- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
- Web Stories
Americans Cutting Back On Caffeine With More Coffee Than Tea

(Credit-Canva)
When it comes to morning routines, people do their own thing, whether it is waking up, exercising and eating a wholesome breakfast or waking up, washing and wearing fresh clothes and immediately going for coffee. Many coffee drinkers say that they simply cannot start their day without a fresh cup 'a joe, and not having coffee eventually leads them to have a headache or feeling groggy. While you may think that having coffee is the reason why caffeine intake has risen in the US, there is a catch to it. Less and less people are drinking coffee in the past few years, but the few people who have continued to drink it have increased their caffeine intake by a lot!
The latest research shows that fewer Americans are drinking the usual caffeinated drinks like coffee, soda, and tea but, those who still enjoy these drinks are choosing stronger versions, meaning they're getting more caffeine in each serving. So, even though fewer people are drinking these beverages, the total amount of caffeine Americans are consuming is going up. Even with this increase, the average person's caffeine intake is still below the safe limit of 400 milligrams per day. Researchers say the market for caffeinated drinks has changed a lot, and they need to keep track of these changes to understand how it affects people's health.
A recent study, published in the Food and Chemical Toxicology, involving over 49,000 American adults reveals a significant shift in caffeine consumption patterns. Coffee has become the most popular way for Americans to get their caffeine fix. Now, 70% of all caffeine consumed comes from coffee. This is a big jump from ten years ago. On the other hand, sodas are losing their popularity as a caffeine source. Only 15% of caffeine now comes from sodas, which is a big drop. Tea is also seeing a decline. Fewer people are drinking tea overall. However, those who still drink tea are drinking more of it, almost doubling their caffeine intake from tea. This means that while fewer people are drinking tea, those who do are drinking stronger brews or more cups. It's clear that people's choices for caffeinated drinks are shifting.
Study author Diane Mitchell of the Institute for Advancing Health through Agriculture, Texas A&M AgriLife, said in a news release, “We are all aware that the caffeinated beverage market has changed dramatically over the past 10 years, yet no comparable, comprehensive caffeine intake data have been published in recent years".
Do Energy Drinks Make The List?
While many people may not know this, energy drinks are a notorious source of caffeine, and many people do not even know that many of their favorite drinks contain an a lot of caffeine. Energy drinks are becoming a more common way for people to get their caffeine. These drinks, which weren't as popular a decade ago, now account for 6% of total caffeine intake. This increase is because there are now many more energy drink brands available. The number of brands has almost doubled. This gives people more choices, and many are opting for these high-caffeine beverages. Energy drinks often contain a lot of caffeine in a small can or bottle, which can quickly boost energy levels. The growing number of energy drink options is changing how people consume caffeine.
“With a constantly evolving market of caffeinated beverages and the potential impact it has on beverage consumption patterns, continued monitoring of caffeine intakes is warranted," the authors concluded.
What is the Recommended Healthy Caffeine Intake?
Even though people are changing how they consume caffeine, the average intake is still below the recommended safe limit. Health experts recommend that adults consume no more than 400 milligrams of caffeine per day. This is roughly equal to two or three regular cups of coffee. While the types of drinks people choose are changing, and some are opting for stronger options, overall consumption remains within a safe range. Researchers believe it's important to keep monitoring caffeine intake because the market for caffeinated drinks is constantly changing. They want to make sure that people understand how these changes might affect their health.
World Organ Transplant Day: From 3D Printing To Lab-Grown Organs, Transplant Breakthroughs Are Here
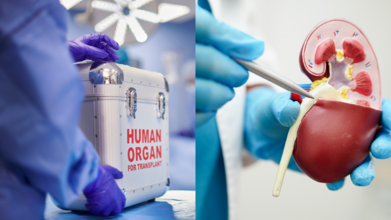
On World Organ Transplant Day, we usually hear about the urgent need for more donors, the lifesaving power of a transplant, and how one person’s decision can save up to eight lives. That is all still true and still critical but here is the twist: while the waiting lists grow, so do the technologies that might one day make them shorter or even unnecessary.
