- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
13 Superfoods High In Omega-3 Fatty Acids

13 Superfoods High In Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are of essential in boosting both brain health and heart health, ensuring general bodily functions are maintained. These healthy fats build structure into cell membranes, assist cognitive functions, provide enhancement in mood stability, and boost immunity. Since the body cannot make all types of omega-3 fatty acids, dietary incorporation is very important.
Omega-3 contents vary with species but, in general, provide adequate DHA and EPA.
Omega-3 fatty acids are necessary to maintain optimal mental and physical well-being. While fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and anchovies are great sources of EPA and DHA, there are plant-based options such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and soybeans that are rich in alpha-linolenic acid or ALA. Adding these 13 foods to your diet will greatly improve heart health, brain function, and your overall well-being. Whichever your preference, fish, legumes, seeds, or even plant-based alternatives, you can find an omega-3.
Here are 13 foods that are very high in Omega-3 fatty acids and are nutritious:
1. Salmon
Salmon is one of the most nutrient-dense foods available and a top source of omega-3 fatty acids. It is rich in both EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), two critical types of omega-3s. Besides, salmon offers many essential nutrients, including vitamin D, vitamin B12, and selenium. Some research findings reveal that consuming salmon regularly will lower your risks for heart diseases, dementia, and mental problems, like depression. Salmon is indeed the epitome of versatility. Salmon may be grilled, baked, smoked, or poached, but will fit into almost any diet.
Omega-3 content: 2,150 mg of EPA and DHA (combined) per 3.5 oz (100 g) serving.
2. Cod Liver Oil
Although technically a supplement, cod liver oil deserves mention for its exceptional concentration of omega-3s.
Extracted from the liver of cod fish, this oil is an incredibly efficient source of essential omega-3 fatty acids. It is also loaded with vitamins A and D. One tablespoon of cod liver oil delivers 170% of the daily recommended value of vitamin D and 453% of vitamin A. It should be consumed in moderation, though as excess vitamin A can cause damage to your body. Cod liver oil has been shown to promote heart health, even brain functioning, and improve bone and immune system response.
3. Oysters
Oysters are a popular shellfish and are an excellent source of zinc, copper, and vitamin B12. They are also high in omega-3 fatty acids. They can be consumed raw, grilled, or baked and provide the best option for those looking for a nutrient-dense appetizer or main dish. Nutritionally, oysters are potent due to their combination of omega-3s and essential trace minerals, which help with heart health, immunity, and recovery from fatigue.
Contains omega-3 content: 500 mg per 3 oz serving
4. Sardines
These small oily fish pack a nutritional punch. Sardines are nutrient-rich and are an excellent source of omega-3s. When eaten whole, you also get the calcium, vitamin B12, and vitamin D that they are so rich in. They come usually canned and can be added to pasta dishes, salads, or eaten alone as a healthy snack.
Omega-3 content: 1,463 mg of EPA and DHA (combined) per cup (149 g) of canned sardines.
5. Anchovies
Anchovies are small, oily fish with both a good taste and nutritional value. They are usually sold canned or dried and have a very pungent flavor, making them suitable for use as ingredients in sauces, pizza toppings, or any other dishes. Not only do anchovies contain an impressive amount of omega-3 fatty acids, but they are also a good source of niacin and selenium. They also contain a good amount of calcium when consumed with bones.
Omega-3 content: 2,053 mg of EPA and DHA (combined) per 3.5 oz (100 g).
6. Shrimp
Shrimp is an ambrosial seafood food widely consumed by people across the world. It has very low calorie levels and high protein, rich in omega-3. It can be grilled, boiled, or mixed with salads and pasta to be a heart-friendly dish. Besides the richness of omega-3, it has a high content of potassium that helps the heart maintain health.
Omega-3 content: 0.12 g of DHA and 0.12 g of EPA per 3 oz (85 g) serving.
