- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
National Anti-Drug Addiction Day 2024: Reintegrating In Society After Rehab

Credits: Canva
On National Anti-Drug Addiction Day, it's crucial to highlight the growing challenge of substance abuse in India. In India, commonly used and easily accessible drugs include cannabis (bhang, ganja, charas), heroin (chitta), opium, prescription drugs (painkillers, sedatives), alcohol, tobacco, etc.
There is a devastating impact of heroin, commonly referred to as 'chitta' in regions like Punjab and Jammu. It's often sold at affordable prices, making it readily accessible to vulnerable populations, including young adults and adolescents. The ease with which drugs like 'chitta' are accessible has created an alarming addiction crisis, affecting countless individuals and their families.
Recovery from drug addiction is a monumental achievement, but the battle doesn’t end with the completion of a rehab program. The post-recovery phase is often the most challenging. Returning home to environments where drugs like 'chitta' are easily available poses a significant risk of relapse.
So, how can someone who has completed a drug abuse recovery program thrive in such high-risk settings?
Building Resilience Through Mental Health Support
Substance abuse recovery is a complex and often arduous journey that involves much more than just overcoming physical dependence on drugs or alcohol. While detoxification and physical rehabilitation are critical first steps, sustaining long-term sobriety requires addressing the profound mental and emotional impacts of addiction since substance abuse and mental health are deeply interconnected. Many individuals who struggle with addiction may also face underlying mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), etc.
The psychological impact of addiction can leave an individual vulnerable to anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges. Regular therapy and counselling can help them manage their emotions and reduce the temptation to relapse. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) are especially effective in helping individuals cope with cravings and triggers.
This is why, rehabilitation centres ensure post-recovery follow-up sessions for continued psychological support and post-recovery assistance.
Addressing Trauma
Many individuals who struggle with addiction may have experienced trauma, whether it’s childhood abuse, violence, or other significant emotional upheavals. Unresolved trauma can act as a persistent emotional burden, driving individuals toward substance use as a way to numb their pain. By addressing the root causes of trauma through therapy, individuals can begin to heal and move forward in their recovery journey with a sense of closure and emotional freedom.
Practicing Mindfulness and Stress Management
Stress is a major trigger for relapse, especially in environments where drugs are easily accessible. Emotions like stress, anxiety, sadness, and anger can all serve as powerful triggers for substance use. Incorporating mindfulness practices like meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises can help recovering individuals manage stress and anxiety. They can be effective in helping the person shift focus from distressing thoughts to calming practices. They help cultivate awareness of one’s thoughts and feelings, allowing for better regulation of emotional responses to stress.
By addressing mental health concerns through therapy and by practicing mindfulness-based exercises, individuals can learn to identify and cope with these emotional triggers in healthier ways.
Physical Wellness
Exercise, in particular, has been shown to reduce cravings and improve mood by releasing endorphins—natural mood-enhancing chemicals in the brain. Regular physical activity can also help reduce anxiety and depression.
Developing Strong Support Systems
Having a solid social network is crucial for anyone trying to maintain sobriety. Friends, family, and loved ones can serve as a vital source of support. Engaging loved ones in the recovery process through family therapy can help them understand the challenges of addiction and provide the individual with much-needed emotional backing. Additionally, surrounding oneself with sober peers or mentors who have successfully navigated recovery can be a strong protective factor. These relationships help to reinforce positive behaviors and create an environment of accountability and encouragement.
Relapse Prevention Planning
A detailed relapse prevention plan should be a key part of the post-recovery process. This plan can help individuals identify personal triggers (such as stress, certain places, or social settings) and develop coping strategies to manage them effectively. Another important aspect of relapse prevention is having an emergency action plan in place.
When drugs are readily available in one's home environment, it’s vital to establish boundaries. This could mean avoiding certain social circles, staying away from known drug hotspots, or moving to a new location if feasible. Changing one’s physical environment, if possible, can significantly reduce the chances of encountering triggers.