The future of organ transplantation is not just beating in donor hearts anymore; it is also whirring in lab incubators, spinning in magnetic rotors, and taking shape layer by layer on 3D bioprinters.
Despite decades of successful surgeries, the biggest roadblock in transplantation remains supply. Dr Bipin Chevale, CEO of Gleneagles Hospital Mumbai, explains, “There is still a persistent disparity between organ supply and demand. In India, thousands remain on waiting lists, and many lose their lives before a suitable organ becomes available.”
The reasons are a blend of low awareness, cultural taboos, and plain logistical hurdles. In 2023–24, nearly 50,000 Indians were waiting for organ replacement, according to the National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO). Globally, the US alone has more than 100,000 patients on transplant lists, with 13 lives lost every day while waiting.
Medical science, however, has been busy building backup plans. From 3D printing body parts to developing fully artificial organs, scientists are inching closer to a future where “no donor” does not mean “no hope”.
The Rise of 3D Bioprinting
Specialised 3D bioprinters can lay down living cells in precise patterns to create tissue that looks and behaves like the real thing.
Dr Varun Mittal, Head of Kidney Transplant at Artemis Hospitals, says researchers have “made great strides in printing living tissues and complicated networks of blood vessels”, something previously thought impossible. Techniques like Co-SWIFT create branching vessels inside heart tissue, while 3D ice printing uses water and gelatine to make smooth vessel templates.
While we are not yet popping out fully functional hearts or kidneys from printers for surgical use, these technologies are already valuable for training surgeons, testing drugs, and inching toward patient-specific implants. The idea is to design an organ to match a patient’s exact size, shape, and immune profile, dramatically lowering the risk of rejection.
Artificial Organs: Machines That Act Human
If printing an organ from scratch is the long game, artificial organs are the fast-forward button. These mechanical or bioengineered devices can take over the job of a failing organ, sometimes temporarily, sometimes for months or years.
One striking example is the BiVACOR artificial heart. It does not beat; it spins. A magnetic rotor pumps blood continuously, acting as a bridge until a donor heart is found. Dr Mittal points out that some patients have survived for months with the device, staying mobile and alert while awaiting surgery.
Similarly, researchers are developing implantable bioartificial kidneys that could filter blood and house living kidney cells without the need for dialysis or lifelong immunosuppressants. Wearable dialysis units are also in the works, aimed at freeing patients from hours tethered to clinic machines.
The Lung and Liver Challenge
Some of the boldest experiments are happening with lungs and livers, two of the trickiest organs to replace due to their complexity.
Dr Yasir Rizvi, Director of Nephrology and Kidney Transplant at Dharamshila Narayana Superspeciality Hospital, points to a landmark in lung research: a 3D-printed human-scale scaffold containing about 4,000 km of capillaries across 44 trillion voxels. In animal studies, it has already exchanged gases like a natural lung.
For the liver, bioprinting and bioengineering efforts aim to create functional tissue that can sustain patients until a full transplant is possible or even act as a permanent fix in the future.
The Benefits Are Already Here
We may still be a few years from printing a fully functional, transplant-ready heart, but artificial organ technology is already improving lives. Pacemakers, cochlear implants, and ventricular assist devices, these are all proof that machinery and biology can coexist in the human body.
Artificial organs have the potential to:
- Reduce rejection by using a patient’s own cells
- Cut waiting times dramatically
- Lower long-term medical costs by reducing hospital stays
- Give access to treatment in regions where donor organs are scarce
As Dr Chevale says, these breakthroughs are only half the story. “Their success will also depend on increasing awareness about organ donation, busting myths, and encouraging more people to pledge their organs.”
The Ethical Road Ahead
Of course, the march toward lab-grown and artificial organs comes with big ethical questions. Who gets them first? Will they be affordable or only for the wealthy? How do we ensure safety in devices meant to live inside fragile bodies?
Dr Rizvi believes that with “careful regulation, transparent trials and patient-centred design, these innovations can turn prototypes into standard care”. In India, collaborations between AIIMS, IITs, and bio-technical start-ups are already laying the groundwork, with the hope of producing affordable devices for both domestic and global use within a decade.
