- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Neurologist Shares How Using Your Non-Dominant Hand For Daily Simple Activities Can Boost Brain Health

Credits: Canva
When was the last time you tried brushing your teeth with the “wrong” hand and ended up with toothpaste on your nose? Or fumbled with your fork as though you had suddenly forgotten how to eat? As it turns out, those awkward, clumsy attempts may actually be doing your brain a massive favour.
Dr Sudhir Kumar, neurologist, explains: “Using your non-dominant hand for daily activities like brushing your teeth, eating, or opening doors can challenge your brain, encourage new neural connections, and may improve cognitive flexibility over time.”
Using Your Weaker Hand Can Boost Brain Health
You have probably heard that your brain is like a muscle, but have you ever thought about putting it through a workout that does not involve solving puzzles? According to Dr Kumar, “Just like muscles, your brain gets stronger with exercise. Switching hands forces your brain to adapt, stimulating regions that are usually less active.”
That means the slip-ups and slowed-down movements are not failures but signals that your brain is firing up areas it does not usually depend on.
Also Read: Does How You Eat Avocado Affect Its Weight-Loss Benefits?
How to practise it
The best thing about this brain exercise is that you do not need different tools or complicated routines. In fact, the things you do every single day are the perfect training ground. Dr Kumar suggests a few easy ways to get started:
1. “Eat or cook with your opposite hand.”
2. “Use it to operate your phone.”
3. “Write a short note.”
4. “Use it to brush teeth, comb your hair or shave.”
5. “Try simple percussion (e.g., drumming) or piano melodies with the non-dominant hand taking the lead.”
Small switches, big rewards
Scientists often talk about neuroplasticity, which is the brain’s ability to rewire itself. While big life changes and new learning experiences are known to boost this, tiny everyday tweaks, like stirring your tea with your left hand if you are right-handed, also count. Over time, these switches may improve focus, problem-solving skills, and adaptability.
Plus, there is something oddly satisfying about realising you have mastered a task you once struggled with. Writing a little something with your left hand may look tough at first, but give it a week and you will notice surprising progress.
Also Read: Life After Chikungunya: Top Tips On Managing Joint Pain and Regaining Mobility
Of course, do not expect your non-dominant hand to suddenly become proficient at everything you do. At first, the tasks might feel frustrating, and your movements clumsy. But that awkwardness is precisely the point; it is your brain stretching itself in new directions. Training your brain with these small hand switches works on the same principle: deliberate struggle leads to growth.
A playful way to future-proof your brain
Brain health often feels like a heavy topic reserved for discussions about memory loss or ageing, but adding a dose of play makes it a whole lot lighter. Using your non-dominant hand is basically an easy game you can play with yourself, without apps, subscriptions, or brain-training gadgets.
Ramadan Fasting: Avoid Excess Salt And Caffeine To Boost Kidney, Prostate Health, Say Experts

Credit: Canva
Dehydration is a serious concern for people fasting during the month-long Ramadan period, and can severely impact kidney and prostate health. Experts suggested that avoiding excess salt and caffeine can help.
While Ramadan fasting is generally safe for people with early-stage chronic kidney disease (CKD), maintaining adequate hydration between iftar and sehri -- the two important meals each day for faithful observing the fasting -- is of significant importance.
Dehydration can lead to acute kidney injury and electrolyte imbalances for individuals with advanced CKD. As prolonged fasting hours -- more than 12 hours a day -- urine becomes concentrated, increasing the risk for kidney stones and Urinary Tract infections (UTIs).
For men with prostate problems, fasting during Ramadan can pose challenges, such as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) or an enlarged prostate, primarily due to dehydration.
“As a practicing urologist and kidney transplant surgeon in India, I often notice a rise in kidney stone pain and urinary infections during Ramzan. When patients fast for long hours -- especially in our warm climate -- urine becomes highly concentrated. That increases the risk of stones and UTIs. Men with prostate enlargement sometimes report worsening urinary flow because they consciously reduce fluid intake,” Dr. Pankaj Panwar, Additional Director, Urology, Fortis Escorts Okhla, New Delhi, told HealthandMe.
The doctor advised people “to hydrate strategically between Iftar and Sehri, avoid excess salt and caffeine”.
How Excess Salt And Caffeine Impact Ramadan Fasting
Consuming high-sodium foods such as processed meats, pickles, salty snacks, and fast food during iftar or sehri can increase thirst and dehydration.
High salt intake forces the body to pull water from cells to dilute the sodium, leading to severe thirst. It can also lead to bloating.
Similarly, caffeine in coffee, tea, chocolate, and energy drinks can be diuretic and cause the body to lose fluids and salts through increased urination. Particularly, drinking coffee or tea at sehri -- the pre-dawn meal -- can lead to faster dehydration during the day.
Caffeine consumption, especially late in the evening, can also interfere with sleep, making it harder to wake up for sehri.
“Ramzan is a sacred month of fasting, but prolonged abstinence from water, especially in hot climates, can increase dehydration risk. Concentrated urine puts stress on the kidneys and may worsen kidney stones or trigger urinary tract infections,” Dr. Mangesh Patil, Urologist at Saifee Hospital, Mumbai, told HealthandMe.
Dehydration during Ramadan fasting can lead to symptoms like headaches, extreme thirst, fatigue, and dizziness. But in case of severe dizziness, fever, confusion, or blurred vision, the experts warned of immediate medical help.
“Do not ignore warning signs like flank pain, fever, or difficulty passing urine. A little planning can prevent an emergency hospital visit,” Panwar said.
Patil said warning signs include severe flank pain, burning urination, fever, vomiting, blood in urine, or reduced urine output. Men with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia may notice worsening urinary symptoms.
