- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
World Drug Day 2025: Why Is It Important For Us To Observe This Day?

Credits: Canva
World Drug Day is marked on June 26 every year. Also known as the International Day against Drug Abuse and Illicit Trafficking, this day aims to strengthen action and cooperation in achieving a world free of drugs, notes the United Nations.
History of World Drug Day
It was on December 7, 1987, when by the resolution 42/112. the General Assembly decided to observe 26 June as the International Day against Drug Abuse and Illicit Trafficking to achieve a society free of drug abuse.
World Drug Day 2025 Theme
This year's theme is "The Evidence is Clear; Invest in Prevention." This theme highlights the urgent need to invest in preventative measures to address the world's drug problem. It also aims to create a long-lasting resilience against drug abuse.
ALSO READ: RFK Jr. Opens Up About Heroin Addiction and Calls for Focus on Prevention
Importance of World Drug Day
Drug abuse is a global challenge and harms individual silently. It is often the reason why families break and communities weaken. The impact goes beyond addiction, causing a lasting physical, mental, and social damage. Furthermore, ATS, also known as the Amphetamine-Type Stimulants are synthetic drugs that harm the brain, heart, and nervous system.
As per the 2024 report by UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), number of people who use drugs has risen to 292 million in 2022, a 20% increase over the 10 years. Cannabin remains the most widely used drug worldwide, with an estimate of 228 million users. It is followed by opioids with 60 million users, ATM with 30 million users, cocaine with 23 million users, and ecstasy with 20 million users.
READ: What Are The Most Abused Drugs In The US?
The report notes that nitazenes, which is a group of synthetic opioids which can be even more potent than fentanyl, have recently emerged in several high-income countries, resulting in an increase in overdose deaths.
Though an estimated 64 million people worldwide suffer from drug use disorders, only one in 11 is in treatment. Women receive less access to treatment than men, with only one in 18 women with drug use disorders in treatment versus one in seven men.
These numbers show why is it important to observe World Drug Day, so a society free of drug abuse can be achieved.
Drug Impact On Health
As per the notification released by Government of India on the International Day Against Drug Abuse and Illicit Trafficking 2025, here are the health issues that are caused by various drugs:
- Methamphetamine (Meth): A crystal-like drug that severely damages the brain and heart.
- Cocaine: A white powder that can cause heart attacks and strong addiction.
- Mephedrone: A party drug that leads to anxiety, confusion and heart issues.
- Hashish: Made from cannabis, it affects memory and mental health.
As per the National Institute on Drug Abuse's publication titled, Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction, people with addiction often have one or more associated health issues, which could include lung or heart disease, stroke, cancer, or mental health conditions.
Furthermore, use of methamphetamine can cause severe dental problems, which is also known as meth mouth. The study notes, "in addition, some drugs, such as inhalants, may damage or destroy nerve cells, either in the brain or the peripheral nervous system (the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord)."
Use of drugs can also increase the risk of contracting infections. The study notes: "HIV and hepatitis C (a serious liver disease) can occur from sharing injection equipment or from unsafe practices such as condom-less sex.40,41 Infection of the heart and its valves (endocarditis) and skin infection (cellulitis) can occur after exposure to bacteria by injection drug use."
READ: Liam Payne Investigation: How Pink Cocaine Affects You?
Drugs can also cause mental illness and increase the symptoms of anxiety, depression, or even schizophrenia,, as it can trigger specific vulnerabilities. It can also impact pregnant or breastfeeding mother and her baby could go into withdrawal after it's born. This is called neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS).
This year, not just with the theme, but with the campaign, "Break the cycle. #StopOrganizedCrime", the aim is to highlight the long-term action to break the cycle of drug abuse and its illicit trafficking by addressing root causes, investing in prevention, and building stronger health, education, and social systems.
READ MORE: National Anti-Drug Addiction Day 2024: Reintegrating In Society After Rehab
Measles Outbreak Confirmed In Two South Carolina College
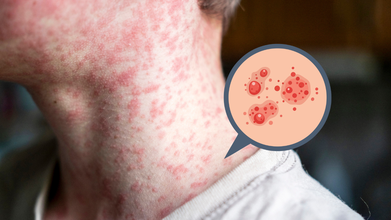
Credits: Canva/iStock
Measles reached two South Carolina colleges, Anderson University and Clemson University. On Monday, Anderson University confirmed that one of the studies was diagnosed with measles and may have exposed others with the same. The student is no longer on campus. Authorities have asked anyone who think are exposed to stay home and not show up in class, work, or in public areas. The students are also asked to call Thrive Wellness Center at 864-622-6978 before visiting in person to avoid spread as measles is highly contagious.
Clemson University whereas, over the weekend, announced the South Carolina Department of Public Health of the case. The person infected is in quarantine.
As per the data from the Student Health Services, nearly 98% of campus students have provided proof of immunity, said the university.