Developing New and Healthy Habits
Boredom and a lack of purpose can often lead to relapse. Individuals need to cultivate new hobbies and interests that provide meaning and fulfillment. Engaging in creative pursuits, volunteering, or taking up new courses can help reduce idle time and provide a positive focus
Moreover, communities should invest in rehabilitation centers, counseling programs, and post-recovery support systems to help individuals reintegrate into society.
National Anti-Drug Addiction Day reminds us that overcoming addiction is not just about detoxifying the body but also about healing the mind. Mental health support, strong social systems, and relapse prevention strategies are essential for maintaining sobriety, especially in high-risk environments.
By integrating psychological therapies, wellness practices, and strong support systems, individuals can not only overcome addiction but also lead fulfilling, meaningful lives in recovery. With continuous support and the right interventions, it is possible for recovering individuals to navigate environments where drugs are prevalent and to reclaim their lives with dignity and hope.
Doctor Explains Why Weight Loss Drugs Like Ozempic Are Truly A Medical Breakthrough

Credits: iStock
Ozempic, Mounjaro, Wegovy, and many more such popular weight loss drugs are now making headlines. They are also dominating social media, dinner table conversation and many more. But, is Ozempic truly a medical breakthrough, a miracle drug? Dr Shubham Vatsya, a gastroenterologist, and hepatologist at Fortis Vasant Kunj explains how did this drug change the weight loss struggle that many people face.
Why Is GLP-1 Drug A Medical Breakthrough?
Dr Vatsya explains that it took 20 years of research for scientists to come up with these medicines. This drug underwent proper lengthy trials, and have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), "which is not obtained by giving any bribe".
Also Read: Fact Check: Is Weight Lifting Safe for Teens? An Expert Explains the Risks and Safer Alternatives
He also noted that when a person is not able to lose weight, Ozempic and drugs alike give a "head start" to them, along with a hope.
Talking about side effects, he says that every drug has its side effects, this is where a doctor's role comes in.
"Now, the person who is not able to lose weight, if you tell him 'you hit 100 kg bench press', he will break his shoulder. He needs a kickstart somewhere. This is what weight loss drugs allow," he says.
He also points out that the scientists who made GLP-1 agonists got a Nobel Prize, which "cannot be a scam". This is what makes weight loss drugs truly different.
What Are GLP-1 Drugs?
GLP-1 Drugs stand for Glucagon-like peptide 1, a naturally occurring hormones that helps regulate blood sugar and appetite after eating. It was first identified almost 50 years ago and scientists have since uncovered its role in type 2 diabetes.
Almost two decades of research went behind it that led to the development of GLP-1 agonists. It was in 2005, when the first GLP-1 medication, exenatide was approved.
Read: Could You Become Addicted To Your Weight Loss Drugs?
These medications have three main functions:
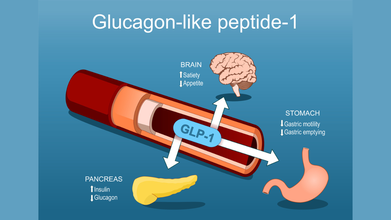
- Stimulating the pancreas to release insulin
- Slow the transit of food in the stomach to help people feel fuller for longer after a meal
- Act on areas of the brain that regulates hunger and fullness, leading to smaller portion sizes and reducing cravings
Popular drugs like Ozempic and Wgovy, which have semaglutide, which is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, or tirzepatide found in Zepbound and Mounjaro are FDA-approved for type 2 diabetes and weight loss.
These drugs work by binding GLP-1 receptors in the body, which in return increase insulin production in response to food intake and suppress glucagon, a hormones that raises blood sugar.
Also Read: How Weight Loss Drugs Change Ones Relationship With Food?
Are The Popular Weight Loss Drugs Addictive?
There is currently no data suggesting that GLP-1 medications cause physiological addiction. Interestingly, some research suggests they may even reduce cravings related to alcohol or opioid use. That directly contradicts the idea that these drugs hijack the brain’s reward system in a traditional addictive way.
