- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
FSSAI Retracts Advisory On A1 And A2 Milk Claims: What You Need To Know And How It Affects Your Health

Credits: Canva
On Monday, August 26, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) withdrew its recent advisory directing food businesses to remove 'A1' and 'A2' milk claims from packaging.
FSSAI stated that the advisory was retracted to allow for further consultations with stakeholders. As a result, food business operators (FBOs) can continue selling and marketing products with 'A1' and 'A2' milk claims.
What Is A1 and A2 Milk?
The main difference between the A1 and A2 milk is their protein content. Casein is the largest group of protein found in the milk which makes up for about 80% of its total protein content. Beta-casein protein is the second most prevalent that exists.
A1 beta-casein: This is the milk from breeds of cows that originate in northern Europe. The breeds include Holstein, Friesian, Ayrshire, and British Shorthorn.
A2 beta-casein: This is found in the breeds that trace their origin in the Channel Islands and southern France. The breeds include Guernsey, Jersey, Charolais, and Limousin cows.
While regular milk contains both A1 and A2 beta-casein, A2 milk only contains the A2 beta-casein.
Why Does It Matter?
Some studies suggest that A1 beta-casein maybe harmful, which is found in regular milk.
When A1 beta-casein is digested, an opioid peptide called the beta-casomorphin-7 (BCM-7) is released, which may be linked to Type 1 diabetes, heart diseases, infant death, autism and digestive problems, as reports Healthline.
However, there is no definite proof of to what extent does BCM-7 get absorbed in healthy adults' blood, but a few tests indicate the presence of BCM-7 in infants.
Multiple studies suggest that consuming A1 milk during childhood may increase the risk of developing type 1 diabetes. However, these findings are based on observational research, meaning they can only show an association, not prove that A1 beta-casein directly causes type 1 diabetes.
Animal studies on the effects of A1 beta-casein have shown mixed results, with some indicating no difference between A1 and A2 beta-casein, while others report protective or adverse effects on type 1 diabetes.
To date, no clinical trials in humans have examined the impact of A1 beta-casein on type 1 diabetes.
Heart Health
In a rabbit study, A1 beta-casein was found to increase fat buildup in injured blood vessels, whereas A2 beta-casein resulted in much lower fat accumulation. Excessive fat buildup can potentially block blood vessels and contribute to heart disease, although the relevance of these findings to humans is still debated.
To date, two studies have examined how A1 milk affects heart disease risk factors in humans. In one trial involving 15 adults at high risk of heart disease, no significant negative effects were noted. Both A1 and A2 beta-casein had similar impacts on blood vessel function, blood pressure, blood fats, and inflammatory markers.
Another study found no significant differences in the effects of A1 and A2 casein on blood cholesterol.
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
A 2011 study called The exogenous opioid peptides and DPPIC serum activity in infants with apnoea expressed as apparent life threatening events (ALTE) found that high levels of BCM-7 in the blood of infants temporarily stopped breathing during their sleep. This is called sleep apnea and can lead to Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS).
Autism
Autism is a mental condition marked by difficulties in social interaction and repetitive behaviours.
Some researchers think that peptides like BCM-7 might be linked to autism, but studies haven't fully supported these ideas.
Another study suggests that cow’s milk might worsen behavioural symptoms in children with autism, but other research found no effect on behaviour. No studies have specifically looked at how A1 and A2 milk affect autism symptoms.
Digestive Health
Lactose intolerance is the inability to fully digest milk sugar (lactose), leading to bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
Both A1 and A2 milk contain the same amount of lactose, but some people find A2 milk causes less bloating. Studies suggest that other milk components, not just lactose, might cause digestive discomfort.
One study showed that A1 milk caused softer stools compared to A2 milk in some people, while another study found A2 milk resulted in less digestive discomfort after meals.
Telangana Flags Children’s Syrup After Toxic Adulteration Found: What Is Ethylene Glycol Poisoning?