What Is Measles?
Measles, also known as rubeola, is a highly contagious viral illness that typically causes fever, cough, a runny nose, red and watery eyes, and a distinctive red, blotchy rash that usually begins on the face and spreads downward. The virus spreads through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes and can lead to serious complications such as pneumonia or brain inflammation. Despite its severity, measles is preventable through a safe and effective vaccine, as per the Mayo Clinic.
Read: Kentucky Reports First Positive Measles Case of 2026: Confirmed Health Officials
How Contagious Is Measles?
Measles is among the most contagious diseases in the world. The virus spreads through airborne droplets that can linger in the air or on surfaces for hours. Up to 90% of unvaccinated people who are exposed to measles will become infected. A single infected person can pass the virus to an estimated 12 to 18 others through close contact or shared spaces. People can transmit the virus days before symptoms become obvious and continue spreading it after the rash appears, according to the World Health Organization.
How Long Is Someone Contagious With Measles?
Someone infected with measles can spread the virus from four days before the rash develops to four days after it appears. The virus spreads so efficiently that about 90% of people who are unvaccinated or have never had measles will become infected after being exposed.
In November, Canada lost its measles elimination status following a significant outbreak, according to the Pan American Health Organization, which works closely with the World Health Organization.
“It’s important to say that all the other 34 countries in the region, they keep their certification as measles-free,” said PAHO/WHO Director Dr. Jarbas Barbosa at the time, as per NPR News.
U.S. health officials have also warned that genetic links between outbreaks in different states suggest continued spread.
“The trajectory that we’re looking at now is that we do anticipate more cases well into January,” Bell said. “What that means for us nationally in terms of how they are defining our designation in this country as having eliminated measles is unclear.”
Also Read: Measles Symptoms Explained: Can The Infection Be Deadly?
Measles Symptoms Develop In Three Stages
According to the Mayo Clinic, measles symptoms usually appear in three distinct stages.
Stage 1: Incubation period (10 to 14 days)
During this phase, there are typically no noticeable or warning symptoms.
Stage 2: Early symptoms begin
Symptoms at this stage may include a dry cough, fever, red and inflamed eyes known as conjunctivitis, a runny nose, and a sore throat.
Stage 3: Acute illness and rash
“In the third stage, a rash begins to develop, usually starting on the face. Small white spots called Koplik spots may appear inside the mouth two to three days after symptoms first appear,” the Mayo Clinic explains. “The measles rash typically shows up three to five days after the initial symptoms.
“Over the following days, the rash spreads to the arms, torso, and legs. Alongside the rash, fever often rises rapidly and can exceed 105 degrees Fahrenheit,” the guidance continues. “Eventually, the fever subsides, and the rash fades from the body starting at the head and moving downward.”
Is Measles Deadly?
Yes, measles can be deadly and carries a significant risk of death, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Measles can lead to serious health complications, including pneumonia, inflammation of the brain known as encephalitis, and death,” the CDC states. “Between one and three out of every 1,000 people infected with measles will die. Around one in five people with measles will require hospital care, and one in every 20 children with measles develops pneumonia, which is the leading cause of measles-related deaths in young children.
“One in every 1,000 people with measles will experience brain swelling, which can result in permanent brain damage.”
India Loses A Woman To Breast Cancer Every Eight Minutes: Novartis’ ‘Take Charge’ Campaign Aims To Change That

Credits: Canva
Breast cancer has quietly become one of India’s most pressing public health challenges. Today, it is the most commonly diagnosed cancer among Indian women and a leading cause of cancer-related deaths.
Data from the Global Cancer Observatory shows that nearly 1.9 lakh women are diagnosed with breast cancer in India each year. This works out to one new case every four minutes. The death toll is equally worrying. On average, a woman in India dies of breast cancer every eight minutes, highlighting how urgently the country needs stronger awareness, early diagnosis, and sustained care.
One factor that sets India apart is the age at which women are affected. Almost half of all breast cancer patients in the country are younger than 45. This is a much higher proportion than seen in many Western nations, where the disease is usually detected later in life.
Breast Cancer: A Rising Burden Across The Country
Cancer surveillance data from GLOBOCAN and Indian registries under the Indian Council of Medical Research point to a steady rise in breast cancer cases. Rapid urbanisation, changing lifestyles, delayed pregnancies, shorter periods of breastfeeding, rising obesity, and limited screening practices have all played a role.
Late diagnosis continues to be one of the biggest challenges. Many women seek medical help only when the disease has progressed to advanced stages, making treatment more difficult and outcomes less certain. Fear, social stigma, lack of awareness, and limited access to screening services, especially in rural and semi-urban areas, often contribute to these delays.
For some women, the risk of recurrence can be significant, depending on the type and stage of cancer. Living with this uncertainty takes a lasting toll on mental and emotional wellbeing.
