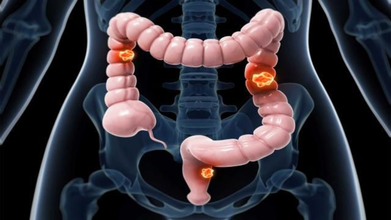
The Common Colon Cancer Sign You Need To Look Out For
Credit: Pinterest
Colon (colorectal) cancer begins when small growths called polyps form on the inner lining of the colon or rectum. Over time, changes in the DNA of these cells can cause the polyps to become cancerous.
As abnormal cells multiply, they replace healthy cells and eventually form a mass known as a tumor. This process develops slowly, often taking up to ten years for a precancerous polyp to turn into cancer and begin showing symptoms.
Colon cancer poses serious health risks because cancerous cells can invade healthy tissues. Over time, they may break away and spread to other parts of the body, making detection more difficult since the symptoms can resemble other conditions.
What Is the First Sign of Colon Cancer You Shouldn’t Ignore?
Colon cancer can be difficult to detect because it often develops without obvious symptoms. However, doctors emphasize that the number one warning sign is rectal bleeding or blood in your stool.
"Colon cancer can be hard to diagnose because it can develop asymptomatically,” said Dr. John Nathanson, a gastroenterologist at New York-Presbyterian Allen Hospital.
Dr. Pratima Dibba adds that this symptom should not be misdiagnosed as hemorrhoids, infection, or constipation, since early signs of colon cancer can look similar.
She urges patients to get checked promptly to rule out serious conditions.
Research from the Cleveland Clinic also shows that blood in stool can originate anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract, including the colon.
Detecting colon cancer early is critical, as survival rates can be as high as 90 percent when caught in its initial stages.
What Are Other Symptoms Of Colon Cancer?
Persistent changes in bowel habits (diarrhea, constipation, or narrowing of stool). Other signs include:
- Abdominal (belly) pain
- Bloated stomach
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Feeling like there’s still poop in your bowel even after you go to the bathroom
- Feeling tired or weak
- Unexplained weight loss
Present Day Scenario In India
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a major health concern worldwide. In India, it is the fourth most common cancer among both men and women. In 2022, there were 64,863 new cases and 38,367 deaths.
Projections suggest that incidence will continue to rise by 2026, reflecting both lifestyle changes and improved detection.
Compared to developed countries, survival rates in India remain lower, largely due to late-stage diagnosis and limited access to screening programs.
The American Cancer Society notes that colorectal cancer is a cancer that starts in the colon or the rectum. Colorectal cancer impacts around 1.9 million people every year, noted the World Health Organization (WHO) as per its 2022 data.
Some of the risk factors include risk factors involve being over the age 50, family history, certain genetic syndromes (like Lynch syndrome), inflammatory bowel diseases, and lifestyle factors (diet high in red meat, alcohol, smoking, inactivity).
The most effective way to prevent colorectal cancer is through annual colonoscopies, screening and stool tests.
Study Finds Strong Links Between Borderline Personality Disorder And Alcohol Use

Credits: Canva
Alcohol use problems are far more common in people living with borderline personality disorder than many clinicians may assume. A large meta analysis has found that more than half of individuals diagnosed with the condition also struggle with alcohol use disorders. The finding strengthens calls for mental health care that treats both issues together rather than separately.
Why Alcohol Is A Major Risk
Borderline personality disorder, often called BPD, is a complex psychiatric condition marked by intense emotional swings, impulsive behavior, unstable relationships, and a fragile sense of self. Many people with BPD experience overwhelming emotional distress and may turn to alcohol as a way to cope, calm themselves, or escape difficult thoughts.
For years, research has hinted at a strong connection between BPD and substance misuse. However, the actual scale of the problem has been unclear because individual studies reported very different numbers. Some suggested moderate overlap while others pointed to extremely high rates.
Alcohol misuse in BPD is not just a side issue. It can worsen mood instability, increase the risk of self harm, and make therapy harder to stick with. People may miss appointments, struggle with medication routines, or act more impulsively while intoxicated. This makes understanding the true prevalence important for both diagnosis and treatment planning.
What Did The Research Find?
To clarify the picture, researchers reviewed 15 studies including 15,603 adults diagnosed with borderline personality disorder. The team analyzed data collected across multiple countries and databases up to March 2024 using established systematic review methods.
The results were striking. About 55.28 percent of people with BPD had an alcohol use disorder. Around 44.59 percent met criteria for alcohol dependence and 18.84 percent for alcohol abuse.
When compared with the general population, the contrast becomes sharper. Alcohol use disorders occur in roughly 8.6 percent of men and 1.7 percent of women overall. The prevalence in BPD is therefore dramatically higher.
In simple terms, alcohol related conditions are not occasional in BPD. They are common and clinically significant.
What This Means For Treat
The findings suggest that mental health services cannot treat borderline personality disorder in isolation. Screening for alcohol misuse should become routine during psychiatric assessment. Likewise, addiction services should look for underlying personality disorders rather than focusing only on drinking behavior.
Integrated treatment approaches are likely to work better. Therapy that addresses emotional regulation, impulsivity, and coping skills alongside addiction support may reduce relapses and improve long term outcomes.
Early identification is key. When both conditions are recognized together, patients are more likely to stay engaged in care and avoid severe complications. The research ultimately highlights a simple but important point. For many patients, recovery depends on treating the person as a whole, not just the diagnosis they first walk in with.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