7. Chia Seeds
Chia seeds are a fantastic plant-based source of ALA, which is a type of omega-3 fatty acid. They're also super versatile and can be used in a number of dishes. With its high fiber and protein content, chia seeds are excellent for digestion and satiety. Commonly used to make chia pudding, sprinkled over salads, or added to smoothies.
Omega-3 content: 5.055 g of ALA per 1 oz serving.
8. Flaxseeds
Other top plants from where sources are gotten include flaxseeds, which contain omega-3 fatty acids. Flaxseed are extremely loaded with fiber, protein, magnesium, and manganese to mention a few. Flaxseed oil is also fantastic since it contains 6.703 g of ALA per tablespoon. Flaxseeds are easy to be included in your diet because they can be easily put on cereals, oatmeal, or salads.
Omega-3 content: 6.703 g of ALA per tbsp.
9. Edamame Beans
Edamame beans are young soybeans, usually eaten as a snack or side dish. A good source of protein, they also contain omega-3 fatty acids, which boost heart health and overall wellbeing. They can be simply steamed, boiled or added to stir-fries, soups, and salads to give an easy, nutritional boost.
Omega-3 content: 0.28 g of ALA per 1/2 cup serving.
10. Kidney Beans
Kidney beans are a staple for hearty stews, chili, and other comfort foods. While not as high in omega-3s as fish sources, they are still a good plant-based option. They are also a good source of dietary fiber, which supports digestion and heart health.
Omega-3 content: 0.10 g of ALA per half-cup serving.
11. Soybeans
Soybeans are versatile legumes rich in fiber, vegetable protein, and several essential vitamins and minerals. Though better known for their omega-6 fatty acids, they do provide a decent amount of omega-3s. Tofu and soy milk products are good sources for heart-healthy benefits and add to the overall intake of omega-3s.
Omega-3 content: 670 mg per serving.
12. Walnuts
Walnuts are an excellent source of ALA omega-3s and are a favorite for their versatility. They can be eaten on their own, mixed into granola, or added to salads and other dishes. Walnuts also provide a hearty dose of healthy fats and contribute to better brain function, cardiovascular health, and overall wellness.
Omega-3 content: 3.346 g of ALA per 1 cup.
13. Seaweed and Algae
For vegetarians and vegans, seaweed and algae are great plant-based sources of omega-3s. They are rich in both EPA and DHA and are widely consumed in sushi, soups, and supplements. Adding seaweed and algae can be a good way to meet daily omega-3 needs without consuming fish.
Ways You Can Add Omega-3 Rich Food To Your Diet
Incorporate these omega-3-rich foods into your daily diet with simple swaps and additions.
Begin by enjoying two servings of fatty fish like salmon, sardines, or shrimp a week.
Sprinkle chia seeds or flaxseeds into smoothies, oatmeal, or yogurt for a plant-based ALA boost. Add edamame or kidney beans to your salads or soups to enhance protein and omega-3s. Use walnuts in your granola, trail mix, or as a snack. Replace regular oils with flaxseed or fish oil for cooking or dressings. Take cod liver oil as a supplement. These little changes will make a big difference in supporting overall health.
Kanpur Food Adulteration: FSSAI Seizes 14,000L of Oil, 1320Kg Rotten Dates And More Ahead Of Festive Season

Credits: FSSAI and Canva
After Indore's Bhagirathpura food contamination and Horlicks adulteration in Odisha, another news of food adulteration comes from the state of Uttar Pradesh where UP Food Safety and Drug Administration or the UPFSDA with Food Safety and Standards Authority of India or FSSAI seized nearly 14,000 litres of adulterated oils during raids in Kanpur.
This has led to the confiscation of 1,000 kilograms of colored waste and other suspicious food items. This happened right ahead of the festive season like Holi, Eid and as Ramadan continues. This is also the time when festive meals are cooked in oil, ghee, and Ramadan fast is also broken with dates that too were found in rotten conditions.
Also Read: Scientists Develop First Antibodies To Block Epstein Barr Virus
Kanpur Food Contamination: What Has Been Seized In The Raid?
