- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
From ADHD To Burnout: Why Modern Life Is Making You Sleepless, Anxious And Insomniac

Credits: Canva
Your struggle to fall asleep, stay asleep, or wake up rested? It’s not just on you. And it never really has been. For centuries, sleep has been a fragile and complicated process. Historically, it took place in overcrowded, uncomfortable homes, alongside families, fire smoke, bugs, animals, and the unpredictable dangers of the night. In those times, people prayed for safety more than they prayed for dreams.
Fast forward to today — temperature-controlled bedrooms, memory foam mattresses, sleep masks, blackout curtains — and yet, millions are still wide awake at 3 AM, staring at the ceiling, wondering what’s broken.
It’s not just about your mattress or screen time. Your body isn’t failing you. It’s that the world you live in is making rest harder than it should be.
Also Read: This Age-Old Killer Is Spreading Fast, Why Super Typhoid Isn’t Just A ‘Poor Country’ Problem Anymore
In 2020, over 14% of adults in the US reported struggling to fall asleep on most days, according to the National Health Interview Survey. About 12% have been diagnosed with chronic insomnia.
A third of American adults don’t get the recommended seven hours of sleep per night. And that lack of rest isn’t distributed equally: Native Hawaiian, Pacific Islander, and Black adults, along with those earning under $15,000 a year, are the most sleep-deprived.
What this really means is: sleep loss isn’t just a personal health issue. It’s a socioeconomic one.
You’re Not Lazy — The System Isn’t Built for Rest
We live in a society that glorifies hustle, devalues downtime, and equates sleep with laziness. We’re constantly connected, bombarded with notifications, and working longer hours — even when we're off the clock.
And then there's revenge bedtime procrastination — the habit of staying up late because it’s the only time you have for yourself. We scroll through emotionally charged or overstimulating content on our phones, even though we know it's sabotaging our sleep. We drink coffee too late. We binge-watch one more episode. We use alcohol to unwind, which only fragments sleep more.
Ironically, even the wellness-obsessed are losing sleep trying to perfect it — tracking every breath, wearing sleep rings, taping their mouths shut, and obsessing over micro-wakeups. Experts say this hyper-focus on sleep performance can actually heighten anxiety and worsen insomnia.
The truth is, many factors that destroy your sleep are beyond your control.
Shift workers — who make up 20% of the US labor force — have sleep cycles dictated by employers, not biology. Irregular schedules disrupt circadian rhythms and increase the risk of sleep disorders. Studies show that people of color are more likely to work alternating shifts, compounding their sleep challenges.
Lack of basic sleep-friendly infrastructure is another major barrier. People living in noisy, polluted, or unsafe neighborhoods — often low-income communities — face chronic sleep disruptions. Bright street lights, traffic noise, subpar housing, no access to air conditioning or heating — these all add up.
And then there’s the toll of racism and discrimination. Research shows that the stress from daily microaggressions and systemic injustice has a measurable impact on sleep quality and duration.
For many, sleep is not just elusive — it’s systematically denied.
Is Parenting and Caregiving Fuelling The Quiet Sleep Crisis?
Caregivers are among the most sleep-deprived populations. Babies, toddlers, aging parents — their needs don’t clock out at night. Sleep training might work for infants, but there's no such system for grown-up responsibilities.
If you're a new parent or a caregiver running on fumes, advice like “just wind down before bed” rings hollow. For people in this group, it’s not about willpower or habits — it's about survival.
Now add neurodivergence to the mix. A new study in BMJ Mental Health finds that adults with higher ADHD traits are significantly more likely to report insomnia, low sleep quality, and — unsurprisingly — a lower quality of life.
The research suggests that insomnia may be the link between ADHD symptoms and reduced life satisfaction. And while ADHD and insomnia both independently affect mood and functioning, their overlap is a major red flag.
The traditional treatment for one often ignores the other. Experts now advocate for targeted sleep therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) or Sleep Restriction Therapy to improve both sleep and daily functioning in adults with ADHD traits.
How Can You Sleep Better?
