- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Is Honey Good Or Bad For You?

Is Honey Good Or Bad For You?
Honey is often marketed as a healthier alternative to regular sugar. This is largely due to it being nutrient-dense and having a large number of antioxidants. However, while some claim that it could be a nutritious ingredient, others claim it to be a high-sugar indulgence.
What Is Honey?
Honey is a naturally sweet, syrup-like substance that bees produce from the nectar of flowering plants. The bees collect the nectar and then consume, digest, and regurgitate it inside the beehive to produce honey. This honey is stored in wax structures called honeycombs, which are gathered by humans through the practice of beekeeping. Although the nutritional value of honey
depends upon its type, a single tablespoon (21 grams) of honey typically consists of 64 calories and 17 grams of carbs with little to no fat, fiber, and protein.
What are the benefits of honey?
High in Antioxidants
High-quality honey is rich in several important antioxidants- such as phenolic acids and flavonoids. Antioxidants are compounds that help fight disease-causing free radicals, thereby reducing your risk of oxidative cell damage. Research has shown that a diet which is high in antioxidants could help an individual prevent chronic diseases as well as mental health issues.
May Improve Heart Health
Swapping out regular sugar for high-quality honey in your diet may improve different aspects of heart health. Numerous studies have shown that it reduces several risk factors of heart disease.
For example, one 30-day study comparing the effects of table sugar and honey in 55 people found that honey helped decrease levels of total and “bad” LDL cholesterol while increasing “good” HDL cholesterol. It was also able to lower triglyceride levels by up to 19%.
Promotes Wound Healing
In some forms of traditional medicine, such as Ayurveda, honey is applied directly to the skin to aid wound healing. This is thought to be due to its antibacterial properties and its ability to decrease the growth of microorganisms that could cause infection.
In one small study, applying manuka honey directly to diabetic foot ulcers was as effective as conventional wound dressings and promoted healing in 97% of ulcers. Similarly, another study of 30 people showed that adding honey to wound dressings enhanced healing in about 43% of diabetic foot ulcers after three months.
Better Than Refined Sugar
While honey is high in sugar, it is still better choice than refined sugar. Processed sugar brings little to the table, while honey is high in antioxidants, including phenolic acids and flavonoids. One study also suggests that using honey instead of table sugar may decrease triglycerides as well as total and "bad" LDL cholesterol to support your heart health. However, while honey may be a better option than refined sugar, it should still be consumed in moderation to prevent adverse effects on your health.
However, It May Contribute To Weight Gain
Honey is high in sugar and calories, packing almost 64 calories into a single tablespoon. While this may not seem so much, even a few servings per day could cause calories to stack up and contribute to obesity. Honey is also high in sugar, which is digested rapidly and can cause your blood sugar levels to spike and crash — resulting in increased hunger and potential long-term weight gain.
Scientists Reveal The Reasons Why Tofu is Better Than Paneer

(Photos: Canva)
In modern days, people are choosing vegan alternatives for sources of protein rather than dairy products.
Paneer and tofu are both foods sold in white blocks that can be added to dishes spanning many Asian cuisines. The production of both foods involves curdling and pressing. Each has a mild taste on its own yet absorbs the flavours of its marinades.
Paneer is made by curdling hot milk with an acidic substance like lemon juice, vinegar, or curd, whereas tofu is made from soy and does not contain animal-based ingredients.
However, scientists say tofu is a superior, lower-calorie, and cholesterol-free alternative to paneer for weight management, offering 75 percent less fat and higher iron.
Here is why:
Heart Health
Tofu provides healthy plant fats, which are better for the heart, including omega-3 fatty acids, which help improve overall cholesterol balance and reduce inflammation in blood vessels.Coronary artery disease, which is caused by plaque build-up up and inflammation in the blood vessels, is one of the leading causes of heart attacks and strokes in the country. However, eating tofu can reduce chances of developing coronary artery disease.