Credits: Canva
The Telangana Drugs Control Administration on Saturday released an urgent advisory asking the public to immediately stop using Almont-Kid Syrup, a medicine commonly given to children for allergies, hay fever, and asthma, after it was allegedly found to be contaminated with Ethylene Glycol (EG), a highly poisonous chemical.
In an official notice, the DCA said it received an alert from the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), East Zone, Kolkata. A laboratory analysis flagged the syrup, which contains Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride and Montelukast Sodium, as adulterated.
Telangana Issues Notice For Children’s Syrup After Toxic Adulteration Found
The Telangana Drugs Control Administration (DCA) issued a warning advising people to stop using Almont-Kid Syrup after tests allegedly found Ethylene Glycol (EG) in the product. The syrup is commonly prescribed to children to relieve allergy-related symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, itching, swelling, nasal congestion, and watery eyes. It is also used to manage asthma and certain skin allergies.
According to the DCA notice, the alert was triggered by a communication from the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), East Zone, Kolkata, following a lab report that declared the Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride and Montelukast Sodium Syrup as adulterated.
The DCA stated, “In light of the above, the public is hereby strongly advised to immediately stop the use of the above syrup, if in possession, and report the same to the nearest Drugs Control Authority without delay.” Officials have instructed Drugs Inspectors and Assistant Directors across Telangana to immediately inform retailers, wholesalers, distributors, and hospitals to freeze any available stock of the affected batch and ensure it is not sold or dispensed under any circumstances. The DCA has also urged members of the public to report if they have the syrup and to avoid using it altogether.
What Is Ethylene Glycol?
Ethylene glycol is a colourless, odourless, and low-volatility liquid, according to Science Direct. It has a low freezing point and a high boiling point, which is why it is widely used in antifreeze and de-icing products. Ethylene glycol has a sweet taste, which increases the risk of accidental ingestion, especially among children. Experts warn that untreated ingestion of ethylene glycol can result in severe illness and can be fatal, as per Cleveland Clinic.
What Is Ethylene Glycol Poisoning?
Ethylene glycol poisoning happens when the substance is swallowed. Once ingested, it is rapidly absorbed into the body, with peak levels usually reached within one to two hours. In the first 30 minutes to 12 hours, symptoms can resemble alcohol intoxication and may include dizziness, euphoria, slurred speech, nausea, vomiting, and problems with coordination. In severe cases, this stage can progress to seizures or coma due to the chemical’s direct toxic effects on the brain.
During the next phase, typically between 12 and 36 hours, the body breaks down ethylene glycol into harmful acids such as glycolic acid. This leads to metabolic acidosis, fast heart rate, rapid breathing, low calcium levels, muscle spasms, and possible heart failure. Without timely medical treatment, this stage can be life-threatening. Between 36 and 72 hours after ingestion, kidney injury may develop as oxalate crystals form, potentially causing acute kidney failure, reduced or absent urine output, brain swelling, and long-term organ damage.
Impact Of Ethylene Glycol Poisoning
Ethylene glycol poisoning can cause serious and potentially fatal complications because its toxic byproducts affect multiple organs. Some of the key impacts, as per Mayo Clinic, include:
Brain and Nervous System Damage: In the early phase, the toxin can cause confusion similar to intoxication, seizures, and coma due to its direct effect on the nervous system. Later on, acid buildup can lead to brain swelling and encephalopathy. If untreated, this may result in permanent brain damage, stroke-like symptoms, or death.
Heart and Lung Failure: Glycolic acid can trigger severe metabolic acidosis, leading to rapid or irregular heartbeats, dangerously high or low blood pressure, and heart failure. This may progress to fluid buildup in the lungs, breathing failure with deep and rapid breaths, and eventual circulatory collapse.
Kidney Damage: The formation of oxalate crystals in the kidneys can cause acute tubular necrosis, flank pain, blood in the urine, and reduced or stopped urine production. In some cases, acute kidney injury progresses to complete kidney failure, which may be permanent and require long-term dialysis or a transplant.