First, stop blaming yourself. Instead of focusing solely on sleep hygiene tips like cool rooms and no screens, try identifying what’s really keeping you up. Is it your work schedule? Your housing situation? Noise? Anxiety? All of the above?
If possible, consult a sleep medicine specialist to rule out disorders like insomnia, apnea, or circadian rhythm disruptions. If therapy is an option, CBT-I has proven effective for many.
For those dealing with unavoidable stressors — think shift work, noisy neighborhoods, caring for kids — small tools may help. White noise machines, blackout curtains, cooling fans, sleep earplugs. They’re not perfect, but they can create small windows of peace.
The goal isn’t eight perfect hours. It’s about carving out enough restorative rest — wherever and however possible — to function and feel human.
Sleep isn’t optional. It’s biological. Your body wants to rest. Your brain needs it. And even though society isn’t built to support that, the rhythm is still there — pulsing under the noise, waiting to be reclaimed.
So, maybe tonight, instead of battling the night like an enemy, trust your body. Dim the lights, breathe and let sleep come — if not easily, then at least without shame because the struggle to sleep isn’t yours alone.
Disclaimer: This article may include interpretations of research, and commentary that reflect individual or editorial perspectives. It is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice
Claire Danes Revealed She Was Shocked At Being Pregnant After 40, Does Age Really Play A Role?

(Credit-Claire Dane/Instagram, Canva)
Claire Danes recently revealed that she was shocked to learn that she was pregnant with her third child at 44. In an interview with Amy Poehler in an episode of Good Hang with Amy Poehler, the Beast In Me actress revealed that she burst into tears at her OB/GYN’s office, explaining that she didn’t know it was possible to be pregnant after 40.
Danes shared that she initially felt a strange sense of embarrassment about the pregnancy. Because she and her husband, Hugh Dancy, weren’t planning for a third, Danes felt like she had stepped outside of normal "parameters."
The debate surrounding pregnancies after 40 has always persisted. Many people like Claire believe that it is impossible to get pregnant after your biological clock runs out. However, in reality, things do not work like that. Dr Rohan Palshetkar, Consultant IVF specialist, at Bloom IVF explains a few factors one should know about.
Can You Get Pregnant After 40?
Yes, Dr Rohan explains that it is completely possible and safe with the current technological advancements. “Earlier we did have fetal medicine specialists, high resolution ultrasounds, better monitoring techniques and safter IVF options”
Screening tests are much more detailed, IVF options are more robust and egg freezing is also an empowering tool for women who wish to have pregnancies later in life, Dr Rohan explained.
However, he also pointed out that post 35 risks of having diabetes and hypertension increases, so consistent monitoring helps a lot.
What Are Some Risks Of Pregnancies After 40?
The chance of having a high-risk pregnancy increases for women above 40, according to the American College of Obstetricians & Gynecologists (ACOG). They explain that since women are born with all the eggs they will ever have, those eggs age right along with the body. As time goes on, the number of eggs decreases, and their quality can change.
While many women have healthy pregnancies in their 40s, here are some specific risks you should know about.
Chromosome Issues
Older eggs are more likely to have certain genetic changes. This means there is a higher chance for the baby to be born with a health condition like Down syndrome instead.
Miscarriage or Stillbirth
Women in their forties face a much higher statistical chance of losing a pregnancy. It is very important to stay in close contact with your doctor to monitor your baby's health.
Low Birth Weight
There is a greater risk that the baby will be born weighing less than what is considered healthy. Small babies often need extra medical care and stay in the hospital longer.
Blood Clots
Being pregnant naturally increases your risk of developing dangerous blood clots. However, this specific medical danger becomes even more likely for mothers who are over the age of thirty-five or forty.
Gestational Diabetes
This is a specific type of high blood sugar that some women develop only while they are pregnant. It requires careful diet management or medication to keep you and baby safe.
Preeclampsia
This is a very serious condition involving high blood pressure that can happen during pregnancy. It can be dangerous for the mother and the baby if it is not treated quickly.
Labor Challenges
Delivery can be more difficult for older mothers, often leading to longer labor times. Because of these complications, doctors are much more likely to recommend a surgical C-section birth instead.
