- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
Balance Diet Helps Manage Asthma-Here's What You Should Eat

Credit: Canva
Asthma is a chronic disease that affects people of all ages, across the globe. It is caused by inflammation and muscle tightening around the airways, which makes it harder to breathe. For individuals living with asthma, managing the condition often involves multiple strategies, that include changes in diet to certain medications. While there is no one-size-fits-all diet for asthma, research suggests that eating a balanced diet may help reduce symptoms and improve overall health.
So How Does A Nutrient-Rich Diet Help Asthma Patients?
Empirical evidence suggests that a well-rounded diet, particularly one rich in fresh fruits and vegetables, may help manage asthma symptoms. A 2019 study found a connection between the shift from fresh foods to processed foods and the rise in asthma cases in recent years. While specific foods haven’t been proven to improve asthma directly, incorporating anti-inflammatory and antioxidant-rich foods into your meals could support lung function and the immune system.Beneficial Foods For Asthma
Several vitamins and minerals have been shown to have positive effects on asthma management. Including these in your diet may help ease symptoms:1. Vitamin C, E, and A/Beta-Carotene: These antioxidants can reduce inflammation and boost the immune system, potentially alleviating asthma flare-ups.
Vitamin C-rich foods include bell peppers, oranges, strawberries, and broccoli.
Vitamin E sources include sunflower seeds, almonds, avocado, and wheat germ oil.
Foods high in Vitamin A and beta-carotene include carrots, sweet potatoes, leafy greens like spinach and kale, and cantaloupe.
2. Vitamin D: Adequate vitamin D levels may help prevent asthma exacerbations. Foods like salmon, fortified milk, eggs, and fortified orange juice are good sources of this vitamin. Be cautious with dairy or eggs if you have known allergies, as they can sometimes trigger asthma symptoms.
3. Selenium and Magnesium: These minerals can help manage asthma symptoms by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation.
Selenium-rich foods include Brazil nuts, fish, chicken, eggs, and brown rice. While Magnesium sources include dark chocolate, tofu, pumpkin seeds, Swiss chard, and salmon.
Foods To Avoid
While adding certain foods may support asthma management, others can trigger symptoms or make them worse. It’s essential to identify your specific triggers, but here are some common culprits:1. Sulfites: Found in foods like wine, dried fruits, pickled foods, and shrimp, sulfites can aggravate asthma for some people.
2. Gas-inducing foods: Foods that cause gas, such as beans, cabbage, onions, garlic, and carbonated drinks, can put pressure on the diaphragm and trigger asthma symptoms, particularly if you have acid reflux.
3. Salicylates: Though rare, some people with asthma are sensitive to salicylates found in coffee, tea, and certain herbs.
4. Artificial ingredients: Preservatives, colourings, and flavourings in processed foods can sometimes trigger allergic reactions or worsen asthma symptoms.
5. Common allergens: If you have food allergies, such as to milk, shellfish, wheat, or tree nuts, these could also exacerbate asthma.
Mediterranean Diet Can Help You Get Healthier Gums
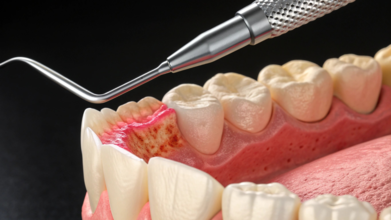
Credits: Canva
A new study published in the Journal of Periodontology highlights that people in the UK who follow a Mediterranean-style diet may enjoy better gum health and lower levels of gum disease. Conducted by researchers at King’s College London, the findings show a link between diet, inflammation, and periodontal disease severity.
What the Study Found
The research evaluated 200 hospital patients who were part of the King’s College London Oral, Dental and Craniofacial Biobank. Participants underwent dental examinations, provided blood samples, and completed detailed dietary questionnaires.
The analysis revealed that individuals whose diets resembled the Mediterranean pattern, rich in legumes, vegetables, fruits, and olive oil, had lower levels of gum disease and systemic inflammation. On the other hand, patients who consumed diets high in red meat and deviated from the Mediterranean model were more likely to present with severe gum disease.
Researchers also measured circulating inflammatory markers. People with less healthy diets showed higher levels of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and C-reactive protein (CRP), both indicators of systemic inflammation. In contrast, those following a plant-rich diet had lower levels of these markers.
Why the Mediterranean Diet Matters
The Mediterranean diet is widely recognized for its emphasis on whole, nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and healthy fats like olive oil. It has already been associated with a reduced risk of major chronic illnesses, including heart disease, certain cancers, and neurodegenerative disorders.
