- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
German Researchers Develop Skin Scan That Can Flag Early Heart Disease Risk
Credits: AI Generated
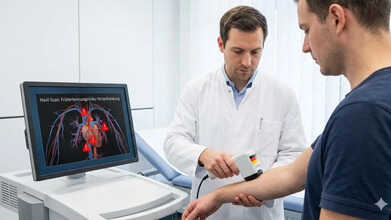
A group of German scientists has introduced a new skin imaging technique that can spot early warning signs of heart disease without breaking the skin. Known as the Fast-RSOM skin scan, the technology can pick up minute changes in blood vessels, oxygen supply, and tissue structure that standard imaging tools cannot detect. It produces clear images of the tiniest blood vessels through the skin and can identify subtle problems in how these vessels widen and narrow, a condition called microvascular endothelial dysfunction (MiVED). Until now, clinicians did not have a precise, noninvasive way to observe or measure these early changes in people.
Researchers from the Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres say that by identifying early cardiovascular risk, the technology could allow doctors to step in sooner, tailor treatment plans more effectively, and support better heart health over time.
German Scientists Create Skin Imaging Scan That Can Detect Heart Disease
Scientists at Helmholtz Munich, working alongside the Technical University of Munich (TUM), have developed Fast-RSOM, an advanced imaging method that captures highly detailed views of the body’s smallest blood vessels directly through the skin, without the need for invasive tests. By uncovering early indicators of cardiovascular risk, the scan could help doctors act earlier, personalise treatment approaches, and improve long-term outcomes for patients with heart disease.
What Is ‘Fast-RSOM’?
RSOM, short for Raster Scan Optoacoustic Mesoscopy, is a noninvasive imaging approach that uses brief pulses of light to create ultrasound signals. These signals are then used to generate high-resolution, three-dimensional images of structures beneath the skin.
Fast-RSOM skin scanning can visualise tiny blood vessels in exceptional detail and detect subtle shifts in blood flow, oxygenation, and tissue composition that are usually missed by conventional imaging techniques. Crucially, it can identify early microvascular endothelial dysfunction (MiVED), a condition closely linked to the earliest stages of cardiovascular disease, according to Medical Xpress.
How Can Fast-RSOM Detect Progression Before Symptoms Appear?
Fast-RSOM delivers high-resolution, dynamic biomarkers of MiVED, capturing small but meaningful impairments in blood vessel function that often exist well before symptoms appear or larger disease signs can be measured. These early changes are frequently associated with risk factors such as smoking, high blood pressure, and obesity. Unlike traditional risk assessments that rely on general health indicators, Fast-RSOM directly measures the actual impact these factors have had on the microvascular system, long before serious complications emerge.By identifying these early signals, Fast-RSOM creates new opportunities for earlier diagnosis, prevention strategies, and more accurate tracking of heart health. The technology may help pinpoint people at greater risk of cardiovascular events with improved precision and allow doctors to monitor how lifestyle changes or treatments are working.
The research team plans to test Fast-RSOM across larger and more varied patient populations and to incorporate its biomarkers into routine clinical practice. Because the device is portable, quick to use, and noninvasive, it could eventually be introduced in outpatient settings as part of regular cardiovascular risk screening, according to Medical Xpress.
Shreyas Talpade Shares 5 Mantras That Helped Him Recover After A Cardiac Episode