How Doctors Support Pregnancies After 40
Being "high-risk" doesn’t mean something will go wrong; it just means your medical team will watch you more closely. Modern medicine has great tools to keep you and your baby safe, such as,
- Prenatal Screening
- Extra Ultrasounds
- Frequent Check-ups
11 Signs From Your Nervous System You Should Never Ignore, According to Neurologists
Credits: iStock
Neurology can sometimes be overwhelming because the nervous system touches almost every part of the body. This means, from memory to speech, to sleep and every sensation, all of them are part of neurology. So, naturally, neurologists deal with a vast range of conditions, including carotid artery disease, seizure disorders, Alzheimer’s and frontotemporal dementia, migraines and facial pain, Parkinson’s disease, muscle disorders, narcolepsy, and many others.
“If there’s a nerve somewhere, a neurologist could get involved,” says Dr. Andrew Dorsch, division chief for general neurology at Rush University System for Health and a specialist in neurologic rehabilitation, as reported by Times. “And there’s nerves everywhere in the body. There’s a lot that can go wrong, and figuring it out often takes real detective work.”
The problem is that many people ignore early neurological symptoms, because it looks like any other normal thing that could happen to anyone under immense stress. Here are 11 symptoms doctors say you should never ignore.
Double vision that comes on suddenly
One overlooked symptom is a specific type of double vision that happens when both eyes are open and improves when either eye is closed. This is known as neurological diplopia and is different from eye-related vision problems.
Dr. Luis Cruz-Saavedra, a neurologist with Memorial Hermann Health System, told Times, this type of double vision can be linked to serious conditions such as multiple sclerosis, stroke, aneurysm, myasthenia gravis, brain tumors, or brain infections.
If double vision starts suddenly, it is an emergency. “Immediately,” he says. Doctors may check for stroke warning signs and order imaging such as a CT scan or MRI to identify the cause.
Weakness in one arm or leg
Subtle weakness is another symptom people tend to ignore. Dragging one foot, limping, dropping objects, or struggling to write with a dominant hand are all red flags.
“I see people come in months after symptoms begin,” Cruz-Saavedra says. Many assume it is a pinched nerve, but weakness can signal stroke, brain tumors, multiple sclerosis, or brain inflammation. Neurologists usually test strength, reflexes, balance, and coordination to narrow down the cause.
Brief episodes of unresponsiveness
Some people suddenly stare blankly for a few seconds and then return to normal with no memory of the episode. These moments are often noticed by family members rather than the patient.
Cruz-Saavedra explains that this can be a sign of temporal lobe seizures, which affect areas of the brain involved in memory and emotion. People may describe it as losing a small chunk of time, which should always be medically evaluated.
Trouble speaking or understanding words
Speech problems are among the most common warning signs of stroke, yet many people delay seeking care.
Dr. Enrique Leira, director of the division of cerebrovascular diseases at the University of Iowa, toles Times, stroke symptoms often appear suddenly. Speech may become slurred, slow, or difficult to understand. Some people struggle to find words or comprehend language altogether. In these cases, urgent medical attention is critical.
Sudden, severe headache during exertion
Most headaches are harmless, but some require immediate attention. A headache that strikes suddenly, feels unusually intense, and occurs during physical effort can indicate something serious, including stroke.
Leira says headaches that do not gradually build up and instead arrive abruptly should always be checked right away.
Persistent numbness in feet or fingers
Dr. Dorsch says numbness commonly affects the feet or fingers and suggests that nerves are failing to send signals properly. This is different from tingling, which usually means nerve irritation.
Numbness may result from diabetes, autoimmune conditions, genetic disorders, or nerve damage. A full neurological workup helps determine which nerves are affected and why.
Frequent déjà vu
Occasional déjà vu is normal. Experiencing it repeatedly is not.
“If it’s happening regularly, that’s not typical,” Dorsch says. Frequent déjà vu episodes can be an early sign of temporal lobe seizures and should be evaluated.