According to the researchers, diet plays a significant role in human health by influencing the immune system and inflammation. This effect largely depends on the types of molecules present in food, including macronutrients, micronutrients, and phytochemicals. Plant-based diets are often rich in these components, which may contribute to reduced inflammation throughout the body.
Implications for Gum Disease
The study’s findings add weight to the idea that gum disease should not only be treated with dental procedures but also considered in the broader context of lifestyle and diet.
Dr. Giuseppe Mainas, first author of the study and postdoctoral researcher at King’s College London, noted:
“Our findings suggest that a balanced, Mediterranean-type diet could potentially reduce gum disease and systemic inflammation. We observed that there may be a connection between periodontal disease severity, diet, and inflammation. These aspects should be holistically considered when assessing treatment for periodontitis in patients.”
A Step Toward Better Oral Health
Professor Luigi Nibali, lead author and Professor of Periodontology at King’s College London, emphasized the growing importance of nutrition in dental health.
“There is emerging evidence about the role that a balanced diet might have in maintaining a periodontal healthy status. Our research shows the potential effect that a nutrient-dense, plant-rich diet could play in improving the nation’s gum health. Nevertheless, more investigation is needed to develop personalized approaches to help people manage their gum health,” he said.
The research is an important step in understanding how dietary choices affect oral and systemic health. While more studies are needed to confirm the long-term effects and create practical dietary guidelines for gum health, the message is clear: what we eat may directly influence not just our heart and brain, but also the health of our gums.
Instagram Influencer Who Lost 55 Pounds In 4 Months Lists 8 Things She Avoided To Lose Weight

(Credit- Canva)
Weight loss is never a linear process, there are highs and lows, and the process can be grueling. Although exercise is a big part of it, your diet needs to be consistent as well. However, stopping yourself from indulging in many of these unhealthy foods can be difficult. Many people even wonder whether cutting out food can help or not.
To put things in perspective, the online weight loss coach shared her own weight loss journey. Online weight loss coach Amaka has gained a following by sharing her own success story of losing 25 kg in just four months. She achieved this through a mix of methods, including intermittent fasting, strength training, and a focus on what she calls "detox drinks." Her advice is all about making sustainable changes, and she recently put together a simple, easy-to-follow guide on her social media.
8 Foods You Should Avoid & Swap For Weight Loss
The guide isn't just about what foods to avoid, but it also gives a list of smart, delicious swaps you can make instead. Amaka's goal is to help people change their eating habits without feeling like they're missing out.
Sugary Drinks
Avoid: Stay away from sodas, sweetened juices, and high-calorie energy drinks, which contain a lot of sugar without any nutritional value.
Swap: Choose healthier options like water, green tea, or black coffee. You can also try making your own detox water with lemon and chia seeds for a flavorful, low-calorie drink.
Fried Foods
Avoid: Skip fried items like french fries and fried chicken. Frying food adds a large amount of fat and calories, making them a poor choice for your waistline.
Swap: Cook your food using healthier methods. Opt for grilled, air-fried, boiled, or baked meals. This simple change can significantly reduce your calorie intake and still give you great flavor.
White Bread & Refined Carbs
Avoid: Refined carbs like white bread and pasta are quickly digested and can cause sugar spikes. They don't provide the lasting energy you need.
Swap: Switch to whole-grain options, which are rich in fiber and keep you feeling full. Good choices include whole-grain bread, brown rice, oats, or nutritious sweet potatoes.
Processed Snacks
Avoid: Packaged snacks like chips and cookies are often loaded with unhealthy fats, salt, and sugar. They are designed to be addictive and offer very little in terms of nutrition.
Swap: Choose healthier, homemade alternatives. Try making your own air-popped popcorn, or snack on carrot and cucumber sticks with a little peanut butter. Greek yogurt with fruit is another great option.
Ice Cream & Sugary Desserts
Avoid: Most ice creams and desserts are packed with sugar and unhealthy fats, making them a major obstacle to weight loss.
Swap: You can still enjoy a treat by making a healthier version. Blend Greek yogurt with bananas and berries, then freeze it in small cups. You can also have a small piece of dark chocolate to satisfy your sweet cravings.
Heavy Creamy Sauces
Avoid: Be mindful of high-calorie sauces and dressings like mayonnaise. They can quickly add hundreds of calories to an otherwise healthy meal.
Swap: Use low-calorie alternatives. A great swap is a dressing made with mashed avocado, olive oil, and lemon. Greek yogurt also works well as a healthy, low-fat sauce.