Multi-Organ Collapse: Ethylene glycol disrupts normal cellular function, leading to low calcium levels, muscle spasms, tremors, and lactic acidosis. In severe and untreated cases, this can result in shock, failure of multiple organs, and death.
Long-Term Consequences: People who survive ethylene glycol poisoning may experience lasting health problems such as chronic kidney disease, nerve damage, or heart complications. Outcomes are significantly worse when treatment is delayed or when the patient develops seizures, coma, or severe acidosis.
Influenza Flu Symptoms May Be Changing As A New Variant Spreads: What To Expect

Credits: Canva
A fast-spreading new flu variant driving a sharp rise in infections across the state is bringing with it symptoms that differ from what many people usually associate with influenza.
With flu activity now classified as “very high” in Illinois, health experts say a mutated and highly contagious strain known as subclade K is changing how the illness shows up, particularly when it comes to fever patterns. One of the biggest differences doctors are seeing is how intense and long-lasting fevers have become, especially among children.
“There’s more fever with the flu this year than people are used to,” said Dr. Mark Loafman, chair of Family and Community Medicine at Cook County Health, speaking to NBC Chicago. “The fever can last five to seven days, and that’s concerning. You feel sick, you don’t feel like you’re improving, and that can be worrying.”
Adding to the concern, Dr. Juanita Mora, national spokesperson for the American Lung Association, as per NBC News, said some patients are finding that common fever-reducing medicines such as Tylenol or Motrin are not working as effectively. “This strain is causing very high fevers,” Mora said. “There’s also a severe cough that just doesn’t go away, a lot of phlegm, vomiting, diarrhoea, and significant joint and muscle pain.”
Influenza Flu Symptoms To Watch For
Vomiting has never been among the most typical flu symptoms, though it does occur more often in children. What doctors are now noticing with this strain is an increase in gastrointestinal symptoms among adults as well.
“Kids with the flu often experience nausea or vomiting,” Loafman explained. “Adults usually don’t as much, but we are hearing more reports of GI symptoms in adults who have this subclade K strain.” Because of this, he said flu should not be ruled out just because stomach symptoms are present.
“If you have GI issues along with body aches, fever, and respiratory symptoms, flu is still very much a possibility,” he said, adding that at-home flu tests can be useful if someone suspects they are infected.
Warnings have already been issued by the Illinois Department of Public Health and several county health departments as flu-related hospital admissions and positive test results continue to climb.
According to the latest state update released Monday, flu activity has reached “very high” levels, the most severe category used by the CDC to track respiratory illness trends.
Health officials say most emergency room visits and hospital admissions related to respiratory illness are currently being driven by flu cases.
Common Flu Symptoms To Know
Flu symptoms typically appear one to four days after exposure, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
The CDC lists the following common symptoms:
- Fever or feeling feverish, along with chills
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Runny or blocked nose
- Muscle or body aches
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Vomiting and diarrhoea, which are more common in children than adults
Not everyone with the flu will develop a fever. However, health officials note that gastrointestinal symptoms are being reported more often in adults with the new strain.
Influenza Flu Warning Signs To Watch For
Because this variant is linked to higher and longer-lasting fevers, Mora said it is crucial to recognise when medical care is needed.
“High fevers that don’t come down are one warning sign,” she said. “Another is trouble breathing, including wheezing, chest muscle use, or a cough that won’t stop. And dehydration is a major concern, especially if someone is barely eating or drinking.”
The CDC outlines different warning signs for children and adults.