Still, wanting or feeling unable to stop a medication because of fear of weight regain or loss of control is very real. That experience should not be dismissed, even if it is not addiction in the clinical sense.
These medications are meant to support long-term habit change, not replace it. Nutrition, movement, sleep, and a healthier relationship with food are meant to develop alongside the medication. When people reach their goal weight, doctors may suggest tapering the dose slowly or moving to a lower maintenance schedule rather than stopping abruptly.
Stopping suddenly can make hunger feel overwhelming. A gradual transition allows the body and mind time to adjust. Some people do successfully maintain weight loss without the medication, but it usually requires strong lifestyle foundations first.
Going Through Cough And Flu? NHS Issues Urgent Cough Syrup Warning

Credits: Canva
As cough and flu season sweeps across the UK, health expert Dr Xand shared crucial guidance during today’s episode of BBC Morning Live (Jan 19) for anyone struggling with a stubborn cough. The discussion focused on coughs and colds, highlighting new research showing that human rhinovirus, a common cause of cold, can also trigger pneumonia in adults.
Flu Season In UK: Warning Signs To Watch For
Speaking with presenters Helen Skelton and Gethin Jones, as per Mirror, Dr Xand, a specialist in public and global health, explained which symptoms indicate a cough should not be ignored. He noted that a persistent cough is one of the key signs of pneumonia.
Gethin asked, "A cough happens with many illnesses, so when should someone really worry?" Dr Xand replied, "This is a big question, and plenty of people at home might be thinking, 'Is this serious?' because coughs can linger for a long time."
He continued: "Viruses like respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) can cause what’s known as the 'hundred-day cough,' and people can be coughing for weeks wondering what’s going on."
Dr Xand advised viewers to follow the NHS guidelines for coughs, saying, "The NHS recommends consulting your doctor if a cough persists for over three weeks. Many coughs last three to four weeks, and you’ll usually notice if they’re improving. Right now, the most common cause is a virus."
Dr Xand’s Cough Syrup Alert
Addressing people from home about cough syrups, Dr Xand highlighted the latest NHS guidance. He suggested trying more natural remedies, which can be just as effective. "The NHS does not actually recommend cough syrup," he explained. "It advises hot lemon with honey instead."
The official NHS website confirms that "hot lemon with honey has a similar effect to cough medicines." This simple remedy can soothe the throat, calm irritation, and reduce the cough reflex. Some studies even suggest it works as effectively as certain over-the-counter medicines, particularly for children over one year old. However, it’s important to note that it doesn’t treat the underlying illness.
What Do Cough Syrup Studies Show?
Research shows that most over-the-counter cough medicines offer minimal benefits. Studies, including those from the Cochrane Collaboration, reveal that they perform little better than a placebo for short-term cough relief in both adults and children.
While these syrups may temporarily ease throat irritation or provide a sense of relief, ingredients such as dextromethorphan and guaifenesin often do no better than sugar pills. Much of the perceived benefit comes from the placebo effect or the body’s natural recovery.
Instead, simpler measures like honey, staying hydrated, and using painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen are often more effective. Most coughs caused by colds simply need time to resolve.
Cough Syrup: Red Flags To Watch For
Dr Xand shared the warning signs people should be aware of. "There are several red flags worth noting. High fever, chills, or unexplained shortness of breath are all reasons to see a doctor immediately. You should be able to breathe normally, and if you can’t, that’s a concern."
He added, "Any chest pain with a cough, very thick mucus, or extreme fatigue are also serious signs. More severe warning signals include trouble breathing, bluish lips or fingertips, confusion, mental changes, prolonged high fever, and a rapid heart rate."
"It’s crucial to act quickly," Dr Xand continued. "I’ve seen cases in my own family where someone went from a mild cough to being extremely unwell in just a day. Sudden deterioration can be life-threatening, so early medical help is essential."