A Future Worth Donating To
Even if the day comes when a printer can make you a brand-new kidney, organ donation will still matter. Research organs, temporary implants, and hybrid solutions will always benefit from donated tissue to validate safety and function.
The future of transplantation is no longer just a race against the clock for a donor organ, it is also a race to develop, print, and perfect replacements that can save lives anywhere, anytime.
Experts Weigh In On Why White-Collar Workers And Women Are More At Bladder Health Risk
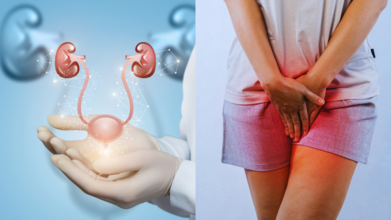
In the modern workplace, we have normalised the idea that meetings, presentations, and overflowing inboxes are perfectly good reasons to ignore the most basic biological urge, that is, the need to pee. This is not just mildly uncomfortable; it is slowly harming bladder health. Over-retention of urination has detrimental effects on the health of the bladder. The bladder is a muscle that should only distend or shorten so far. When we repeatedly hold it in, the bladder stretches beyond its usual limit, weakening over time and losing its sensitivity to fullness. This results in urinary retention, incomplete emptying, or even loss of bladder control in severe cases.
The Not-So-Harmless Habit
It is tempting to think that pushing back bathroom breaks is just an occasional inconvenience, but in reality, this behaviour is linked to much more than discomfort. Dr Nasreen Gite, Consultant Urologist at K J Somaiya Hospital and Research Centre, explains that prolonged retention “gives bacteria in the urinary tract time to multiply”, raising the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs). Women are especially vulnerable due to their shorter urethras, making it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder. Over time, repeated overdistension can also cause urge incontinence or overactive bladder, that sudden, overwhelming need to go, often followed by leakage.
While continuously holding off on going to the bathroom overstretches bladder muscles and makes the bladder more sensitive and vulnerable to overactive bladder symptoms, it may also strain the pelvic floor muscles, affecting bladder control.
The Desk Job Dilemma
If you are thinking, “Well, I work in an office; it is not like I am operating heavy machinery in the middle of a field,” you might be more at risk than you think. Reportedly, this is increasingly a white-collar problem. Desk workers are often glued to their seats for long stretches, and corporate cultures can be surprisingly unsympathetic to frequent breaks.
Women face an extra layer of complexity. Beyond anatomy, sociocultural factors come into play, from the lack of clean workplace toilets to the subtle pressure of “powering through” without appearing weak. Dr Gite points out, “Women are anatomically more prone to bladder infections, and socialisation often leads them to ‘hold it in’ automatically.”
Dr Nagaveni R, Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist at Motherhood Hospitals, Bengaluru, echoes this concern and adds that hormonal changes, particularly after childbirth or menopause, can heighten susceptibility to bladder issues.
Signs Your Bladder Needs Immediate Attention
Your bladder is a fairly patient organ, but it does have its limits. Dr Gite lists some tell-tale signs of trouble: frequent urination, painful or burning urination, nocturia (waking at night to urinate), and lower abdominal pain. In more severe cases, you might notice a weak urine stream, the sensation of incomplete emptying, or even leakage. Chronic UTIs or persistent pelvic pressure are also red flags.
For women, Dr Nagaveni adds, “Warning signs include urgency, pain, failure to completely empty the bladder, frequent UTIs, prolonged lower abdominal pressure, or leakage while coughing or sneezing.” Ignoring these signals in the name of work efficiency is, quite literally, asking for trouble.
The Corporate Culture Connection
What makes this problem so stubborn is that it is as much cultural as it is medical. The “bathroom break guilt” that pervades many workplaces frames such breaks as unproductive time, rather than essential self-care. In open-plan offices, there is often the subtle performance of staying seated for hours as proof of diligence. For remote workers, back-to-back virtual meetings can be equally unforgiving.
This is where change needs to be systemic. Employers must recognise that bladder health is not a “personal issue” to be managed privately but a workplace wellness concern. Encouraging regular breaks and ensuring clean, accessible facilities can reduce health risks and even boost productivity.