Unlike other dairy sources of protein, tofu is low in saturated fat and significantly lowers the risk of bad cholesterol, which is a leading factor for heart problems.
Prevents Chronic Diseases
Soy protein and compounds in tofu may help the body use insulin more effectively, reducing the risk of Type-2 diabetes.It contains antioxidants that prevent cells from damage that can lead to cancer. Research suggests that regular intake may reduce chances of breast, prostate and colon cancer.
Maintains Bone Health
Both protein and tofu are rich sources of calcium, but tofu comparatively contains more calcium.Isoflavones in tofu may reduce bone breakdown, particularly in postmenopausal women who are more prone to osteoporosis.
Rich In Nutrients A detailed nutrient comparison reveals that 100 grams of tofu has only about 70–80 calories and around eight grams of protein. Paneer, in comparison, has roughly 265–300 calories and 12–15 grams of saturated fat per 100 grams.
Vegan Alternative Tofu is a lighter, plant-based alternative suitable for those seeking better heart health, weight control, or a vegan diet.
Being dairy-free, it is suitable for vegans, lactose-intolerant individuals, and those who avoid animal-based foods for ethical, health, or religious reasons.
Diverse Dishes
It is a versatile source of protein that can be added to various Asian cuisine dishes. Tossed with veggies and salt and pepper or added in Pad Thai noodles.Morning Vs Evening Workouts: Which Is More Productive
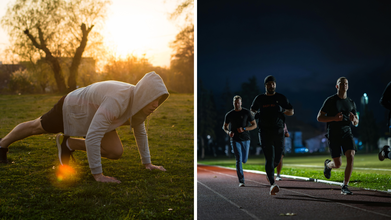
(Photos: Canva)
While morning sun beams are said to be a productive and a consistent start to the day, evening workouts are known for reducing stress after a monotonous routine.
But while experts have dividing views on which time is better for a session, research shows that both have their own benefits.
Here’s why getting a quick workout done before work is good for you:
1. Improve Cognitive Function And Productivity
Starting the day with a good exercise routine can give you consistent energy and focus at work, giving you a much-needed boost for the hectic day.Morning exercises also stimulates the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine (feel-good) and norepinephrine (fight-to flight), increasing blood flow which keeps you attentive throughout the day.
2.) Reduced Muscle And Joint Stiffness
After a good sleep you need to release all that build up stiffness in your body, Movement in the morning increases circulation improving joint mobility. Exercising in the morning allows the body to adapt to activity, warm up stretches and light cardio increases blood flow, lubricates the joints and reduces stress on knees and hips.Seated knee extensions, hamstring stretches and mini squats ease inflammation in knees and joints, which further improves mobility.
3.) Boost Metabolism and Positive food choices
A 2018 study published in the International Journal of Obesity noted that 2,680 college students who completed a 15-week exercise program were more likely to choose healthier options rather than fried food.By utilising store fat as fuel, exercising in the early hours stabilizes blood sugar and reduces cravings for unhealthy food. Workouts also allow muscles to absorb glucose from the blood preventing spikes after breakfast and during the day, preventing the development of Type-2 diabetes in the future.
4.) Positive Psychological Impact
Exercising early distracts you from anxious thoughts, it also helps release happy and stress relieving hormones like endorphins, dopamine and serotonin, that ultimately reduces stress, anxiety and symptoms of depression.You will feel a sense of accomplishment and achievement before starting the day which can boost overall brain health.
However, evening workouts also have many advantages including:
1.) Enhanced Physical Performance
Body temperature peaks in the late afternoon due to natural immune response which can lead to inflammatory cytokines.This leverages the body's natural circadian rhythm in the evening which increases flexibility, strength and potentially allows for more vigorous workouts.
Research shows that individuals may take up to 20 percent longer to reach exhaustion, allowing time for heavy weightlifting and intense cardio effective for weight loss.
2.) Promotes Better Sleep
After a long day, evening workouts are perfect for helping you escape the frustration of a tiring day.Exercising in the evening, improves blood vessel elasticity and reduce vascular resistance that overall helps to regulate cardiovascular health.