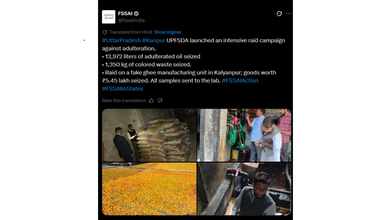
As per the official statement, enforcement teams seized 13,972 litres of adulterated oil and 1,350 of colored waste during inspection across the city.
Officials were also able to spot fake ghee in the manufacturing unit of Kalyanpur. Fake ghee worth approximately Rs. 5.45 lakh were confiscated. The seized samples have been sent to a laboratory for further testing and analysis.
The raids were launched as a part of wider effort to curb food adulteration before the festive season when the demands for such edible also rise sharply.
Kanpur Food Contamination: Dates, Sweets, And More Seized
Surprise inspections were also conducted at several food outlets, cold storage facilities and dairies across Kanpur that brought out a concerning image. These places have come under the scanner. Authorities inspected Swaroop Cold Storage in Aishbagh and Himalayan Cold Storage on Ayodhya Roads. Further raids were carried out on dairies in the Havetmau area and Rae Bareli Road. Samples from sweet shops and other eateiers have also been collected.
The raid collected rotten dates from the cold storage. Followings have been collected and recovered:
- 1,320 kilograms of dates were seized
- 1,418 kilograms of colored kachri were confiscated
- Food items also recovered from warehouse in Aminabad
Officials confirmed that strict actions will be taken against them and this will continue throughout the festive period.
Raids Not Just In Kanpur
FSDA intensified raids and checks in Lucknow too during Ramadan and Holi. These inspections will be done in warehouses, food outlets, and dairy units to prevent sale of adulterated and substandard products. Raids from Hapur too have led to confiscation of adulterated food. UPFSDA plans to conduct further raids during the festive season. On X, formerly Twitter, the UPFSDA posted that it has seized 25,000 kg of Suji (valued at ₹10 Lakhs) from M/s Raj Sneh Agro Foods Pvt Ltd due to packaging regulation violations. Samples of Jaggery Powder, Gur, and Suji have been sent for lab testing.
What Happens To Your Health When You Consume Adulterated Foods?
Food adulteration happens when there is an intentional addition of foreign or inferior substance to original food products. A 2024 study published in SAGE Open Medicine notes various health impact of adulterated food which include:
- Cancer
- Lathyrism
- Liver disease
- Cardiac failure
- Kidney disease
- Nervous system-related diseases
The study also notes that adulteration could also lead to allergic reactions. Pregnant woman, children and elderly are more prone to getting any illness if adulterated food is consumed.
Indore Food Contamination: 6 People Hospitalized In Bhagirathpura

Credits: Canva
Not too long ago, Indore made headlines in water contamination case where a 67-year-old woman, identified as Parvati Bai Kondla also showed signs of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Bacteria like E coli. and Klebsiella were found in the water sample of Bhagirathpura, the epicentre of water contamination.
Indore's Bhagirathpura is again on the news, this time for food contamination.
Also Read: Woman Lost Weight On Mounjaro But Her Breasts Didn't Stop Growing, This Is Why...
Indore Food Contamination: What Happened?
Six people have been admitted to a hospital after they consumed contaminated food in Bhagirathpura. At a birthday party in Bhagirathpura on a late Saturday night, 60 people ate the food and some of them developed health problems. Chief Medical and Health Officer (CMHO) Dr Madhav Hasani stated on Monday.
Bhagirathpura was the epicentre of water contamination that claimed 22 lives earlier. The minister said that affected individuals were treated and as a precaution, six of them were admitted to the Government Maharaja Yashwantrao Hospital.
Indore Municipal Corporation Commissioner Dilip Kumar said, “We have found that in case of the construction of the toilet, no safety tank was constructed beneath it. We are also probing the other lapses.”
As per the official statement, all patients are doing well after the treatment.
Indore Food Contamination: What Happened In Indore Before?