Difficulty standing up from a chair
Struggling to rise from a chair on a regular basis is not just about aging or stiff joints. Dorsch says neurologists want to rule out problems involving muscles, nerves, or the spinal cord, including Parkinson’s disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Changes in voice
Neurologists pay close attention to voice changes. Dr. Alexandru Olaru of University of Maryland St. Joseph Medical Center notes that an unusually soft or breathy voice may indicate Parkinson’s disease. Slurred speech can point to stroke.
Another concerning sign is a wet or gurgly voice caused by saliva pooling in the throat. This can occur in conditions like Parkinson’s disease, ALS, and multiple sclerosis.
Muscle twitches that do not stop
Muscle twitches are common and often harmless. But when they occur repeatedly in the same location, they should be discussed with a doctor.
Olaru explains that these fasciculations may be benign or linked to conditions such as spinal stenosis, ALS, or autoimmune nerve disorders. Tests like electromyography can help identify the cause.
Sudden personality or behavior changes
Abrupt shifts in behavior, including paranoia, withdrawal, impulsivity, or inappropriate behavior, can signal neurological disease.
Cruz-Saavedra says conditions like autoimmune encephalitis or frontotemporal dementia may show up as personality changes long before memory problems appear. New obsessive behaviors or hoarding can also be warning signs.
Drinking Alcohol Could Damage Your DNA, Not Just Your Liver Or Heart
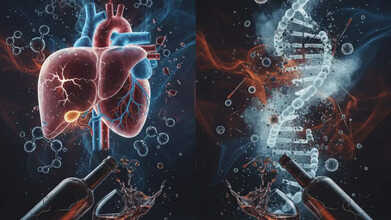
Credits: AI Generated
Alcohol is often seen as harmful mainly for the liver or heart, but its impact goes much deeper—reaching down to our DNA. Even moderate drinking can silently cause changes at a cellular level, raising long-term health risks that may not be immediately visible. According to Dr. Amit Miglani, Director & HOD – Gastroenterology, Asian Hospital, the breakdown of alcohol in the body produces a toxic chemical called acetaldehyde, which can directly damage DNA inside our cells.
Alcohol Can Damage Your DNA, Not Just Your Liver And Heart
This damage disrupts the body’s natural repair mechanisms, allowing mutations to accumulate over time. Such mutations are linked to several cancers, including cancers of the mouth, throat, liver, breast, and colon. The insidious nature of this damage means that even when you feel healthy, harmful changes may be occurring beneath the surface.
How Alcohol Interferes With DNA Repair
DNA damage can be complex to understand, but its consequences are serious, explains Dr. Arun Kumar Giri, Director – Surgical Oncology, Aakash Healthcare. Normally, the body constantly repairs minor DNA errors. However, alcohol disrupts this repair process, leaving cells vulnerable to mutation and abnormal growth.
Dr. Giri adds that some people have genetic variations that make them break down alcohol more slowly. For these individuals, alcohol stays in the body longer, increasing the likelihood of DNA damage. Over years of repeated exposure, this can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and eventually cancer.
No Completely Safe Level of Alcohol For DNA Health
One of the most important points, Dr. Giri emphasizes, is that there is no entirely safe level of alcohol when it comes to DNA. The risk increases with both the frequency and quantity of drinking. Even occasional binge drinking can be harmful, meaning that how often you drink can be as important—or even more so—than how much you drink at one time.
This perspective shifts the discussion from asking “How much alcohol is too much?” to “How often am I exposing my cells to alcohol-induced damage?” Protecting DNA health requires regular monitoring and mindful drinking habits, even for those who feel healthy today.
Alcohol: Long-Term Health Implications
Alcohol-induced DNA damage is not just a short-term concern. Over time, the accumulation of mutations can significantly increase cancer risk and other serious diseases. Regular health check-ups, a balanced lifestyle, and moderation, or complete avoidance of alcohol are crucial steps for safeguarding your genetic health and overall well-being.
Dr. Amit Miglani highlights that “It’s not just about the organs you can feel being affected today; it’s about protecting your long-term health, especially your DNA, for the future.”
Dr. Arun Kumar Giri advises, “Understanding the cellular impact of alcohol helps people make informed choices about their drinking habits. Even small changes can significantly reduce the risk of long-term damage.”
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