Consistent evening exercise stabilises heart health, experts observe that workouts can keep blood pressure lower for up to 24 hours.
3.) Increased Calorie Burn
The body is physically and mentally prepared for an active workout session, which allows heavier lifting and more intense cardio workouts leading to faster fat loss and more calories to burn.In the evening, the body is better able to absorb and transport oxygen to active muscles leading to improved energy during exercise.
4.) Appetite Regulation
Cravings at night usually arrive from hormonal shifts or due to the body's circadian rhythm. Physical activity redirects blood flow away from the stomach toward muscles to improve insulin sensitivity and manages late night cravings.High-intensity evening exercises can reduce levels of ghrelin, the hormone that triggers hunger, which manages calories and regulates appetite.
AI-generated Videos of Chia Seeds Have Got Doctors Concerned About Its Use

Credits: iStock
AI-generated videos with deep, dramatic voiceovers are flooding TikTok and Instagram, promising that a spoonful of chia seeds in water can fix digestion, melt fat and transform gut health almost overnight. The clips look slick, confident and science-backed. But experts say this latest wellness trend needs a reality check.
The chia seed challenge and the social media hype
The so-called chia seed challenge has exploded online, with millions of views across platforms. Health and wellbeing influencers, along with AI creators, are pushing the tiny seeds as a cure-all for weight loss and bloating. While chia seeds are not new to nutrition science, dieticians and media experts warn that social media often stretches the truth.
With so much content out there, it has become harder to tell what is genuine health advice and what is exaggerated clickbait.
What exactly are chia seeds?
Chia seeds come from the flowering plant Salvia hispanica, which resembles lavender. Native to Mexico, chia was a staple in the Aztec diet and has since been introduced to parts of Australia, including the Northern Territory, Queensland and Western Australia’s Ord Valley in the Kimberley.
They are commonly added to smoothies, overnight oats, puddings and even homemade jams. Found in supermarket health aisles, chia seeds can be black or white, with no nutritional difference between the two.
Are chia seeds actually good for you?
Amelia Harray, a dietician at the University of Western Australia, told ABC News, chia seeds deserve their reputation as a nutritious food, just not the miracle status social media gives them.
“Like lots of nuts and seeds, chia seeds are absolutely superfoods,” Dr Harray said. “They are about 24 per cent protein and they are a complete protein source, meaning they contain all nine essential amino acids.”
Chia seeds are also high in fibre, around 33 per cent, including both soluble and insoluble fiber. According to Dr Harray, fibre supports gut health, helps lower cholesterol and keeps you feeling full for longer.
However, she warned against suddenly consuming large amounts. “If someone has a very low-fiber diet and then starts eating lots of chia seeds, they might experience bloating or abdominal cramps,” she said.
Read: Superfood Chia Seeds Can Also Be Risky For Some, Know Who They Are
Do you need to soak chia seeds first?
One popular claim online is that chia seeds must be soaked to “activate” their benefits. Dr Harray says that is not true.
“We know you do not need to soak chia seeds to get the nutritional benefits,” she said. “That idea is not supported by evidence.”
Chia seeds can be eaten soaked or unsoaked, sprinkled over yoghurt or cereal. When soaked, they form a gel, which some people find easier on digestion. Dr Harray does caution against eating dry chia seeds by the spoonful, as they can swell and become a choking risk.
Why you should question viral health videos
Tama Leaver, a professor of internet studies at Curtin University, says the chia trend is part of what he calls the “wellness loop.”
“Some creators stick close to health advice, but others push it as a miracle cure,” Professor Leaver said. “That exaggeration is how they get clicks and make money.”
He added that AI-generated videos make it even harder to trust what you see. “We cannot take anything at face value,” he said, urging users to check who is behind the content and whether claims are backed by real evidence.
In short, chia seeds can be a healthy addition to your diet. Just do not believe every booming AI voice that promises they will change your life overnight.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