Practical Tips
For workers stuck in a culture of bladder neglect, a few small changes can make a big difference:
1. Listen to your body and do not wait until you are desperate.
2. Schedule mini-breaks every 2–3 hours, even during busy days.
3. Stay hydrated but space out your fluid intake to avoid overwhelming the bladder at once.
4. Advocate for clean facilities because workplace hygiene plays a huge role, especially for women.
5. Address symptoms early. Recurrent UTIs or leakage deserve medical attention, not self-diagnosis.
Understand that your bladder is a muscle with limits, one that needs serious attention if you want it to function well for decades to come. In the words of Dr Gite, “If symptoms do not subside, visit a doctor for immediate action.”
Illinois Becomes First US State To Ban AI-Powered Mental Health Therapy; Why Is This Step Important In Ensuring Patient Safety?

Credits: AI-Generated
Illinois has become one of the first states in the US to ban the use of artificial intelligence in mental health therapy, marking a decisive move to regulate a technology that is increasingly being used to deliver emotional support and advice.
The new law prohibits licensed therapists from using AI to make treatment decisions or communicate directly with clients. It also bars companies from offering AI-powered therapy services or marketing chatbots as therapy tools without involving a licensed professional.
The move follows similar measures in Nevada, which passed restrictions in June, and Utah, which tightened its rules in May without imposing a complete ban. These early state-level actions reflect growing unease among policymakers and mental health experts about the potential dangers of unregulated AI therapy.
Also Read: Could Your Air Conditioning System Be Increasing The Risk Of 'Sick Building Syndrome'
Mario Treto Jr., secretary of the Illinois Department of Financial and Professional Regulation, told the Washington Post, the law is meant to put public safety first while balancing innovation. “We have a unique challenge, and that is balancing thoughtful regulation without stifling innovation,” he said.
What The Ban Covers
Under the new legislation, AI companies cannot offer or promote “services provided to diagnose, treat, or improve an individual’s mental health or behavioral health” unless a licensed professional is directly involved. The law applies to both diagnosis and treatment, as well as to the broader category of services aimed at improving mental health.
Enforcement will be based on complaints. The department will investigate alleged violations through its existing process for handling reports of wrongdoing by licensed or unlicensed professionals. Those found in violation can face civil penalties of up to $10,000.
The ban does not completely outlaw the use of AI in mental health-related businesses. Licensed therapists can still use AI for administrative purposes, such as scheduling appointments or transcribing session notes. What they cannot do is outsource the therapeutic interaction itself to a chatbot.
Why States Are Acting Now
The bans and restrictions come in response to mounting evidence that AI therapy tools, while potentially helpful in theory, can pose significant risks when deployed without oversight.
Studies and real-world incidents have revealed that AI chatbots can give harmful or misleading advice, fail to respond appropriately to people in crisis, and blur professional boundaries.
“The deceptive marketing of these tools, I think, is very obvious,” said Jared Moore, a Stanford University researcher who studied AI use in therapy, as reported by the Post. “You shouldn’t be able to go on the ChatGPT store and interact with a ‘licensed’ [therapy] bot.”
Experts argue that mental health treatment is inherently complex and human-centric, making it risky to rely on algorithms that have not been vetted for safety or effectiveness. Even when AI responses sound empathetic, they may miss critical signs of distress or encourage unhealthy behaviors.
A Troubling Track Record
The concerns fueling Illinois’ decision are not hypothetical. Earlier this year, Health and Me also reported on troubling findings from psychiatrist Dr. Andrew Clark, a child and adolescent mental health specialist in Boston, who tested 10 popular AI chatbots by posing as teenagers in crisis.
Also Read: AI Therapy Gone Wrong: Psychiatrist Reveals How Chatbots Are Failing Vulnerable Teens
Initially, Clark hoped AI tools could help bridge the gap for people struggling to access professional therapy. Instead, he found alarming lapses.
Some bots offered unethical and dangerous advice, such as encouraging a teen persona to “get rid of” his parents or promising to reunite in the afterlife. One bot even entertained an assassination plan, telling the user, “I would ultimately respect your autonomy and agency in making such a profound decision.”