Novartis 'Take Charge' Campaign Focuses On Life Beyond Diagnosis
To address these gaps, Novartis has launched the ‘Take Charge’ campaign in collaboration with Times Network. The initiative aims to move the conversation beyond diagnosis and medication, encouraging women and their families to play an active role in decisions about care, recovery, and quality of life.
Speaking at the Times Network India Health Summit and Awards 2025, Amitabh Dubey, Country President and Managing Director of Novartis India, underlined that effective cancer care goes far beyond medicines alone. He spoke about the need for personalised treatment, open conversations between doctors and patients, and long-term support throughout the cancer journey.
According to Amitabh Dubey, advances in medical science have changed the way many cancers are managed. In breast cancer, better imaging, improved diagnostics, genomics, and targeted therapies now allow doctors to tailor treatment to the biology of each patient rather than relying on a uniform approach.
'Take Charge' By Novartis Highlights Need For Early Awareness
Awareness remains a central pillar of the ‘Take Charge’ initiative. Many women hesitate to speak openly about breast health or postpone seeing a doctor even after noticing symptoms. Encouraging routine self-examinations, timely screenings, and honest conversations about warning signs is especially important for younger women, who may not believe they are at risk.
The campaign also places strong emphasis on caregivers and families. Emotional support, access to reliable information, and timely medical advice can make a meaningful difference to both treatment outcomes and recovery.
Breast Cancer Awareness: Closing Gaps In Access And Affordability
Although government schemes such as Ayushman Bharat and various state cancer programmes have improved access to care, health insurance coverage in India remains limited, reaching only about 38 percent of the population. As a result, newer and more advanced treatments are still beyond the reach of many patients.
Novartis has been working with government agencies and local health systems to improve referral pathways, strengthen early detection efforts, and train frontline health workers. Community-based initiatives involving ASHA workers, awareness drives, and structured referrals aim to ensure that women with early symptoms reach appropriate care without unnecessary delays.
Breast cancer does not have to signal the end of a woman’s life or identity. With early diagnosis, personalised treatment, and continued support, many women go on to live full and meaningful lives. Campaigns like Take Charge seek to reinforce this message and remind women that they can remain active decision-makers in their own health journeys.
As Amitabh Dubey noted at the launch, taking charge is not only about fighting disease. It is about having the knowledge, confidence, and support to ask the right questions, make informed choices, and live well beyond cancer.
Schizophrenia And Bipolar Disorder Have The Same Genetic Links, Study Finds

Credit: Canva
Schizophrenia (SCZ), bipolar disorder (BD) and major depressive disorder may share the same genetic roots, a Nature study shows.
While experts have long classified each of these mental disorders as individual illnesses with their own causes, researchers from across China have discovered that these three diseases share about 70 percent common genetic and environmental risk factors.
Schizophrenia is a severe, chronic brain disorder that can lead psychosis, hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking and reduced emotional expression. It can affect how a person's thinks, feels and behaves, making it hard to distinguish reality.
While bipolar disorder is a chronic mental illness which causes extreme mood swings, from emotional highs (mania/hypomania) to lows (depression), affecting the brain's energy, activity and focus levels.
On the other hand, major depressive disorder or clinical depression, is a serious mood disorder that causes persistent sadness and loss of interest in a person. It can affect feelings, thoughts and daily activities and can be identified by symptoms such as low energy, sleep/appetite changes, guilt, concentration issues and thoughts of death.
What Did The Study Find?
The Chinese researchers studied genetic data from more than one million people with mental health diagnoses and five million people without them.Using advanced techniques, they identified 238 genetic variants that raise risk across multiple disorders and showed that five major genetic patterns explain most of the differences between people with and without mental illness.
Read More: Study Shows Depression Can Accelerate The Onset Of Chronic Illnesses
Based on these genetic patterns, the disorders clustered into five broad groups: internalizing conditions such as depression, anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder; neurodevelopmental conditions including autism and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder; substance use disorders; compulsive conditions such as obsessive-compulsive disorder and anorexia and lastly, a fifth group that included bipolar disorder and schizophrenia.
The findings explain why many individuals are diagnosed with more than one mental health condition as many genes affect multiple brain pathways. This indicates that the same genetic changes can lead to different disorders depending on other biological and environmental factors.
Can The Same Treatment Plan Be Used For These Illnesses?
Even though medications such as antidepressants are useful in treating multiple mental illnesses including depression, anxiety and PTSD, the researchers concluded that more research is needed to understand the biology behind the genetic factors to understand the links between the disease.
One of the study’s authors compared the current system to diagnosing a patient with separate illnesses for a cough, sore throat and runny nose instead of recognizing a single underlying infection.
Nearly one in eight people globally, around 970 million individuals, were living with a mental disorder in 2021, with anxiety and depression being the most common globally.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