Pneumonia Can Be Subtle but Serious
Dr Xand emphasized, "Pneumonia can sometimes develop quietly. It isn’t always dramatic, but it can be fatal. That’s why it’s so important to monitor symptoms and seek medical help promptly if things are getting worse."
Vitamin B12 And D3 Deficiencies Could Lead To Serious Health Issues, Experts Warn

Credits: AI Generated
Vitamin deficiencies are often brushed aside as minor nutritional gaps. Many people assume they can be fixed later or ignored until something feels seriously wrong. According to Dr Prabhat Ranjan Sinha, Senior Consultant, Internal Medicine at Aakash Healthcare, this casual attitude can be risky, especially when it comes to Vitamin D3 and Vitamin B12. Both nutrients play a central role in bone strength, nerve function, immunity, and energy levels. When their levels drop, the damage may build quietly and surface only when daily life starts to feel difficult.
Vitamin D3 and Vitamin B12 are essential for overall wellbeing. Their deficiency may not cause obvious symptoms at first, but over time they can affect how the body functions, how often a person falls sick, and how energetic or mentally sharp they feel.
Vitamin B12 And D3 Deficiencies: The Sunshine Vitamin And Why It Matters
Vitamin D3, often called the sunshine vitamin, is produced by the body when skin is exposed to sunlight. Along with calcium, it helps maintain strong bones and reduces the risk of fractures. Low levels of Vitamin D3 can weaken muscles, increase the risk of falls, and raise the chances of bone disorders such as osteoporosis. In children, severe deficiency can lead to rickets, a condition that affects normal bone growth.
Dr Sinha explains that Vitamin D3 does more than support bone health. It also plays a key role in immune function. People with low levels may fall sick more often and take longer to recover from infections. Research has also linked deficiency to higher levels of inflammation in the body.
Despite living in a country with abundant sunlight, Vitamin D3 deficiency is widespread. Urban lifestyles keep many people indoors for long hours. Regular use of sunscreen, limited outdoor activity, and aging all reduce the body’s ability to produce and absorb this vitamin. Diet alone rarely provides enough Vitamin D3, which is why deficiency remains common even among people who eat well.
Vitamin B12 And Its Silent Impact
Vitamin B12 is equally important but often overlooked. It is essential for nerve health, brain function, and the production of healthy red blood cells. Unlike some deficiencies that show early warning signs, B12 deficiency tends to develop slowly. Its symptoms are often mistaken for stress, aging, or routine fatigue.
Low Vitamin B12 levels can cause weakness, persistent tiredness, tingling or numbness in the hands and feet, memory problems, mood changes, and difficulty concentrating. Over time, untreated deficiency can lead to nerve damage and anemia.
Certain groups are at higher risk. Vegetarians and vegans often do not get enough B12 because it is mainly found in animal-based foods. Older adults may struggle to absorb B12 due to reduced stomach acid. People with digestive disorders and those taking long-term acid-reducing medications are also more vulnerable.
Why These Deficiencies Are Missed?
One of the biggest challenges with Vitamin D3 and B12 deficiencies is that their symptoms overlap with many common health complaints. Ongoing fatigue, joint pain, low mood, or frequent illness are often blamed on work stress, poor sleep, or lifestyle habits. As a result, people delay medical advice until symptoms start interfering with everyday life.
Dr Sinha notes that this delay can make recovery slower and complications more likely.
Vitamin B12 And D3 Deficiencies Diagnosis And Timely Care
Simple blood tests can accurately detect Vitamin D3 and B12 deficiencies. However, many people only get tested once symptoms become severe. Early diagnosis allows for timely treatment, which may include supplements, dietary changes, and lifestyle adjustments under medical guidance.
Addressing these deficiencies early is one of the simplest ways to protect long-term health. Adequate sunlight exposure, balanced nutrition, and routine screening can help maintain healthy levels. Taking Vitamin D3 and B12 deficiencies seriously is a small step that can prevent lasting health problems and support healthier aging.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