In children:
- Rapid or laboured breathing
- Bluish lips or face
- Ribs pulling in with each breath
- Chest pain
- Severe muscle pain or refusal to walk
- Signs of dehydration such as no urine for eight hours, dry mouth, or no tears when crying
- Lack of alertness or interaction
- Seizures
- Fever above 104°F that does not respond to medication
- Any fever in infants under 12 weeks
- Symptoms that improve and then worsen
- Worsening of existing medical conditions
In adults:
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Ongoing chest or abdominal pain
- Dizziness, confusion, or difficulty waking
- Seizures
- Little or no urination
- Severe muscle pain
- Extreme weakness or unsteadiness
- Symptoms that return or worsen after improving
- Worsening of chronic illnesses
How Long Is Flu Contagious?
According to the CDC, people can spread the flu starting about one day before symptoms appear and up to seven days afterward. Most people are most contagious around three days into the illness. Young children and those with weakened immune systems may remain contagious longer.
“It’s usually about five to seven days from when symptoms start before people stop shedding high levels of the virus,” Loafman said. “Ten days is very cautious, but not always necessary.”
He advised masking around vulnerable people during the first week, practicing good hand hygiene, and staying home whenever possible. “If you can stay in, stay home,” he said, as per NBC News.
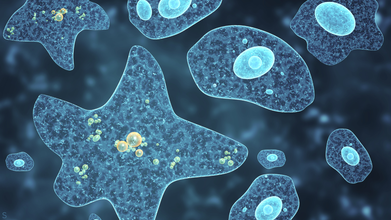
The Invisible “Brain-Eating” Bacteria Lurking in Water Pipes That Can Cause Deadly Infections
Credit: Canva
Environmental and public health scientists have begun warning against the dangers of having free living amoeba in water systems that are capable of triggering severe diseases in humans.
In a recent perspective article published in Biocontaminant, the researchers noted that climate change, deteriorating water infrastructure and limited systems for monitoring and detection are the key factors that have allowed these pathogens to spread and persist.
Corresponding author Longfei Shu of Sun Yat sen University explained: "What makes these organisms particularly dangerous is their ability to survive conditions that kill many other microbes.
"They can tolerate high temperatures, strong disinfectants like chlorine and even live inside water distribution systems that people assume are safe."
The scientists also emphasized that not only can amoebae spread illnesses on its own, it can also act as hidden carriers for other harmful microbes.
By sheltering bacteria and viruses inside their cells, amoeba these unicelled organisms protect these pathogens from disinfection and help them persist and spread in drinking water systems. This so-called Trojan horse effect may also contribute to the spread of antibiotic resistance among humans.
How Dangerous Is Amoeba?
Amoeba are single-celled organisms that naturally live in soil and water. Most species do not cause harm yet some can prove to be fatal.
Some of the diseases caused by this kind of bacteria include Amebiasis (Amoebic Dysentery), an intestinal infection by Entamoeba histolytica, causing diarrhea, cramps and potential liver abscesses as well as Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM) from Naegleria fowleri, a rare but nearly always fatal brain infection from contaminated water entering the nose.
Effects of amoeba-caused infections range from intestinal issues (liver abscesses, anemia, peritonitis) to severe neurological damage (coma, seizures, death) from brain-eating types, with Acanthamoeba causing eye infections (keratitis).
Experts recommend thoroughly washing your hands after toilet use and before handling food, drinking clean water especially in unsanitary conditions and avoiding getting water up your nose in warm freshwater to prevent such infections.
The Indore Crisis
This comes days after the recent Indore sewage water controversy which has claimed the lives 10 people and left over 1,400 people hospitalized, according to Indore Mayor Pushyamitra Bhargava.
However, locals claim that the outbreak has instead caused the death of 17 residents, including a six-month-child. The situation has also left Parvati Bai, 67, with kidney failure, a brain stroke and symptoms of Guillain-Barré Syndrome, or GBS.
GBS is a rare condition where your immune system attacks the nervous system and can cause paralysis as well as death, in certain cases.
The outbreak occurred due to lapses in civic infrastructure. Investigation revealed that a toilet constructed directly above a main drinking pipeline near a police outpost, without a mandatory safety tank resulted in the sewage mixing with drinking water.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

