- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
You Are What You Eat, And When: How Intermittent Fasting Work?

Image Credit: Health and me
Like me, if you too have been curious to know more about intermittent fasting (IF) and how it might transform your approach to health and weight loss? Well this popular trend isn't just about what you eat—it's about when you eat. From time-restricted eating to alternate-day fasting, IF offers a variety of approaches tailored to your lifestyle. Emerging studies, including a comprehensive 2019 analysis, highlight its potential to lower BMI, reduce fat mass, and improve metabolic health. Intriguingly, research shows eating earlier in the day can curb appetite and boost fat burning.
With a focus not just on what you eat, but when, IF challenges traditional meal schedules and reshapes our understanding of healthy eating patterns. Backed by evolving science, this approach highlights the impact of timing on our metabolism, energy levels, and even cellular health. Intermittent fasting is not a one-size-fits-all approach, but it offers a promising alternative to traditional dieting.
What Is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting isn't a novel concept. Historically, fasting has roots in cultural and religious practices. However, modern IF takes a more structured approach, dividing periods of fasting and eating into deliberate cycles. Popular methods include:
1. Time-Restricted Eating
Eating is limited to a specific window of the day, such as 8 a.m. to 8 p.m., with fasting outside of these hours.
2. Alternate-Day Fasting
Alternating days of normal eating with days of calorie restriction or complete fasting.
3. 5:2 Diet
Eating normally for five days and drastically reducing calorie intake for the other two days.
4. 16:8 Diet
Fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window, often aligning meal times with natural daylight hours.
How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
The fundamental premise of IF is to optimize the body's natural metabolic processes. Prolonged periods of fasting push the body to shift from relying on carbohydrates for energy to burning fat, entering a state called ketosis. This metabolic switch is linked to numerous health benefits, including weight loss and improved cellular repair processes.
According to Johns Hopkins Medicine, IF also aligns with the body’s circadian rhythm—our internal biological clock that influences sleep, digestion, and hormone regulation. Studies suggest that eating in sync with this rhythm, such as having larger meals earlier in the day, can enhance metabolic health and regulate appetite.
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
Emerging research highlights the promising advantages of intermittent fasting (IF). A 2019 study in the Journal of Clinical Medicine found that IF significantly lowers BMI and fat mass compared to traditional calorie-restricted diets by naturally reducing calorie intake through limited eating hours. Additionally, a 2019 review in The New England Journal of Medicine emphasizes IF’s role in improving metabolic health by reducing belly fat, enhancing insulin sensitivity, and lowering inflammation. A small 2019 study in Obesity revealed that early time-restricted feeding, such as eating between 8 a.m. and 2 p.m., boosts fat oxidation and reduces appetite.
Furthermore, fasting periods trigger autophagy, a cellular repair mechanism that eliminates damaged components, which is associated with increased longevity and a lower risk of chronic diseases.
Risks of Intermittent Fasting
While the benefits of IF are promising, it’s not without challenges or risks. Certain groups should avoid IF or approach it with caution:
- Prolonged fasting may deprive individuals of essential nutrients, especially if meal quality is poor.
- Excessive calorie restriction may interfere with menstrual cycles or lower testosterone levels.
- For individuals with a history of eating disorders, IF might exacerbate unhealthy behaviors.
Common Intermittent Fasting Mistakes To Avoid
To reap the benefits of IF, it’s crucial to avoid these pitfalls:
- Starting Too Aggressively- Diving into extreme fasting schedules can shock the body and lead to burnout.
- Inadequate Meal Planning- Eating calorie-dense, nutrient-poor foods during eating windows can sabotage weight loss and health goals.
- Neglecting Hydration- Fasting periods can dehydrate the body if water intake isn’t prioritized.
- Unsustainable Schedules- Choosing a plan that doesn’t align with your lifestyle increases the likelihood of quitting.
How to Maximize the Benefits of Intermittent Fasting?
For those ready to incorporate IF into their routine, here are a few tips to ensure success:
- Eat Balanced Meals: Focus on vegetables, lean proteins, healthy fats, and whole grains during eating windows.
- Time Your Meals Wisely: Consume larger meals earlier in the day to align with your circadian rhythm.
- Stay Active: Moderate exercise can complement fasting by enhancing fat burn and improving energy levels.
- Listen to Your Body: Adjust your fasting plan if you experience fatigue, irritability, or other adverse effects.
As always, consult a healthcare professional before embarking on any new diet regimen, particularly if you have underlying health conditions. After all, the old adage “you are what you eat” is evolving—and now, it’s also about when you eat.
Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Health, Aging, and Disease. The New England Journal Of Medicine. 2019
Intermittent Fasting in Cardiovascular Disorders-An Overview. Nutrients. 2019
Early Time-Restricted Feeding Reduces Appetite and Increases Fat Oxidation But Does Not Affect Energy Expenditure in Humans. Obesity. 2019
Edible Cactus Can Cure Diabetes And Heart Troubles, Experts Say

Credit: Pixabay
Edible cactus, especially varieties from the genus Opuntia, has moved far beyond traditional cuisine and into the world of functional foods. Often eaten as cactus pads known as cladodes or as the fruit called prickly pear, this plant has been studied for its possible benefits in diabetes, cholesterol management and overall metabolic health.