Processed Meats
Avoid: Meats like sausages and hotdogs are often high in fat, sodium, and preservatives. They can be very unhealthy for your body and your weight loss goals.
Swap: Go for lean, healthy proteins. Good choices include grilled chicken, fish, turkey, and eggs. These foods provide the protein you need to build muscle and stay full without all the extra calories.
Excess Alcohol
Avoid: Beer, cocktails, and shots are often high in calories and can slow down your metabolism, making it harder to lose weight.
Swap: Drink alcohol in moderation. A small glass of red wine is a better option. You can also try sparkling water with fresh lemon and mint for a refreshing, calorie-free alternative.
Kennedy's MAHA Report Will Not Solve Food Problem In US, Here's What Experts Believe

Credits: Canva
Food policy experts had cautiously hoped that the new health secretary, Robert F. Kennedy Jr., might finally address the nation’s poor diet and reduce reliance on ultraprocessed foods. But many expressed disappointment following Tuesday’s White House report detailing the Make America Healthy Again (MAHA) commission’s plans to tackle childhood chronic disease.
While the report includes promising initiatives such as offering healthier meals in schools and promoting breastfeeding, it remains vague about how these policies would be implemented or funded. The New York Times quoted Kelly Brownell, professor emeritus at Duke University’s Sanford School of Public Policy, saying, “Even if all of the initiatives in the report were put into action, the industry will not be required to change how it manipulates and markets foods that drive poor health in children.”
Contrast With Previous Report
The new report contrasts sharply with MAHA’s first report in May, which focused on identifying drivers of poor health in American children. Jerold Mande, adjunct professor of nutrition at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and former federal food policymaker, described the initial report as “revolutionary in its focus” on ultraprocessed foods and the companies producing them.
“[The new report] seems more in line with food industry interests than the previous one, as if it was written to just maintain the status quo,” Mr. Mande told The New York Times. Ultraprocessed foods were mentioned only a few times, primarily in describing efforts to define them.
Industry Response
Following the report’s release, industry groups largely welcomed its recommendations. The Food Industry Association, representing producers and retailers, issued a statement of support, and the Consumer Brands Association called it “a very ambitious” set of policy recommendations it would help implement, The New York Times reported.
The report also permits schools and federal nutrition programs to offer whole milk instead of just lower-fat options, a change long supported by the dairy industry. Marion Nestle, professor emerita of nutrition and public health at New York University, highlighted this as a key example of industry-favored policy.
Limits of Voluntary Industry Cooperation
So far, Mr. Kennedy has relied on voluntary cooperation from the food industry rather than mandating change. This approach has succeeded in some areas, such as reducing artificial dyes in foods. However, experts note that larger drivers of ultraprocessed food consumption, low cost, heavy marketing, and high fat, sugar, and salt content, are unlikely to be addressed without regulation.
Christina Roberto, director of the Center for Food and Nutrition Policy at the University of Pennsylvania, told The New York Times, “The issues they’re focused on for food and nutrition are really spot on. But the devil is completely in the details.” She added that policies like sugary drink taxes, which have proven effective in other countries, could reduce consumption and improve health outcomes.
Support for Some Proposals, Gaps in Regulation
The report also lists measures that policy experts support, such as expanding research on nutrition, improving hospital and federal program meals, scrutinizing food additives, and closing the longstanding “GRAS loophole” that allows companies to introduce new chemicals without FDA approval.
Yet, experts said the report lacks clarity on how the FDA would increase oversight, particularly amid staffing and funding cuts. Jennifer Pomeranz, associate professor of public health policy at NYU, told The New York Times that even if additives like artificial dyes are removed, foods could remain high in sugar, sodium, and fat.
A draft version obtained by The New York Times in August proposed “ways to lower added sugar and sodium in packaged foods,” a line removed from the final report. “You assume that food industry lobbying got that taken out,” Dr. Nestle said. She also criticized vague language suggesting that companies would police themselves to limit marketing unhealthy foods to children.
Longstanding Challenges Remain
Experts noted a tension between the administration’s stated goal of improving public health and its actions, such as cuts to SNAP benefits and the elimination of large-scale nutrition education programs. Many see the report as similar to past administrations’ efforts: a list of reasonable proposals without strong enforcement mechanisms.
“Administration after administration, independent of the political party, has been unwilling to tackle the food industry,” Dr. Brownell told The New York Times. “As long as the industry isn’t required to change, it won’t.”
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