Earlier in January, Mayor Pushyamitra Bhargav reported that due to lapses in civic infrastructure. Investigation revealed that a toilet constructed directly above a main drinking pipeline near a police outpost, without a mandatory safety tank resulted in the sewage mixing with drinking water.
Read: Sewage Mixing With Drinking Water Kills 7 in Madhya Pradesh’s Indore, Over 100 Remain Hospitalized
Speaking to The Indian Express, Indore Municipal Corporation Commissioner Dilip Kumar said, “We have found that in case of the construction of the toilet, no safety tank was constructed beneath it. We are also probing the other lapses.”
What Is E. Coli Bacteria?
Escherichia coli, commonly known as E. coli, refers to a group of bacteria that naturally live in the intestines of humans and animals. Most of these strains are harmless and even play a role in digestion. However, certain types can trigger illness when they enter parts of the body where they do not belong or release harmful toxins.
These disease-causing strains attach themselves to body cells and produce toxins, leading to infection and inflammation.
What Is Guillain-Barré syndrome?
Guillain-Barré syndrome is a rare autoimmune condition in which your immune system attacks your peripheral nerves, leading to symptoms like numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness that progress to paralysis. However, with treatment, most people fully recover from the condition.
Doctors say GBS occurs at any age, but it most commonly affects people between 30 and 50 years of age.
Guillain-Barré syndrome is rare. About 100,000 people worldwide develop GBS every year. To put that into perspective, the world population is about 7.8 billion. That means healthcare providers diagnose GBS in about 1 in 78,000 people each year.
Horlicks Controversy: Why Is This Popularly Branded 'Health' Drink Suddenly Under The Scanner In Odisha

Credits: ANI and Horlicks Website
Branded as a health drink, Horlicks has come under the scanner in Odisha as the government raised alarm over the growing incidence of food adulteration. On Monday, Odisha's Health Minister Mukesh Mahaling revealed that adulterated batches of Horlicks were seized from multiple districts. He raised serious concerns over food safety across the state.
This came in the backdrop of Congress MLA Tara Prasad Bahinipati asking for clarification on reports of food adulteration. The attention was focused on the everyday food products consumed by households.
Also Read: Fact Check: Should You Change Your Underwear In Every 6 Months?
Horlicks Controversy: Adulteration In 'Health' Drink

Mahaling responded to MLA Bahinipati's query in the Assembly and said that batches of Horlicks have been seized from Baugh and Dhenkanal districts. Furthermore, other reports of confiscation also came form Jagatsinghpur and Mayurbhanj.
Officials have conducted inspections and seized suspect stock during routine checks, however, the Minister did not specify the exact quantity of the adulteration involved, neither the nature of adulteration was revealed.
This has triggered concerns among the consumers who are parents of young children and elderly citizens who regularly rely on health drinks like Horlicks for nutritional supplements.
Horlicks Controversy: Adulteration In Other Food Items
The Minister said that adulteration is not just limited to packaged health drinks, but has affected a wide range of commonly consumed food items:
- Chhena
- Curd and milk
- Bread
- Spices
- Chhatua
- Sauces
- Soybeans
- Ghee
- Salt
- Sugar
- Papad
- Chocolate
- Maida
As per the Health Department, some samples were found to contain harmful and toxic substances, and severe levels in Khurda district. The Health Minister said that the department has intensified inspections, raids and enforcement measures to curb the malpractice and safeguard public health.
Read: Bacteria Found in Amul Milk Pouches, Officials Urge Pasteurization
'Health' and 'Nutritional' Drink Controversy Case Study
In 2023-24, a controversy on Bournvita, which is marketed as a health drink began when influencer Revant Himatsingka of Food Pharmer alleged in a viral video that the drink contained excessive sugar, which is approximately 50 per cent by the weight. He also said that the drink contained harmful additives and that it contradicted from the marketing of it as a health drink.
Afterwards, a legal notice was sent to Mondelez-owned Cadbury and Bournvita reduced its added sugar content by 14.4 per cent and faced regulatory orders to remove the "health drink" tag from its packaging.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