Credits: Shreyas Talpade Instagram/Canva
Actor Shreyas Talpade recalls that during a shoot for Single Salma in Lucknow, he felt unusually drained after an intense action sequence. In an interview with the Times of India, he revealed, along with the fatigue, there was an odd sensation in his throat, something he had never experienced before. He sat down briefly, brushed it aside, and convinced himself that he was fine.
Yet, something did not sit right with him. Concerned, Shreyas decided to consult a doctor. He underwent an ECG and a 2D echo, and both reports came back normal. While he did not completely ignore what his body was telling him, he also did not probe further. He assumed the medical reports meant there was nothing to worry about.
Months later, in December 2023, Shreyas Talpade suffered a major cardiac episode, an experience that would alter his life in ways he never imagined.
Shreyas Talpade Had No Classic Risk Factors, Yet He Suffered a Heart Attack
Shreyas was only in his mid-40s when the incident occurred, but it changed him both physically and emotionally.
Physically, he now follows lifelong precautions to ensure such an episode does not recur. Regular medication, scheduled follow-ups, routine checkups, and strict adherence to medical advice have become a permanent part of his life.
Emotionally, the impact was even more intense. Shreyas points out that he had none of the four common risk factors associated with heart attacks. He did not smoke or drink. He was neither diabetic nor hypertensive. And yet, the cardiac episode happened.
Shreyas Talpade’s Five Mantras For Heart Health
- Listen to your body: If something feels unusual, do not delay or dismiss it.
- Get tested early: The sooner you detect a problem, the faster you can respond.
- Stay consistent: Fixed timings for meals, medicines, and sleep are essential. A healthy life depends on routine, not randomness.
- Rest adequately: Seven to eight hours of uninterrupted sleep is non-negotiable. It plays a vital role in healing and recovery.
- Monitor your heart regularly: ECGs, 2D echo tests, stress tests, and calcium score screenings can save lives. Prevention is always better than cure.
- Manage stress: Stress is unavoidable, but learning to manage it is crucial. Focus on what you can control and let go of the rest.
Shreyas believes that while life brings uncertainty, many aspects of health remain within our control. After an experience like his, priorities naturally shift. Family becomes the top priority, and staying healthy becomes essential to spend meaningful time with loved ones. That, he says, means sleeping well, exercising four to five times a week, and eating nutritious meals on time.
Heart Attack: Why Timely Meals Matter More Than Extreme Diets
Shreyas clarifies that a proper diet does not mean surviving on salads alone. He eats a variety of foods, but in moderation. Fried and sugary items are limited, though he does include a small amount of ghee in his meals.He stresses that while nutritious food is important, eating at regular times is even more critical. Maintaining fixed meal schedules helps the body function better. Having dinner early allows the digestive system enough time to rest. Even the healthiest food, he notes, loses its benefit if meal timings are irregular.
His earlier discipline with clean eating and regular workouts played a significant role in his recovery. Shreyas also believes that post-pandemic health changes and the Covid vaccine may have triggered complications, but his active lifestyle helped him bounce back faster.
According to him, proper nutrition, regular exercise, quality sleep, and balance strengthen the body. Without these habits, the outcome could have been very different. He firmly believes the body responds to the care it receives.
Learning To Handle Stress And Let Go
Shreyas acknowledges that stress is an unavoidable part of life. However, he believes learning how to manage it is essential.
Over time, he has realised that not everything lies within one’s control. Letting go of what cannot be changed is just as important as addressing what can be managed. Wisdom often comes with age, but when someone shares their experiences, he feels it is important to listen.
His message is clear: do not wait for a personal crisis to learn lessons the hard way.
US Withdraws From WHO, What It Means For The World

Credits: iStock and Wikimedia Commons
The United States under President Donald Trump’s administration has completed its withdrawal from the World Health Organization (WHO). The US Department of Health and Human Services confirmed the news on Thursday. This has been a longstanding goal of President Trump.
Trump’s Goal To Exit From WHO
During Trump’s first term, he tried to leave WHO, then gave a notice through an executive order on the first day of his second term. It noted that the US would leave the organization. As per law, the US must give WHO a one-year notice and pay all outstanding fees before its departure. This means the US still owes WHO roughly $260 million. However, legal experts said that US is unlikely to pay up and WHO will have little recourse.
Dr. Lawrence Gostin, an expert on global health law and public health at Georgetown University told CNN, “As a matter of law, it is very clear that the United States cannot officially withdraw from WHO unless it pays its outstanding financial obligations. But WHO has no power to force the US to pay what it owes.”
WHO could pass a resolution saying that US cannot withdraw until it pays, however, it won’t risk creating any further tension that there already is.
The HHS on Thursday confirmed that all US government funding to WHO has been terminated and all personnel and contractors assigned or embedded within the organization have been recalled. It also said the US had ceased official participation in WHO-sponsored committees, leadership bodies, governance structures and technical working groups.
What the US Exit From WHO Means for the World
The US government has said it is moving ahead with its decision to exit the World Health Organization (WHO), arguing that the country has not received enough value for the money, staff, and support it has given to the global health body over the years.
Senior officials from HHS said the WHO acted against US interests, especially during the Covid-19 pandemic. They accused the organization of delaying the declaration of a global public health emergency and of praising China’s early response despite signs of underreporting, information suppression, and delays in confirming human-to-human transmission.
HHS also criticized the WHO for being slow to acknowledge airborne spread of Covid-19 and for downplaying the role of people without symptoms in spreading the virus. According to officials, these missteps cost the world precious time as the virus spread rapidly.
While the US has been the WHO’s largest funder, officials pointed out that no American has ever served as the organization’s director-general. “A promise made and a promise kept,” one senior official said, adding that US health policies should not be shaped by “unaccountable foreign bureaucrats.”
That said, the administration has not completely ruled out cooperation with the WHO. When asked whether the US would take part in an upcoming WHO meeting on next year’s flu vaccine composition, officials said discussions are still ongoing.
The government has insisted that leaving the WHO does not mean stepping away from global health leadership. Instead, the US plans to work directly with individual countries, health ministries, non-governmental organizations, and religious groups on disease surveillance and data sharing. This effort is expected to be led by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Global Health Center. Officials have promised more announcements on this strategy in the coming months.
However, many public health experts are deeply concerned. Some warn that replacing the WHO with country-by-country agreements will create a fragmented system that lacks coordination and adequate funding. Former CDC officials note that the CDC has staff in about 60 countries, far fewer than the global reach of the WHO.
Critics say the move could leave both the US and the world vulnerable to future outbreaks. Experts argue that infectious diseases do not respect borders and that global cooperation is essential for early detection, data sharing, and rapid response.
Several health leaders have called the decision dangerous and short-sighted, warning that without WHO membership, the US could lose timely access to critical data, virus samples, and genomic information needed to develop vaccines and treatments. WHO’s director-general has described the US withdrawal as a “lose-lose” situation, saying both America and the rest of the world stand to suffer.
Sunita Williams Retires After 27 Years: Health Challenges She Faced After Spending 600+ Days in Space