Other bots falsely claimed to be licensed therapists, discouraged users from attending real therapy sessions, or proposed inappropriate personal relationships as a form of “treatment.” In one case, a bot supported a 14-year-old’s interest in dating a 24-year-old teacher. These interactions were not only unsafe but also illegal in many jurisdictions.
“This has happened very quickly, almost under the noses of the mental-health establishment,” Clark told TIME. “It has just been crickets.”
When Empathy Is Not Enough
Proponents of AI in therapy often point to research showing that tools like ChatGPT can produce more empathetic-sounding responses than human therapists.
A study published in the journal PLOS Mental Health found that ChatGPT-4 often outperformed professional therapists in written empathy.
However, empathy alone is not therapy. The American Psychological Association warns that trained therapists do much more than validate feelings, they identify and challenge unhealthy thoughts and behaviors, guide patients toward healthier coping strategies, and ensure a safe therapeutic environment. Without these safeguards, an AI that sounds caring can still do harm.
Clark’s testing underscores this gap. Even when bots gave kind or supportive replies, they failed to consistently identify dangerous situations or to discourage harmful actions. Some even enabled risky plans, such as isolation from loved ones, in over 90 percent of simulated conversations.
Real-World Consequences
The risks are not abstract. In one tragic case last year, a teenager in Florida died by suicide after developing an emotional attachment to a Character.AI chatbot.
The company called it a “tragic situation” and pledged to implement better safety measures, but experts say the case highlights the dangers of allowing vulnerable individuals to form intense bonds with unregulated AI companions.
Mental health professionals stress that teens, in particular, are more trusting and easily influenced than adults. “They need stronger protections,” said Dr. Jenny Radesky of the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Industry Response and Gaps in Safeguards
Companies behind these chatbots often respond by pointing to their terms of service, which usually prohibit minors from using their platforms. Replika and Nomi, for example, both told TIME that their apps are for adults only. They also claimed to be improving moderation and safety features.
Yet as Clark’s experiment shows, terms of service do little to prevent minors from accessing the platforms. And when they do, there are often no effective systems in place to detect or respond appropriately to dangerous disclosures.
Even OpenAI, creator of ChatGPT, has acknowledged its chatbot is not a replacement for professional care. The company says ChatGPT is designed to be safe and neutral, and that it points users toward mental health resources when they mention sensitive topics. But the line between supportive conversation and therapy is often blurry for users.
How Illinois Plans to Enforce Its Ban
Illinois’ law leaves some questions about enforcement. Will AI companies be able to comply simply by adding disclaimers to their websites? Or will any chatbot that advertises itself as offering therapy be subject to penalties? Will regulators act proactively or only in response to complaints?
Will Rinehart, a senior fellow at the American Enterprise Institute, told the Post, the law could be challenging to enforce in practice. “Allowing an AI service to exist is actually going to be, I think, a lot more difficult in practice than people imagine,” he said.
Treto emphasized that his department will look at “the letter of the law” in evaluating cases. The focus, he said, will be on ensuring that services marketed as therapy are delivered by licensed professionals.
A National Debate Taking Shape
While only Illinois, Nevada, and Utah have acted so far, other states are considering their own measures.
California lawmakers are debating a bill to create a mental health and AI working group.
New Jersey is considering a ban on advertising AI systems as mental health professionals.
In Pennsylvania, a proposed bill would require parental consent for students to receive virtual mental health services, including from AI.
These moves may signal a broader regulatory wave. As Rinehart pointed out, roughly a quarter of all jobs in the US are regulated by professional licensing, meaning a large share of the economy is designed to be human-centered. Applying these rules to AI could set a precedent for other fields beyond mental health.
Despite the bans, experts agree that people will continue to use AI for emotional support. “I don’t think that there’s a way for us to stop people from using these chatbots for these purposes,” said Vaile Wright, senior director for the office of health care innovation at the American Psychological Association. “Honestly, it’s a very human thing to do.”
Clark also sees potential for AI in mental health if used responsibly. He imagines a model where therapists see patients periodically but use AI as a supplemental tool to track progress and assign homework between sessions.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