But how strong is the evidence? Here is a clear and scientific look at what research says:
What Is Edible Cactus?
The most commonly studied species is Opuntia ficus-indica, widely consumed in Mexico and other arid regions. According to 2011 Journal of Food Science and Technology study, cactus cladodes are rich in dietary fiber, antioxidants, vitamins and minerals.
A 2025 Scientific Reports study also shows that cactus pear accessions contain bioactive compounds such as polyphenols, betalains, and flavonoids, which may help prevent chronic illnesses like cancer, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, while supporting immune function, gut health and cognitive health.
Another 2021 Food Chemistry study describes cactus species as underutilized plants with strong nutritional potential. They are particularly high in soluble fiber which are important for blood sugar and cholesterol regulation.
How Could Cactus Help Blood Sugar?
Multiple researchers suggest that edible cactus can lower control blood sugar levels due to its high fiber and bioactive compounds.A 2022 Medicina study reviewed the use of prickly pear cladodes as a functional ingredient for hyperglycemia management and found evidence suggesting that consuming cactus pads with meals may reduce fasting glucose levels.
Normal postprandial (post-meal) blood sugar for adults without diabetes is typically below 140 mg/dL two hours after eating. For individuals with diabetes, the target is generally less than 180 mg/dL.
A systematic review by a 2019 Medicina study examined human trials on Opuntia consumption and found reductions in blood glucose and insulin levels, especially in individuals with Type 2 diabetes. However, the results were not entirely consistent across all trials.
More recent analytical research by the Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry suggests that cactus bioactive compounds may inhibit enzymes such as alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase, both key digestive enzymes that work sequentially to break down starch into glucose in the body.
These enzymes are involved in carbohydrate digestion. By slowing their activity, cactus components may reduce the speed at which glucose enters the bloodstream, suggetsing that cactus may help the body handle carbohydrates more gradually.
What About Cholesterol?
Cholesterol management is another area of interest. The high fiber content of cactus is again central and soluble fiber can bind bile acids in the intestine, increasing their excretion. As bile acids are made from cholesterol, the body may use circulating cholesterol to produce more bile, which can lower LDL levels.A Nutrition review and meta-analysis conducted randomized clinical trials on cactus pear and cardiovascular risk factors. They found significant reductions in body weight and some lipid parameters, though the overall quality of evidence varied.
Another 2024 Nutrition study also highlighted the potential of Opuntia species in managing obesity and related metabolic conditions, including dyslipidemia. Some studies reported reductions in total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol, particularly in individuals with metabolic syndrome.
However, the magnitude of these changes is generally described as moderate rather than dramatic.
But Are There Any Limitations?
While the findings are promising, the evidence has limitations.Many studies involve small sample sizes. Some trials are short-term. Preparation methods also vary widely, from fresh cladodes to powders, extracts, or capsules. Dosage differences make it difficult to compare results directly.
In addition, cactus should not be viewed as a replacement for medical treatment. For individuals with diabetes or high cholesterol, it may be a supportive dietary addition rather than a standalone therapy.
So, Can Edible Cactus Help?
Based on current research, edible cactus appears to have potential benefits for improving post-meal blood glucose and possibly lowering cholesterol levels. The effects are likely due to a combination of soluble fiber, enzyme inhibition, and antioxidant activity.However, the improvements observed in studies are generally modest. Cactus works best as part of an overall balanced diet rich in fiber, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
In summary, edible cactus is not a miracle cure, but it is a scientifically interesting and nutritionally valuable food. As research continues, especially with better-designed human trials, we may gain clearer answers about how strong its metabolic benefits truly are.
Kanpur Food Adulteration: FSSAI Seizes 14,000L of Oil, 1320Kg Rotten Dates And More Ahead Of Festive Season

Credits: FSSAI and Canva
After Indore's Bhagirathpura food contamination and Horlicks adulteration in Odisha, another news of food adulteration comes from the state of Uttar Pradesh where UP Food Safety and Drug Administration or the UPFSDA with Food Safety and Standards Authority of India or FSSAI seized nearly 14,000 litres of adulterated oils during raids in Kanpur.
This has led to the confiscation of 1,000 kilograms of colored waste and other suspicious food items. This happened right ahead of the festive season like Holi, Eid and as Ramadan continues. This is also the time when festive meals are cooked in oil, ghee, and Ramadan fast is also broken with dates that too were found in rotten conditions.
Also Read: Scientists Develop First Antibodies To Block Epstein Barr Virus
Kanpur Food Contamination: What Has Been Seized In The Raid?
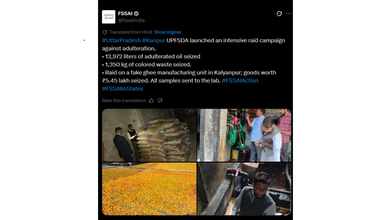
As per the official statement, enforcement teams seized 13,972 litres of adulterated oil and 1,350 of colored waste during inspection across the city.