Credits: Wikimedia Commons
Sunita L Williams has retired from NASA after 27 year of spacefaring career. The astronaut went on three long missions to the International Space Station (ISS), which meant she logged 608 days in space, with a record breaking nine spacewalks. She was also stranded in ISS with Butch Wilmore. The mission was supposed to be 8-day-long, however it extended up to nine months due to a Starliner spacecraft problem. During this stay, she faced certain health issues. Photos showed significant weight loss, with sunken cheekbones.
Recently, Williams appeared on Raj Shamani podcast, where she talked about her experience of spending 286 days in space.
Also Read: Law on Assisted Dying in Jersey Could Be Passed Soon After Draft Approval
What Health Challenges Sunita Williams Faced In Space?

When Shamani asked her about her health challenges, she pointed out that it is when you land back on earth is when you feel the most uncomfortable. “Initially when you come back, you are not feeling very good. But then it goes away pretty good,” she said.
Shamani then asked how does she feel when she lands on earth. “For me it is nauseas. When we were landing in the water, everyone was focusing on the dolphins, but I was thinking if the capsule goes upside down, it is not going to be very good. The capsule was bobbing for a few seconds like a cork,” she said.
She explains that when you are in the space, your neuro vestibular system, which is body’s internal balance and orientation system, located in the inner ear does not work. “When you are out in space, gravity and inner balance are not needed and when you come back, it is suddenly there.”
She said that she felt nauseas for 24 to 48 hours. Furthermore, she said that when she wears the spacesuit and pinches her head through that, it makes her a “little sick”.
While in space, she explains, “all the balance muscles that you use here on earth, you do not even realize are not in use. After landing, they suddenly have to be put to use, so they have to be recharged. For me, it takes about a month to get used to it.”
How Does The Space To Earth Transition Work?
“We also get trainers who examine our progress and how we are doing back on earth. It is actually pretty cool to see how your body works and to human yourself again or to earth yourself again.”
Shamani asked if coming back to earth and adapting to gravity takes time. He asked, “do you feel like if you pick something and leave it, it won’t drop, rather it will flow?” “It happens, but you get back to gravity pretty quickly,” she said.
What Are The Health Risks Of Staying In Space?

Space agencies like NASA and the German Space Agency (DLR) studied the effects of space on human body. In 2024, the journal Nature published over 40 studies focused on aerospace medicine and space biology. One such study, called TWINS compared astronaut Scott Kelly, who spent a year on the ISS with his identical twin, Mark, who stayed on Earth.
The study highlighted a significant risk of prolonged space missions: radiation exposure.
Read: NASA Astronaut Sunita Williams’ Health Deteriorates During Extended Mission: Experts Raise Concerns
Radiation in space can damage DNA, increasing cancer risks and oxidative stress in the body. Bailey explained that space radiation exposure is a major concern for astronauts. Space agencies must find ways to protect astronauts during space travel and long-term stays on the Moon or Mars. They have set limits on the amount of radiation astronauts can be exposed to over their careers.
Another challenge is microgravity that causes bone density loss of 1-1.5% per month. When astronauts come down to Earth. They may struggle with physical activities like dancing due to weak bones and it can also affect vision. The fluids that shift to the head put pressure on the eyes. This can also lead to Spaceflight Associated Neuro-ocular Syndrome, which can permanently impact vision.
Other risks involve fluid redistribution that can lead to facial puffiness and decreased fluid volume in legs, disruption of cardiovascular functions, complicating blood pressure and even risks to the urinary systems. The risk of kidney stone too is high.
Nutrition deficiencies was another concern which was raised when photos of Williams revealed a significant weight loss. Her sunken cheekbones raised worries about her eating habits. There were also speculations of her being on a calorie-deficit diet. This meant that she ate less than her body required to sustain the high energy she needs for space travels.
In terms of physical activities, astronauts in microgravity must exercise for 2.5 hours daily. This helps them maintain muscle bone health. However, challenging environment could lead to weight loss.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