Tips To Prevent Complications
- Drink 2-3 liters of water between iftar and sehri
- Include water-rich fruits
- Avoid excess salt and caffeine
- Individuals with kidney disease, stones, UTIs, or prostate issues should consult their doctor before fasting.
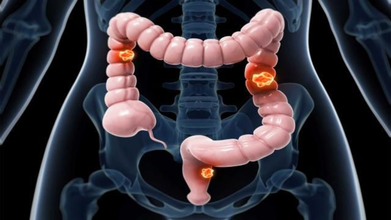
The Common Colon Cancer Sign You Need To Look Out For
Credit: Pinterest
Colon (colorectal) cancer begins when small growths called polyps form on the inner lining of the colon or rectum. Over time, changes in the DNA of these cells can cause the polyps to become cancerous.
As abnormal cells multiply, they replace healthy cells and eventually form a mass known as a tumor. This process develops slowly, often taking up to ten years for a precancerous polyp to turn into cancer and begin showing symptoms.
Colon cancer poses serious health risks because cancerous cells can invade healthy tissues. Over time, they may break away and spread to other parts of the body, making detection more difficult since the symptoms can resemble other conditions.
What Is the First Sign of Colon Cancer You Shouldn’t Ignore?
Colon cancer can be difficult to detect because it often develops without obvious symptoms. However, doctors emphasize that the number one warning sign is rectal bleeding or blood in your stool.
"Colon cancer can be hard to diagnose because it can develop asymptomatically,” said Dr. John Nathanson, a gastroenterologist at New York-Presbyterian Allen Hospital.
Dr. Pratima Dibba adds that this symptom should not be misdiagnosed as hemorrhoids, infection, or constipation, since early signs of colon cancer can look similar.
She urges patients to get checked promptly to rule out serious conditions.
Research from the Cleveland Clinic also shows that blood in stool can originate anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract, including the colon.
Detecting colon cancer early is critical, as survival rates can be as high as 90 percent when caught in its initial stages.
What Are Other Symptoms Of Colon Cancer?
Persistent changes in bowel habits (diarrhea, constipation, or narrowing of stool). Other signs include:
- Abdominal (belly) pain
- Bloated stomach
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Feeling like there’s still poop in your bowel even after you go to the bathroom
- Feeling tired or weak
- Unexplained weight loss
Present Day Scenario In India
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a major health concern worldwide. In India, it is the fourth most common cancer among both men and women. In 2022, there were 64,863 new cases and 38,367 deaths.
Projections suggest that incidence will continue to rise by 2026, reflecting both lifestyle changes and improved detection.
Compared to developed countries, survival rates in India remain lower, largely due to late-stage diagnosis and limited access to screening programs.
The American Cancer Society notes that colorectal cancer is a cancer that starts in the colon or the rectum. Colorectal cancer impacts around 1.9 million people every year, noted the World Health Organization (WHO) as per its 2022 data.
Some of the risk factors include risk factors involve being over the age 50, family history, certain genetic syndromes (like Lynch syndrome), inflammatory bowel diseases, and lifestyle factors (diet high in red meat, alcohol, smoking, inactivity).
The most effective way to prevent colorectal cancer is through annual colonoscopies, screening and stool tests.
Chinese Scientists Could Reverse Type 2 Diabetes Through Stem Cell Therapy
Credits: Canva
For the longest we have been told that Type-2 diabetes though can be maintained, cannot be fully reversed. However, Chinese scientists may have found a cure, thanks to stem cell therapy. Chinese scientists have achieved the first case in the world in reversal of type-2 diabetes.
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition characterized by high blood sugar (glucose) levels. It develops when the pancreas either doesn't produce enough insulin, doesn't produce any insulin at all, or when the body doesn't respond properly to insulin, a condition known as insulin resistance.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes and occurs when your body doesn't use insulin properly. The risk of developing Type 2 diabetes increases if you are overweight or obese, or if you have a family history of the condition.
What Did The Study Find?
First, researchers collected stem cells, either from the patient’s own body or from a donor. These cells are valuable because they can develop into many different specialised cell types and take over specific biological functions.
In the laboratory, scientists exposed the stem cells to carefully designed chemical signals and genetic instructions. This guided them to become pancreatic islet cells, more precisely, beta cells, the body’s natural insulin-producing cells.
Once reprogrammed, the cells were grown into small clusters that resemble real pancreatic tissue damaged in diabetes. These clusters are capable of sensing blood sugar levels and releasing insulin when required.
Next came transplantation. The insulin-producing clusters were implanted into the patient’s body, in this case, the abdomen. After implantation, they connected to the bloodstream and began functioning within the body.
After transplantation, the new cells begin behaving like healthy pancreatic beta cells. They sense rising blood glucose levels and release insulin in response, helping bring sugar levels down naturally and reducing, or sometimes removing, the need for insulin injections.
Doctors then closely monitor the patient over time to make sure the cells survive, continue producing insulin, and do not trigger immune rejection or other complications.
This approach falls under regenerative medicine, where the goal is not just to manage type-2 diabetes but to repair the underlying problem by rebuilding the body’s insulin-producing ability.
The early outcome is encouraging, but caution is essential. The success comes from a single case, and that alone cannot prove the treatment works broadly. Larger clinical trials across diverse patient groups are necessary to confirm both safety and effectiveness before it can be considered a reliable therapy.
Why Does This Study Matters Especially For India?
Many experts have recognized India as the diabetes capital, with type-2 diabetes being the most common cost. Globally, diabetes affects about 90 million adults between the ages 20 to 70 years, with over 90 per cent of these cases are of type-2 diabetes. India had 89.8 million adults between ages 20 to 79 years living with diabetes in 2024 and the numbers are expected to increase to 100 million by the end of 2026. This is why this stem cell therapy could prove to be of great help in controlling the numbers, especially for insulin-dependent patients.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