Officials were also able to spot fake ghee in the manufacturing unit of Kalyanpur. Fake ghee worth approximately Rs. 5.45 lakh were confiscated. The seized samples have been sent to a laboratory for further testing and analysis.
The raids were launched as a part of wider effort to curb food adulteration before the festive season when the demands for such edible also rise sharply.
Kanpur Food Contamination: Dates, Sweets, And More Seized
Surprise inspections were also conducted at several food outlets, cold storage facilities and dairies across Kanpur that brought out a concerning image. These places have come under the scanner. Authorities inspected Swaroop Cold Storage in Aishbagh and Himalayan Cold Storage on Ayodhya Roads. Further raids were carried out on dairies in the Havetmau area and Rae Bareli Road. Samples from sweet shops and other eateiers have also been collected.
The raid collected rotten dates from the cold storage. Followings have been collected and recovered:
- 1,320 kilograms of dates were seized
- 1,418 kilograms of colored kachri were confiscated
- Food items also recovered from warehouse in Aminabad
Officials confirmed that strict actions will be taken against them and this will continue throughout the festive period.
Raids Not Just In Kanpur
FSDA intensified raids and checks in Lucknow too during Ramadan and Holi. These inspections will be done in warehouses, food outlets, and dairy units to prevent sale of adulterated and substandard products. Raids from Hapur too have led to confiscation of adulterated food. UPFSDA plans to conduct further raids during the festive season. On X, formerly Twitter, the UPFSDA posted that it has seized 25,000 kg of Suji (valued at ₹10 Lakhs) from M/s Raj Sneh Agro Foods Pvt Ltd due to packaging regulation violations. Samples of Jaggery Powder, Gur, and Suji have been sent for lab testing.
What Happens To Your Health When You Consume Adulterated Foods?
Food adulteration happens when there is an intentional addition of foreign or inferior substance to original food products. A 2024 study published in SAGE Open Medicine notes various health impact of adulterated food which include:
- Cancer
- Lathyrism
- Liver disease
- Cardiac failure
- Kidney disease
- Nervous system-related diseases
The study also notes that adulteration could also lead to allergic reactions. Pregnant woman, children and elderly are more prone to getting any illness if adulterated food is consumed.
Indore Food Contamination: 6 People Hospitalized In Bhagirathpura

Credits: Canva
Not too long ago, Indore made headlines in water contamination case where a 67-year-old woman, identified as Parvati Bai Kondla also showed signs of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Bacteria like E coli. and Klebsiella were found in the water sample of Bhagirathpura, the epicentre of water contamination.
Indore's Bhagirathpura is again on the news, this time for food contamination.
Also Read: Woman Lost Weight On Mounjaro But Her Breasts Didn't Stop Growing, This Is Why...
Indore Food Contamination: What Happened?
Six people have been admitted to a hospital after they consumed contaminated food in Bhagirathpura. At a birthday party in Bhagirathpura on a late Saturday night, 60 people ate the food and some of them developed health problems. Chief Medical and Health Officer (CMHO) Dr Madhav Hasani stated on Monday.
Bhagirathpura was the epicentre of water contamination that claimed 22 lives earlier. The minister said that affected individuals were treated and as a precaution, six of them were admitted to the Government Maharaja Yashwantrao Hospital.
Indore Municipal Corporation Commissioner Dilip Kumar said, “We have found that in case of the construction of the toilet, no safety tank was constructed beneath it. We are also probing the other lapses.”
As per the official statement, all patients are doing well after the treatment.
Indore Food Contamination: What Happened In Indore Before?
Earlier in January, Mayor Pushyamitra Bhargav reported that due to lapses in civic infrastructure. Investigation revealed that a toilet constructed directly above a main drinking pipeline near a police outpost, without a mandatory safety tank resulted in the sewage mixing with drinking water.
Read: Sewage Mixing With Drinking Water Kills 7 in Madhya Pradesh’s Indore, Over 100 Remain Hospitalized
Speaking to The Indian Express, Indore Municipal Corporation Commissioner Dilip Kumar said, “We have found that in case of the construction of the toilet, no safety tank was constructed beneath it. We are also probing the other lapses.”
What Is E. Coli Bacteria?
Escherichia coli, commonly known as E. coli, refers to a group of bacteria that naturally live in the intestines of humans and animals. Most of these strains are harmless and even play a role in digestion. However, certain types can trigger illness when they enter parts of the body where they do not belong or release harmful toxins.
These disease-causing strains attach themselves to body cells and produce toxins, leading to infection and inflammation.
What Is Guillain-Barré syndrome?
Guillain-Barré syndrome is a rare autoimmune condition in which your immune system attacks your peripheral nerves, leading to symptoms like numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness that progress to paralysis. However, with treatment, most people fully recover from the condition.
Doctors say GBS occurs at any age, but it most commonly affects people between 30 and 50 years of age.
Guillain-Barré syndrome is rare. About 100,000 people worldwide develop GBS every year. To put that into perspective, the world population is about 7.8 billion. That means healthcare providers diagnose GBS in about 1 in 78,000 people each year.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

